diff options
| author | robot-contrib <[email protected]> | 2023-08-11 00:10:17 +0300 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | robot-contrib <[email protected]> | 2023-08-11 01:27:23 +0300 |
| commit | 33235edbd06ce6e3968605e269f60ad5caaecdd7 (patch) | |
| tree | 503da571707a72fc37cc47890d7722b26c77c156 | |
| parent | 28f697a118317926707211701d4152920ea78a4c (diff) | |
Update contrib/libs/xxhash to 0.8.2
| -rw-r--r-- | contrib/libs/xxhash/CHANGELOG | 43 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | contrib/libs/xxhash/LICENSE | 24 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | contrib/libs/xxhash/README.md | 239 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | contrib/libs/xxhash/SECURITY.md | 13 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.c | 2 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.h | 4551 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | contrib/libs/xxhash/ya.make | 8 |
7 files changed, 3474 insertions, 1406 deletions
diff --git a/contrib/libs/xxhash/CHANGELOG b/contrib/libs/xxhash/CHANGELOG index 23870756bb4..3040855fffd 100644 --- a/contrib/libs/xxhash/CHANGELOG +++ b/contrib/libs/xxhash/CHANGELOG @@ -1,3 +1,46 @@ +v0.8.2 +- fix : XXH3 S390x vector implementation (@hzhuang1) +- fix : PowerPC vector compilation with IBM XL compiler (@MaxiBoether) +- perf : improved WASM speed by x2/x3 using SIMD128 (@easyaspi314) +- perf : improved speed (+20%) for XXH3 on ARM NEON (@easyaspi314) +- cli : Fix filename contain /LF character (@t-mat) +- cli : Support # comment lines in --check files (@t-mat) +- cli : Support commands --binary and --ignore-missing (@t-mat) +- build: fix -Og compilation (@easyaspi314, @t-mat) +- build: fix pkgconfig generation with cmake (@ilya-fedin) +- build: fix icc compilation +- build: fix cmake install directories +- build: new build options XXH_NO_XXH3, XXH_SIZE_OPT and XXH_NO_STREAM to reduce binary size (@easyaspi314) +- build: dedicated install targets (@ffontaine) +- build: support DISPATCH mode in cmake (@hzhuang1) +- portability: fix x86dispatch when building with Visual + clang-cl (@t-mat) +- portability: SVE vector implementation of XXH3 (@hzhuang1) +- portability: compatibility with freestanding environments, using XXH_NO_STDLIB +- portability: can build on Haiku (@Begasus) +- portability: validated on m68k and risc-v +- doc : XXH3 specification (@Adrien1018) +- doc : improved doxygen documentation (@easyaspi314, @t-mat) +- misc : dedicated sanity test binary (@t-mat) + +v0.8.1 +- perf : much improved performance for XXH3 streaming variants, notably on gcc and msvc +- perf : improved XXH64 speed and latency on small inputs +- perf : small XXH32 speed and latency improvement on small inputs of random size +- perf : minor stack usage improvement for XXH32 and XXH64 +- api : new experimental variants XXH3_*_withSecretandSeed() +- api : update XXH3_generateSecret(), can no generate secret of any size (>= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) +- cli : xxhsum can now generate and check XXH3 checksums, using command `-H3` +- build: can build xxhash without XXH3, with new build macro XXH_NO_XXH3 +- build: fix xxh_x86dispatch build with MSVC, by @apankrat +- build: XXH_INLINE_ALL can always be used safely, even after XXH_NAMESPACE or a previous XXH_INLINE_ALL +- build: improved PPC64LE vector support, by @mpe +- install: fix pkgconfig, by @ellert +- install: compatibility with Haiku, by @Begasus +- doc : code comments made compatible with doxygen, by @easyaspi314 +- misc : XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER is no longer necessary, all functions can accept NULL input pointers, as long as size == 0 +- misc : complete refactor of CI tests on Github Actions, offering much larger coverage, by @t-mat +- misc : xxhsum code base split into multiple specialized units, within directory cli/, by @easyaspi314 + v0.8.0 - api : stabilize XXH3 - cli : xxhsum can parse BSD-style --check lines, by @WayneD diff --git a/contrib/libs/xxhash/LICENSE b/contrib/libs/xxhash/LICENSE index fa20595dc62..e4c5da7234e 100644 --- a/contrib/libs/xxhash/LICENSE +++ b/contrib/libs/xxhash/LICENSE @@ -1,5 +1,5 @@ xxHash Library -Copyright (c) 2012-2020 Yann Collet +Copyright (c) 2012-2021 Yann Collet All rights reserved. BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php) @@ -24,25 +24,3 @@ LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. - ----------------------------------------------------- - -xxhsum command line interface -Copyright (c) 2013-2020 Yann Collet -All rights reserved. - -GPL v2 License - -This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify -it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by -the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or -(at your option) any later version. - -This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, -but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of -MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the -GNU General Public License for more details. - -You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along -with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., -51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA. diff --git a/contrib/libs/xxhash/README.md b/contrib/libs/xxhash/README.md index 01637f499df..eea13e2769f 100644 --- a/contrib/libs/xxhash/README.md +++ b/contrib/libs/xxhash/README.md @@ -1,91 +1,94 @@ + xxHash - Extremely fast hash algorithm ====================================== -<!-- TODO: Update. --> -xxHash is an Extremely fast Hash algorithm, running at RAM speed limits. -It successfully completes the [SMHasher](https://code.google.com/p/smhasher/wiki/SMHasher) test suite -which evaluates collision, dispersion and randomness qualities of hash functions. -Code is highly portable, and hashes are identical on all platforms (little / big endian). +xxHash is an Extremely fast Hash algorithm, processing at RAM speed limits. +Code is highly portable, and produces hashes identical across all platforms (little / big endian). +The library includes the following algorithms : +- XXH32 : generates 32-bit hashes, using 32-bit arithmetic +- XXH64 : generates 64-bit hashes, using 64-bit arithmetic +- XXH3 (since `v0.8.0`): generates 64 or 128-bit hashes, using vectorized arithmetic. + The 128-bit variant is called XXH128. + +All variants successfully complete the [SMHasher](https://code.google.com/p/smhasher/wiki/SMHasher) test suite +which evaluates the quality of hash functions (collision, dispersion and randomness). +Additional tests, which evaluate more thoroughly speed and collision properties of 64-bit hashes, [are also provided](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/tree/dev/tests). |Branch |Status | |------------|---------| -|master | [](https://travis-ci.org/Cyan4973/xxHash?branch=master) | -|dev | [](https://travis-ci.org/Cyan4973/xxHash?branch=dev) | - +|release | [](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/actions?query=branch%3Arelease+) | +|dev | [](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/actions?query=branch%3Adev+) | Benchmarks ------------------------- -The benchmark uses SMHasher speed test, compiled with Visual 2010 on a Windows Seven 32-bit box. -The reference system uses a Core 2 Duo @3GHz - - -| Name | Speed | Quality | Author | -|---------------|--------------------|:-------:|-------------------| -| [xxHash] | 5.4 GB/s | 10 | Y.C. | -| MurmurHash 3a | 2.7 GB/s | 10 | Austin Appleby | -| SBox | 1.4 GB/s | 9 | Bret Mulvey | -| Lookup3 | 1.2 GB/s | 9 | Bob Jenkins | -| CityHash64 | 1.05 GB/s | 10 | Pike & Alakuijala | -| FNV | 0.55 GB/s | 5 | Fowler, Noll, Vo | -| CRC32 | 0.43 GB/s † | 9 | | -| MD5-32 | 0.33 GB/s | 10 | Ronald L.Rivest | -| SHA1-32 | 0.28 GB/s | 10 | | - -[xxHash]: https://www.xxhash.com - -Note †: SMHasher's CRC32 implementation is known to be slow. Faster implementations exist. - -Q.Score is a measure of quality of the hash function. -It depends on successfully passing SMHasher test set. -10 is a perfect score. -Algorithms with a score < 5 are not listed on this table. - -A more recent version, XXH64, has been created thanks to [Mathias Westerdahl](https://github.com/JCash), -which offers superior speed and dispersion for 64-bit systems. -Note however that 32-bit applications will still run faster using the 32-bit version. - -SMHasher speed test, compiled using GCC 4.8.2, on Linux Mint 64-bit. -The reference system uses a Core i5-3340M @2.7GHz - -| Version | Speed on 64-bit | Speed on 32-bit | -|------------|------------------|------------------| -| XXH64 | 13.8 GB/s | 1.9 GB/s | -| XXH32 | 6.8 GB/s | 6.0 GB/s | - -This project also includes a command line utility, named `xxhsum`, offering similar features to `md5sum`, -thanks to [Takayuki Matsuoka](https://github.com/t-mat)'s contributions. - - -### License - -The library files `xxhash.c` and `xxhash.h` are BSD licensed. -The utility `xxhsum` is GPL licensed. - - -### New hash algorithms +The benchmarked reference system uses an Intel i7-9700K cpu, and runs Ubuntu x64 20.04. +The [open source benchmark program] is compiled with `clang` v10.0 using `-O3` flag. + +| Hash Name | Width | Bandwidth (GB/s) | Small Data Velocity | Quality | Comment | +| --------- | ----- | ---------------- | ----- | --- | --- | +| __XXH3__ (SSE2) | 64 | 31.5 GB/s | 133.1 | 10 +| __XXH128__ (SSE2) | 128 | 29.6 GB/s | 118.1 | 10 +| _RAM sequential read_ | N/A | 28.0 GB/s | N/A | N/A | _for reference_ +| City64 | 64 | 22.0 GB/s | 76.6 | 10 +| T1ha2 | 64 | 22.0 GB/s | 99.0 | 9 | Slightly worse [collisions] +| City128 | 128 | 21.7 GB/s | 57.7 | 10 +| __XXH64__ | 64 | 19.4 GB/s | 71.0 | 10 +| SpookyHash | 64 | 19.3 GB/s | 53.2 | 10 +| Mum | 64 | 18.0 GB/s | 67.0 | 9 | Slightly worse [collisions] +| __XXH32__ | 32 | 9.7 GB/s | 71.9 | 10 +| City32 | 32 | 9.1 GB/s | 66.0 | 10 +| Murmur3 | 32 | 3.9 GB/s | 56.1 | 10 +| SipHash | 64 | 3.0 GB/s | 43.2 | 10 +| FNV64 | 64 | 1.2 GB/s | 62.7 | 5 | Poor avalanche properties +| Blake2 | 256 | 1.1 GB/s | 5.1 | 10 | Cryptographic +| SHA1 | 160 | 0.8 GB/s | 5.6 | 10 | Cryptographic but broken +| MD5 | 128 | 0.6 GB/s | 7.8 | 10 | Cryptographic but broken + +[open source benchmark program]: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/tree/release/tests/bench +[collisions]: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/wiki/Collision-ratio-comparison#collision-study + +note 1: Small data velocity is a _rough_ evaluation of algorithm's efficiency on small data. For more detailed analysis, please refer to next paragraph. + +note 2: some algorithms feature _faster than RAM_ speed. In which case, they can only reach their full speed potential when input is already in CPU cache (L3 or better). Otherwise, they max out on RAM speed limit. + +### Small data + +Performance on large data is only one part of the picture. +Hashing is also very useful in constructions like hash tables and bloom filters. +In these use cases, it's frequent to hash a lot of small data (starting at a few bytes). +Algorithm's performance can be very different for such scenarios, since parts of the algorithm, +such as initialization or finalization, become fixed cost. +The impact of branch mis-prediction also becomes much more present. + +XXH3 has been designed for excellent performance on both long and small inputs, +which can be observed in the following graph: -Starting with `v0.7.0`, the library includes a new algorithm named `XXH3`, -which is able to generate 64 and 128-bit hashes. +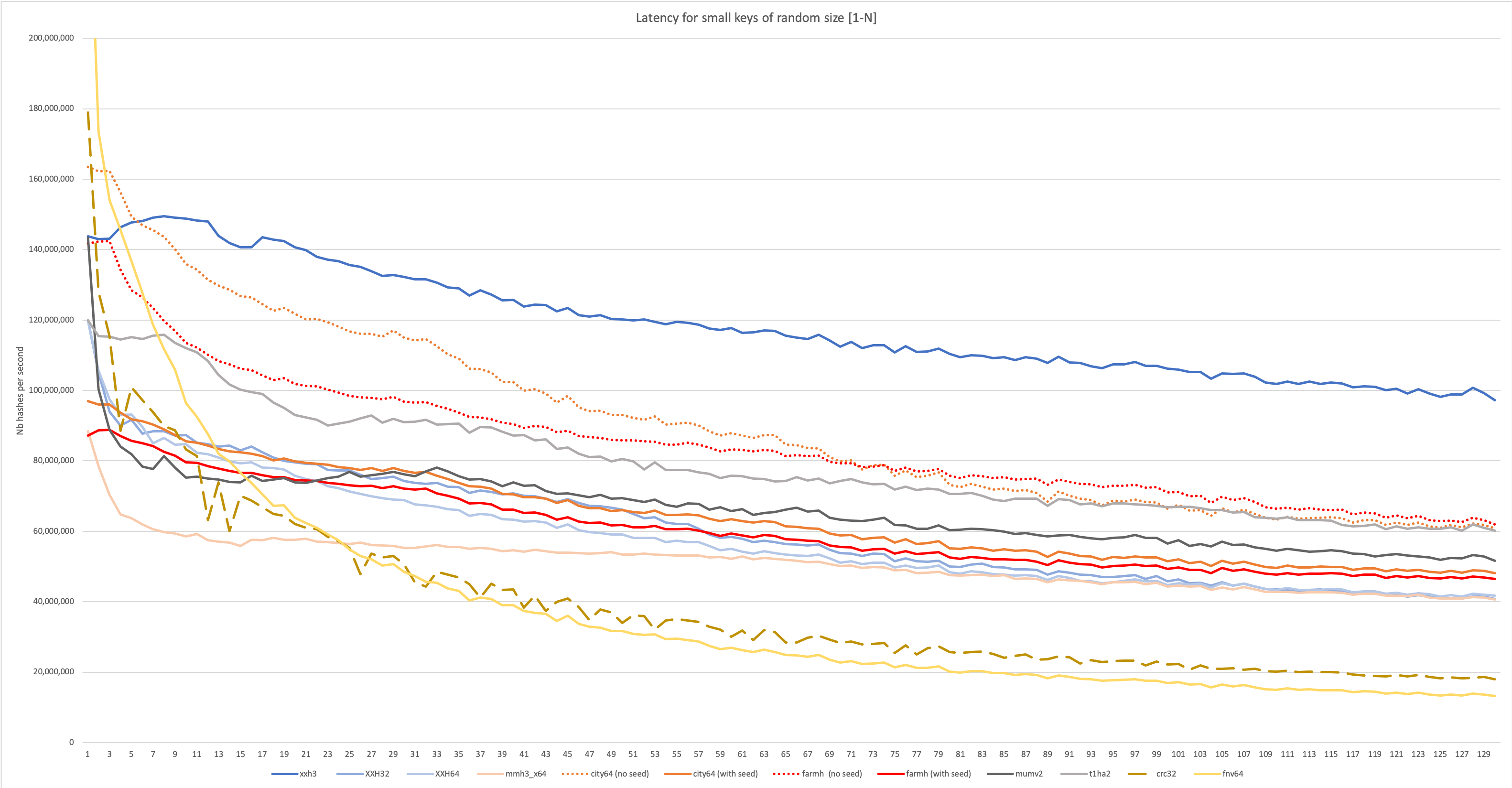 -The new algorithm is much faster than its predecessors for both long and small inputs, -which can be observed in the following graphs: +For a more detailed analysis, please visit the wiki : +https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/wiki/Performance-comparison#benchmarks-concentrating-on-small-data- -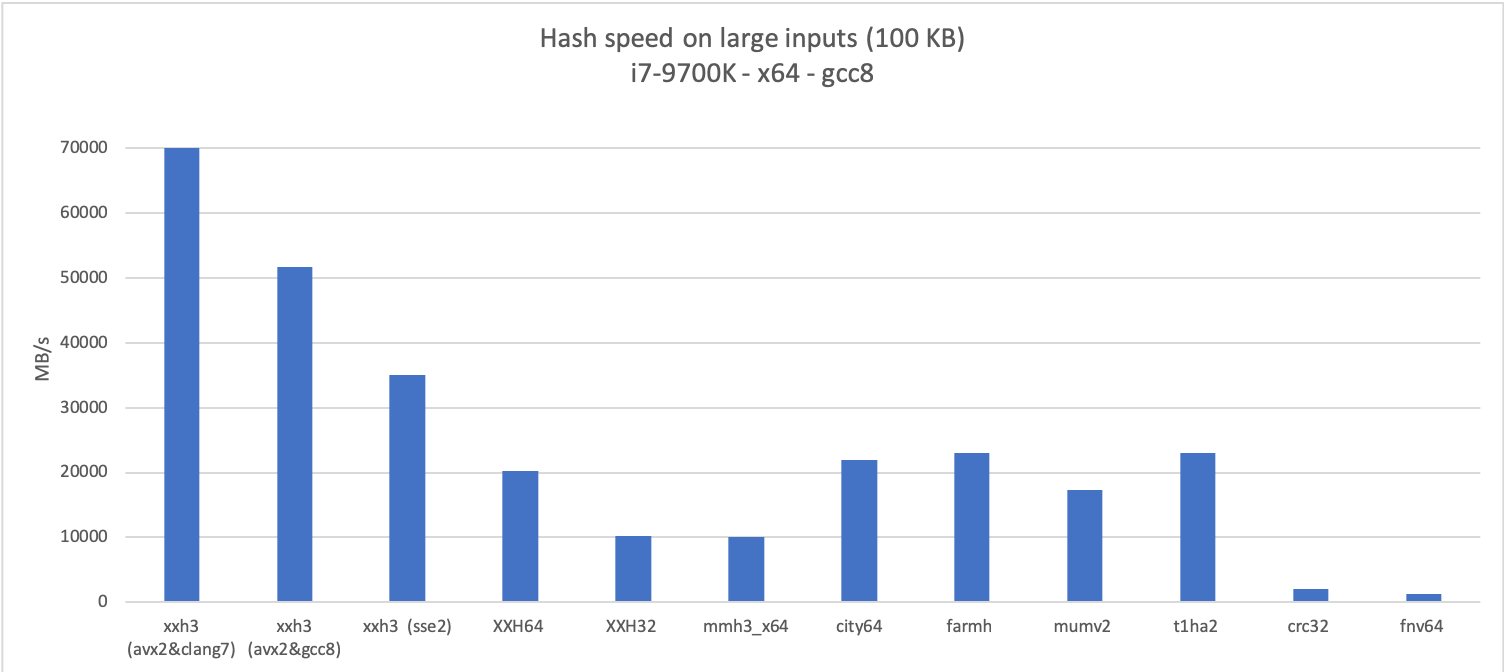 +Quality +------------------------- - +Speed is not the only property that matters. +Produced hash values must respect excellent dispersion and randomness properties, +so that any sub-section of it can be used to maximally spread out a table or index, +as well as reduce the amount of collisions to the minimal theoretical level, following the [birthday paradox]. -To access these new prototypes, one needs to unlock their declaration, using the build macro `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`. +`xxHash` has been tested with Austin Appleby's excellent SMHasher test suite, +and passes all tests, ensuring reasonable quality levels. +It also passes extended tests from [newer forks of SMHasher], featuring additional scenarios and conditions. -The algorithm is currently in development, meaning its return values might still change in future versions. -However, the API is stable, and can be used in production, -typically for generation of ephemeral hashes (produced and consumed in same session). +Finally, xxHash provides its own [massive collision tester](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/tree/dev/tests/collisions), +able to generate and compare billions of hashes to test the limits of 64-bit hash algorithms. +On this front too, xxHash features good results, in line with the [birthday paradox]. +A more detailed analysis is documented [in the wiki](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/wiki/Collision-ratio-comparison). -`XXH3` has now reached "release candidate" status. -If everything remains fine, its format will be "frozen" and become final. -After which, return values of `XXH3` and `XXH128` will no longer change in future versions. -`XXH3`'s return values will be officially finalized upon reaching `v0.8.0`. +[birthday paradox]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Birthday_problem +[newer forks of SMHasher]: https://github.com/rurban/smhasher ### Build modifiers @@ -98,49 +101,60 @@ The following macros can be set at compilation time to modify libxxhash's behavi with performance improvements observed in the +200% range . See [this article](https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2018/03/xxhash-for-small-keys-impressive-power.html) for details. - `XXH_PRIVATE_API`: same outcome as `XXH_INLINE_ALL`. Still available for legacy support. - The name underlines that `XXH_*` symbols will not be exported. + The name underlines that `XXH_*` symbol names will not be exported. - `XXH_NAMESPACE`: Prefixes all symbols with the value of `XXH_NAMESPACE`. This macro can only use compilable character set. Useful to evade symbol naming collisions, in case of multiple inclusions of xxHash's source code. Client applications still use the regular function names, as symbols are automatically translated through `xxhash.h`. -- `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS`: The default method `0` uses a portable `memcpy()` notation. - Method `1` uses a gcc-specific `packed` attribute, which can provide better performance for some targets. - Method `2` forces unaligned reads, which is not standards compliant, but might sometimes be the only way to extract better read performance. - Method `3` uses a byteshift operation, which is best for old compilers which don't inline `memcpy()` or big-endian systems without a byteswap instruction - `XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK`: Use a faster direct read path when input is aligned. This option can result in dramatic performance improvement when input to hash is aligned on 32 or 64-bit boundaries, when running on architectures unable to load memory from unaligned addresses, or suffering a performance penalty from it. It is (slightly) detrimental on platform with good unaligned memory access performance (same instruction for both aligned and unaligned accesses). This option is automatically disabled on `x86`, `x64` and `aarch64`, and enabled on all other platforms. -- `XXH_VECTOR` : manually select a vector instruction set (default: auto-selected at compilation time). Available instruction sets are `XXH_SCALAR`, `XXH_SSE2`, `XXH_AVX2`, `XXH_AVX512`, `XXH_NEON` and `XXH_VSX`. Compiler may require additional flags to ensure proper support (for example, `gcc` on linux will require `-mavx2` for AVX2, and `-mavx512f` for AVX512). -- `XXH_NO_PREFETCH` : disable prefetching. XXH3 only. -- `XXH_PREFETCH_DIST` : select prefecting distance. XXH3 only. +- `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS`: The default method `0` uses a portable `memcpy()` notation. + Method `1` uses a gcc-specific `packed` attribute, which can provide better performance for some targets. + Method `2` forces unaligned reads, which is not standard compliant, but might sometimes be the only way to extract better read performance. + Method `3` uses a byteshift operation, which is best for old compilers which don't inline `memcpy()` or big-endian systems without a byteswap instruction. +- `XXH_VECTOR` : manually select a vector instruction set (default: auto-selected at compilation time). Available instruction sets are `XXH_SCALAR`, `XXH_SSE2`, `XXH_AVX2`, `XXH_AVX512`, `XXH_NEON` and `XXH_VSX`. Compiler may require additional flags to ensure proper support (for example, `gcc` on linux will require `-mavx2` for `AVX2`, and `-mavx512f` for `AVX512`). +- `XXH_NO_PREFETCH` : disable prefetching. Some platforms or situations may perform better without prefetching. XXH3 only. +- `XXH_PREFETCH_DIST` : select prefetching distance. For close-to-metal adaptation to specific hardware platforms. XXH3 only. +- `XXH_NO_STREAM`: Disables the streaming API, limiting it to single shot variants only. +- `XXH_SIZE_OPT`: `0`: default, optimize for speed + `1`: default for `-Os` and `-Oz`: disables some speed hacks for size optimization + `2`: makes code as small as possible, performance may cry - `XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS`: By default, xxHash uses `__attribute__((always_inline))` and `__forceinline` to improve performance at the cost of code size. Defining this macro to 1 will mark all internal functions as `static`, allowing the compiler to decide whether to inline a function or not. This is very useful when optimizing for smallest binary size, and is automatically defined when compiling with `-O0`, `-Os`, `-Oz`, or `-fno-inline` on GCC and Clang. This may also increase performance depending on compiler and architecture. -- `XXH_REROLL`: Reduces the size of the generated code by not unrolling some loops. - Impact on performance may vary, depending on platform and algorithm. -- `XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER`: if set to `1`, when input is a `NULL` pointer, - xxHash'd result is the same as a zero-length input - (instead of a dereference segfault). - Adds one branch at the beginning of each hash. -- `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`: gives access to the state declaration for static allocation. +- `XXH32_ENDJMP`: Switch multi-branch finalization stage of XXH32 by a single jump. + This is generally undesirable for performance, especially when hashing inputs of random sizes. + But depending on exact architecture and compiler, a jump might provide slightly better performance on small inputs. Disabled by default. +- `XXH_NO_STDLIB`: Disable invocation of `<stdlib.h>` functions, notably `malloc()` and `free()`. + `libxxhash`'s `XXH*_createState()` will always fail and return `NULL`. + But one-shot hashing (like `XXH32()`) or streaming using statically allocated states + still work as expected. + This build flag is useful for embedded environments without dynamic allocation. +- `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`: gives access to internal state declaration, required for static allocation. Incompatible with dynamic linking, due to risks of ABI changes. -- `XXH_NO_LONG_LONG`: removes compilation of algorithms relying on 64-bit types (XXH3 and XXH64). Only XXH32 will be compiled. +- `XXH_NO_XXH3` : removes symbols related to `XXH3` (both 64 & 128 bits) from generated binary. + Useful to reduce binary size, notably for applications which do not employ `XXH3`. +- `XXH_NO_LONG_LONG`: removes compilation of algorithms relying on 64-bit types (`XXH3` and `XXH64`). Only `XXH32` will be compiled. Useful for targets (architectures and compilers) without 64-bit support. - `XXH_IMPORT`: MSVC specific: should only be defined for dynamic linking, as it prevents linkage errors. -- `XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN`: By default, endianess is determined by a runtime test resolved at compile time. +- `XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN`: By default, endianness is determined by a runtime test resolved at compile time. If, for some reason, the compiler cannot simplify the runtime test, it can cost performance. It's possible to skip auto-detection and simply state that the architecture is little-endian by setting this macro to 1. Setting it to 0 states big-endian. +- `XXH_DEBUGLEVEL` : When set to any value >= 1, enables `assert()` statements. + This (slightly) slows down execution, but may help finding bugs during debugging sessions. -For the Command Line Interface `xxhsum`, the following environment variables can also be set : +When compiling the Command Line Interface `xxhsum` using `make`, the following environment variables can also be set : - `DISPATCH=1` : use `xxh_x86dispatch.c`, to automatically select between `scalar`, `sse2`, `avx2` or `avx512` instruction set at runtime, depending on local host. This option is only valid for `x86`/`x64` systems. - +- `XXH_1ST_SPEED_TARGET` : select an initial speed target, expressed in MB/s, for the first speed test in benchmark mode. Benchmark will adjust the target at subsequent iterations, but the first test is made "blindly" by targeting this speed. Currently conservatively set to 10 MB/s, to support very slow (emulated) platforms. +- `NODE_JS=1` : When compiling `xxhsum` for Node.js with Emscripten, this links the `NODERAWFS` library for unrestricted filesystem access and patches `isatty` to make the command line utility correctly detect the terminal. This does make the binary specific to Node.js. ### Building xxHash - Using vcpkg @@ -154,10 +168,10 @@ You can download and install xxHash using the [vcpkg](https://github.com/Microso The xxHash port in vcpkg is kept up to date by Microsoft team members and community contributors. If the version is out of date, please [create an issue or pull request](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) on the vcpkg repository. - ### Example -Calling xxhash 64-bit variant from a C program: +The simplest example calls xxhash 64-bit variant as a one-shot function +generating a hash value from a single buffer, and invoked from a C/C++ program: ```C #include "xxhash.h" @@ -167,7 +181,8 @@ Calling xxhash 64-bit variant from a C program: } ``` -Using streaming variant is more involved, but makes it possible to provide data incrementally: +Streaming variant is more involved, but makes it possible to provide data incrementally: + ```C #include "stdlib.h" /* abort() */ #include "xxhash.h" @@ -189,17 +204,17 @@ XXH64_hash_t calcul_hash_streaming(FileHandler fh) /* Feed the state with input data, any size, any number of times */ (...) - while ( /* any condition */ ) { + while ( /* some data left */ ) { size_t const length = get_more_data(buffer, bufferSize, fh); if (XXH64_update(state, buffer, length) == XXH_ERROR) abort(); (...) } (...) - /* Get the hash */ + /* Produce the final hash value */ XXH64_hash_t const hash = XXH64_digest(state); - /* State can be re-used; in this example, it is simply freed */ + /* State could be re-used; but in this example, it is simply freed */ free(buffer); XXH64_freeState(state); @@ -208,19 +223,31 @@ XXH64_hash_t calcul_hash_streaming(FileHandler fh) ``` +### License + +The library files `xxhash.c` and `xxhash.h` are BSD licensed. +The utility `xxhsum` is GPL licensed. + + ### Other programming languages -Aside from the C reference version, -xxHash is also available in many different programming languages, -thanks to many great contributors. -They are [listed here](https://www.xxhash.com/#other-languages). +Beyond the C reference version, +xxHash is also available from many different programming languages, +thanks to great contributors. +They are [listed here](http://www.xxhash.com/#other-languages). + + +### Packaging status + +Many distributions bundle a package manager +which allows easy xxhash installation as both a `libxxhash` library +and `xxhsum` command line interface. + +[](https://repology.org/project/xxhash/versions) -### Branch Policy +### Special Thanks -> - The "master" branch is considered stable, at all times. -> - The "dev" branch is the one where all contributions must be merged - before being promoted to master. -> + If you plan to propose a patch, please commit into the "dev" branch, - or its own feature branch. - Direct commit to "master" are not permitted. +- Takayuki Matsuoka, aka @t-mat, for creating `xxhsum -c` and great support during early xxh releases +- Mathias Westerdahl, aka @JCash, for introducing the first version of `XXH64` +- Devin Hussey, aka @easyaspi314, for incredible low-level optimizations on `XXH3` and `XXH128` diff --git a/contrib/libs/xxhash/SECURITY.md b/contrib/libs/xxhash/SECURITY.md new file mode 100644 index 00000000000..2a8b4c8e5a1 --- /dev/null +++ b/contrib/libs/xxhash/SECURITY.md @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ +# Security Policy + +## Supported Versions + +Security updates are applied only to the latest release. + +## Reporting a Vulnerability + +If you have discovered a security vulnerability in this project, please report it privately. **Do not disclose it as a public issue.** This gives us time to work with you to fix the issue before public exposure, reducing the chance that the exploit will be used before a patch is released. + +Please disclose it at [security advisory](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/security/advisories/new). + +This project is maintained by a team of volunteers on a reasonable-effort basis. As such, please give us at least 90 days to work on a fix before public exposure. diff --git a/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.c b/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.c index 0fae88c5d67..083b039d70d 100644 --- a/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.c +++ b/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.c @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ /* * xxHash - Extremely Fast Hash algorithm - * Copyright (C) 2012-2020 Yann Collet + * Copyright (C) 2012-2021 Yann Collet * * BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php) * diff --git a/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.h b/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.h index 2d56d23c5d0..c4ad3591019 100644 --- a/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.h +++ b/contrib/libs/xxhash/xxhash.h @@ -1,7 +1,7 @@ /* * xxHash - Extremely Fast Hash algorithm * Header File - * Copyright (C) 2012-2020 Yann Collet + * Copyright (C) 2012-2021 Yann Collet * * BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php) * @@ -33,43 +33,141 @@ * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash */ -/* TODO: update */ -/* Notice extracted from xxHash homepage: - -xxHash is an extremely fast hash algorithm, running at RAM speed limits. -It also successfully passes all tests from the SMHasher suite. - -Comparison (single thread, Windows Seven 32 bits, using SMHasher on a Core 2 Duo @3GHz) - -Name Speed Q.Score Author -xxHash 5.4 GB/s 10 -CrapWow 3.2 GB/s 2 Andrew -MumurHash 3a 2.7 GB/s 10 Austin Appleby -SpookyHash 2.0 GB/s 10 Bob Jenkins -SBox 1.4 GB/s 9 Bret Mulvey -Lookup3 1.2 GB/s 9 Bob Jenkins -SuperFastHash 1.2 GB/s 1 Paul Hsieh -CityHash64 1.05 GB/s 10 Pike & Alakuijala -FNV 0.55 GB/s 5 Fowler, Noll, Vo -CRC32 0.43 GB/s 9 -MD5-32 0.33 GB/s 10 Ronald L. Rivest -SHA1-32 0.28 GB/s 10 - -Q.Score is a measure of quality of the hash function. -It depends on successfully passing SMHasher test set. -10 is a perfect score. - -Note: SMHasher's CRC32 implementation is not the fastest one. -Other speed-oriented implementations can be faster, -especially in combination with PCLMUL instruction: -https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2019/03/presenting-xxh3.html?showComment=1552696407071#c3490092340461170735 - -A 64-bit version, named XXH64, is available since r35. -It offers much better speed, but for 64-bit applications only. -Name Speed on 64 bits Speed on 32 bits -XXH64 13.8 GB/s 1.9 GB/s -XXH32 6.8 GB/s 6.0 GB/s -*/ +/*! + * @mainpage xxHash + * + * xxHash is an extremely fast non-cryptographic hash algorithm, working at RAM speed + * limits. + * + * It is proposed in four flavors, in three families: + * 1. @ref XXH32_family + * - Classic 32-bit hash function. Simple, compact, and runs on almost all + * 32-bit and 64-bit systems. + * 2. @ref XXH64_family + * - Classic 64-bit adaptation of XXH32. Just as simple, and runs well on most + * 64-bit systems (but _not_ 32-bit systems). + * 3. @ref XXH3_family + * - Modern 64-bit and 128-bit hash function family which features improved + * strength and performance across the board, especially on smaller data. + * It benefits greatly from SIMD and 64-bit without requiring it. + * + * Benchmarks + * --- + * The reference system uses an Intel i7-9700K CPU, and runs Ubuntu x64 20.04. + * The open source benchmark program is compiled with clang v10.0 using -O3 flag. + * + * | Hash Name | ISA ext | Width | Large Data Speed | Small Data Velocity | + * | -------------------- | ------- | ----: | ---------------: | ------------------: | + * | XXH3_64bits() | @b AVX2 | 64 | 59.4 GB/s | 133.1 | + * | MeowHash | AES-NI | 128 | 58.2 GB/s | 52.5 | + * | XXH3_128bits() | @b AVX2 | 128 | 57.9 GB/s | 118.1 | + * | CLHash | PCLMUL | 64 | 37.1 GB/s | 58.1 | + * | XXH3_64bits() | @b SSE2 | 64 | 31.5 GB/s | 133.1 | + * | XXH3_128bits() | @b SSE2 | 128 | 29.6 GB/s | 118.1 | + * | RAM sequential read | | N/A | 28.0 GB/s | N/A | + * | ahash | AES-NI | 64 | 22.5 GB/s | 107.2 | + * | City64 | | 64 | 22.0 GB/s | 76.6 | + * | T1ha2 | | 64 | 22.0 GB/s | 99.0 | + * | City128 | | 128 | 21.7 GB/s | 57.7 | + * | FarmHash | AES-NI | 64 | 21.3 GB/s | 71.9 | + * | XXH64() | | 64 | 19.4 GB/s | 71.0 | + * | SpookyHash | | 64 | 19.3 GB/s | 53.2 | + * | Mum | | 64 | 18.0 GB/s | 67.0 | + * | CRC32C | SSE4.2 | 32 | 13.0 GB/s | 57.9 | + * | XXH32() | | 32 | 9.7 GB/s | 71.9 | + * | City32 | | 32 | 9.1 GB/s | 66.0 | + * | Blake3* | @b AVX2 | 256 | 4.4 GB/s | 8.1 | + * | Murmur3 | | 32 | 3.9 GB/s | 56.1 | + * | SipHash* | | 64 | 3.0 GB/s | 43.2 | + * | Blake3* | @b SSE2 | 256 | 2.4 GB/s | 8.1 | + * | HighwayHash | | 64 | 1.4 GB/s | 6.0 | + * | FNV64 | | 64 | 1.2 GB/s | 62.7 | + * | Blake2* | | 256 | 1.1 GB/s | 5.1 | + * | SHA1* | | 160 | 0.8 GB/s | 5.6 | + * | MD5* | | 128 | 0.6 GB/s | 7.8 | + * @note + * - Hashes which require a specific ISA extension are noted. SSE2 is also noted, + * even though it is mandatory on x64. + * - Hashes with an asterisk are cryptographic. Note that MD5 is non-cryptographic + * by modern standards. + * - Small data velocity is a rough average of algorithm's efficiency for small + * data. For more accurate information, see the wiki. + * - More benchmarks and strength tests are found on the wiki: + * https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/wiki + * + * Usage + * ------ + * All xxHash variants use a similar API. Changing the algorithm is a trivial + * substitution. + * + * @pre + * For functions which take an input and length parameter, the following + * requirements are assumed: + * - The range from [`input`, `input + length`) is valid, readable memory. + * - The only exception is if the `length` is `0`, `input` may be `NULL`. + * - For C++, the objects must have the *TriviallyCopyable* property, as the + * functions access bytes directly as if it was an array of `unsigned char`. + * + * @anchor single_shot_example + * **Single Shot** + * + * These functions are stateless functions which hash a contiguous block of memory, + * immediately returning the result. They are the easiest and usually the fastest + * option. + * + * XXH32(), XXH64(), XXH3_64bits(), XXH3_128bits() + * + * @code{.c} + * #include <string.h> + * #include "xxhash.h" + * + * // Example for a function which hashes a null terminated string with XXH32(). + * XXH32_hash_t hash_string(const char* string, XXH32_hash_t seed) + * { + * // NULL pointers are only valid if the length is zero + * size_t length = (string == NULL) ? 0 : strlen(string); + * return XXH32(string, length, seed); + * } + * @endcode + * + * @anchor streaming_example + * **Streaming** + * + * These groups of functions allow incremental hashing of unknown size, even + * more than what would fit in a size_t. + * + * XXH32_reset(), XXH64_reset(), XXH3_64bits_reset(), XXH3_128bits_reset() + * + * @code{.c} + * #include <stdio.h> + * #include <assert.h> + * #include "xxhash.h" + * // Example for a function which hashes a FILE incrementally with XXH3_64bits(). + * XXH64_hash_t hashFile(FILE* f) + * { + * // Allocate a state struct. Do not just use malloc() or new. + * XXH3_state_t* state = XXH3_createState(); + * assert(state != NULL && "Out of memory!"); + * // Reset the state to start a new hashing session. + * XXH3_64bits_reset(state); + * char buffer[4096]; + * size_t count; + * // Read the file in chunks + * while ((count = fread(buffer, 1, sizeof(buffer), f)) != 0) { + * // Run update() as many times as necessary to process the data + * XXH3_64bits_update(state, buffer, count); + * } + * // Retrieve the finalized hash. This will not change the state. + * XXH64_hash_t result = XXH3_64bits_digest(state); + * // Free the state. Do not use free(). + * XXH3_freeState(state); + * return result; + * } + * @endcode + * + * @file xxhash.h + * xxHash prototypes and implementation + */ #if defined (__cplusplus) extern "C" { @@ -79,21 +177,80 @@ extern "C" { * INLINE mode ******************************/ /*! - * XXH_INLINE_ALL (and XXH_PRIVATE_API) + * @defgroup public Public API + * Contains details on the public xxHash functions. + * @{ + */ +#ifdef XXH_DOXYGEN +/*! + * @brief Gives access to internal state declaration, required for static allocation. + * + * Incompatible with dynamic linking, due to risks of ABI changes. + * + * Usage: + * @code{.c} + * #define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY + * #include "xxhash.h" + * @endcode + */ +# define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY +/* Do not undef XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY for Doxygen */ + +/*! + * @brief Gives access to internal definitions. + * + * Usage: + * @code{.c} + * #define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY + * #define XXH_IMPLEMENTATION + * #include "xxhash.h" + * @endcode + */ +# define XXH_IMPLEMENTATION +/* Do not undef XXH_IMPLEMENTATION for Doxygen */ + +/*! + * @brief Exposes the implementation and marks all functions as `inline`. + * * Use these build macros to inline xxhash into the target unit. * Inlining improves performance on small inputs, especially when the length is * expressed as a compile-time constant: * - * https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2018/03/xxhash-for-small-keys-impressive-power.html + * https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2018/03/xxhash-for-small-keys-impressive-power.html * * It also keeps xxHash symbols private to the unit, so they are not exported. * * Usage: + * @code{.c} * #define XXH_INLINE_ALL * #include "xxhash.h" - * + * @endcode * Do not compile and link xxhash.o as a separate object, as it is not useful. */ +# define XXH_INLINE_ALL +# undef XXH_INLINE_ALL +/*! + * @brief Exposes the implementation without marking functions as inline. + */ +# define XXH_PRIVATE_API +# undef XXH_PRIVATE_API +/*! + * @brief Emulate a namespace by transparently prefixing all symbols. + * + * If you want to include _and expose_ xxHash functions from within your own + * library, but also want to avoid symbol collisions with other libraries which + * may also include xxHash, you can use @ref XXH_NAMESPACE to automatically prefix + * any public symbol from xxhash library with the value of @ref XXH_NAMESPACE + * (therefore, avoid empty or numeric values). + * + * Note that no change is required within the calling program as long as it + * includes `xxhash.h`: Regular symbol names will be automatically translated + * by this header. + */ +# define XXH_NAMESPACE /* YOUR NAME HERE */ +# undef XXH_NAMESPACE +#endif + #if (defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) || defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API)) \ && !defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL_31684351384) /* this section should be traversed only once */ @@ -116,29 +273,80 @@ extern "C" { /* * This part deals with the special case where a unit wants to inline xxHash, - * but "xxhash.h" has previously been included without XXH_INLINE_ALL, such - * as part of some previously included *.h header file. + * but "xxhash.h" has previously been included without XXH_INLINE_ALL, + * such as part of some previously included *.h header file. * Without further action, the new include would just be ignored, * and functions would effectively _not_ be inlined (silent failure). * The following macros solve this situation by prefixing all inlined names, * avoiding naming collision with previous inclusions. */ -# ifdef XXH_NAMESPACE -# error "XXH_INLINE_ALL with XXH_NAMESPACE is not supported" - /* - * Note: Alternative: #undef all symbols (it's a pretty large list). - * Without #error: it compiles, but functions are actually not inlined. - */ -# endif + /* Before that, we unconditionally #undef all symbols, + * in case they were already defined with XXH_NAMESPACE. + * They will then be redefined for XXH_INLINE_ALL + */ +# undef XXH_versionNumber + /* XXH32 */ +# undef XXH32 +# undef XXH32_createState +# undef XXH32_freeState +# undef XXH32_reset +# undef XXH32_update +# undef XXH32_digest +# undef XXH32_copyState +# undef XXH32_canonicalFromHash +# undef XXH32_hashFromCanonical + /* XXH64 */ +# undef XXH64 +# undef XXH64_createState +# undef XXH64_freeState +# undef XXH64_reset +# undef XXH64_update +# undef XXH64_digest +# undef XXH64_copyState +# undef XXH64_canonicalFromHash +# undef XXH64_hashFromCanonical + /* XXH3_64bits */ +# undef XXH3_64bits +# undef XXH3_64bits_withSecret +# undef XXH3_64bits_withSeed +# undef XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed +# undef XXH3_createState +# undef XXH3_freeState +# undef XXH3_copyState +# undef XXH3_64bits_reset +# undef XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed +# undef XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret +# undef XXH3_64bits_update +# undef XXH3_64bits_digest +# undef XXH3_generateSecret + /* XXH3_128bits */ +# undef XXH128 +# undef XXH3_128bits +# undef XXH3_128bits_withSeed +# undef XXH3_128bits_withSecret +# undef XXH3_128bits_reset +# undef XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed +# undef XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret +# undef XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecretandSeed +# undef XXH3_128bits_update +# undef XXH3_128bits_digest +# undef XXH128_isEqual +# undef XXH128_cmp +# undef XXH128_canonicalFromHash +# undef XXH128_hashFromCanonical + /* Finally, free the namespace itself */ +# undef XXH_NAMESPACE + + /* employ the namespace for XXH_INLINE_ALL */ # define XXH_NAMESPACE XXH_INLINE_ /* - * Some identifiers (enums, type names) are not symbols, but they must - * still be renamed to avoid redeclaration. + * Some identifiers (enums, type names) are not symbols, + * but they must nonetheless be renamed to avoid redeclaration. * Alternative solution: do not redeclare them. - * However, this requires some #ifdefs, and is a more dispersed action. - * Meanwhile, renaming can be achieved in a single block + * However, this requires some #ifdefs, and has a more dispersed impact. + * Meanwhile, renaming can be achieved in a single place. */ -# define XXH_IPREF(Id) XXH_INLINE_ ## Id +# define XXH_IPREF(Id) XXH_NAMESPACE ## Id # define XXH_OK XXH_IPREF(XXH_OK) # define XXH_ERROR XXH_IPREF(XXH_ERROR) # define XXH_errorcode XXH_IPREF(XXH_errorcode) @@ -157,15 +365,13 @@ extern "C" { # undef XXHASH_H_STATIC_13879238742 #endif /* XXH_INLINE_ALL || XXH_PRIVATE_API */ - - /* **************************************************************** * Stable API *****************************************************************/ #ifndef XXHASH_H_5627135585666179 #define XXHASH_H_5627135585666179 1 -/* specific declaration modes for Windows */ +/*! @brief Marks a global symbol. */ #if !defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) && !defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API) # if defined(WIN32) && defined(_MSC_VER) && (defined(XXH_IMPORT) || defined(XXH_EXPORT)) # ifdef XXH_EXPORT @@ -178,19 +384,6 @@ extern "C" { # endif #endif -/*! - * XXH_NAMESPACE, aka Namespace Emulation: - * - * If you want to include _and expose_ xxHash functions from within your own - * library, but also want to avoid symbol collisions with other libraries which - * may also include xxHash, you can use XXH_NAMESPACE to automatically prefix - * any public symbol from xxhash library with the value of XXH_NAMESPACE - * (therefore, avoid empty or numeric values). - * - * Note that no change is required within the calling program as long as it - * includes `xxhash.h`: Regular symbol names will be automatically translated - * by this header. - */ #ifdef XXH_NAMESPACE # define XXH_CAT(A,B) A##B # define XXH_NAME2(A,B) XXH_CAT(A,B) @@ -219,23 +412,28 @@ extern "C" { # define XXH3_64bits XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits) # define XXH3_64bits_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_withSecret) # define XXH3_64bits_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_withSeed) +# define XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed) # define XXH3_createState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_createState) # define XXH3_freeState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_freeState) # define XXH3_copyState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_copyState) # define XXH3_64bits_reset XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_reset) # define XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed) # define XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret) +# define XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecretandSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecretandSeed) # define XXH3_64bits_update XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_update) # define XXH3_64bits_digest XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_digest) # define XXH3_generateSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_generateSecret) +# define XXH3_generateSecret_fromSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_generateSecret_fromSeed) /* XXH3_128bits */ # define XXH128 XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH128) # define XXH3_128bits XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits) # define XXH3_128bits_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_withSeed) # define XXH3_128bits_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_withSecret) +# define XXH3_128bits_withSecretandSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_withSecretandSeed) # define XXH3_128bits_reset XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_reset) # define XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed) # define XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret) +# define XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecretandSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecretandSeed) # define XXH3_128bits_update XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_update) # define XXH3_128bits_digest XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_digest) # define XXH128_isEqual XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH128_isEqual) @@ -246,60 +444,139 @@ extern "C" { /* ************************************* +* Compiler specifics +***************************************/ + +/* specific declaration modes for Windows */ +#if !defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) && !defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API) +# if defined(WIN32) && defined(_MSC_VER) && (defined(XXH_IMPORT) || defined(XXH_EXPORT)) +# ifdef XXH_EXPORT +# define XXH_PUBLIC_API __declspec(dllexport) +# elif XXH_IMPORT +# define XXH_PUBLIC_API __declspec(dllimport) +# endif +# else +# define XXH_PUBLIC_API /* do nothing */ +# endif +#endif + +#if defined (__GNUC__) +# define XXH_CONSTF __attribute__((const)) +# define XXH_PUREF __attribute__((pure)) +# define XXH_MALLOCF __attribute__((malloc)) +#else +# define XXH_CONSTF /* disable */ +# define XXH_PUREF +# define XXH_MALLOCF +#endif + +/* ************************************* * Version ***************************************/ #define XXH_VERSION_MAJOR 0 #define XXH_VERSION_MINOR 8 -#define XXH_VERSION_RELEASE 0 +#define XXH_VERSION_RELEASE 2 +/*! @brief Version number, encoded as two digits each */ #define XXH_VERSION_NUMBER (XXH_VERSION_MAJOR *100*100 + XXH_VERSION_MINOR *100 + XXH_VERSION_RELEASE) -XXH_PUBLIC_API unsigned XXH_versionNumber (void); + +/*! + * @brief Obtains the xxHash version. + * + * This is mostly useful when xxHash is compiled as a shared library, + * since the returned value comes from the library, as opposed to header file. + * + * @return @ref XXH_VERSION_NUMBER of the invoked library. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_CONSTF unsigned XXH_versionNumber (void); /* **************************** -* Definitions +* Common basic types ******************************/ #include <stddef.h> /* size_t */ -typedef enum { XXH_OK=0, XXH_ERROR } XXH_errorcode; +/*! + * @brief Exit code for the streaming API. + */ +typedef enum { + XXH_OK = 0, /*!< OK */ + XXH_ERROR /*!< Error */ +} XXH_errorcode; /*-********************************************************************** * 32-bit hash ************************************************************************/ -#if !defined (__VMS) \ +#if defined(XXH_DOXYGEN) /* Don't show <stdint.h> include */ +/*! + * @brief An unsigned 32-bit integer. + * + * Not necessarily defined to `uint32_t` but functionally equivalent. + */ +typedef uint32_t XXH32_hash_t; + +#elif !defined (__VMS) \ && (defined (__cplusplus) \ || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L) /* C99 */) ) # include <stdint.h> typedef uint32_t XXH32_hash_t; + #else # include <limits.h> # if UINT_MAX == 0xFFFFFFFFUL typedef unsigned int XXH32_hash_t; +# elif ULONG_MAX == 0xFFFFFFFFUL + typedef unsigned long XXH32_hash_t; # else -# if ULONG_MAX == 0xFFFFFFFFUL - typedef unsigned long XXH32_hash_t; -# else -# error "unsupported platform: need a 32-bit type" -# endif +# error "unsupported platform: need a 32-bit type" # endif #endif /*! - * XXH32(): - * Calculate the 32-bit hash of sequence "length" bytes stored at memory address "input". - * The memory between input & input+length must be valid (allocated and read-accessible). - * "seed" can be used to alter the result predictably. - * Speed on Core 2 Duo @ 3 GHz (single thread, SMHasher benchmark): 5.4 GB/s + * @} + * + * @defgroup XXH32_family XXH32 family + * @ingroup public + * Contains functions used in the classic 32-bit xxHash algorithm. + * + * @note + * XXH32 is useful for older platforms, with no or poor 64-bit performance. + * Note that the @ref XXH3_family provides competitive speed for both 32-bit + * and 64-bit systems, and offers true 64/128 bit hash results. * - * Note: XXH3 provides competitive speed for both 32-bit and 64-bit systems, - * and offers true 64/128 bit hash results. It provides a superior level of - * dispersion, and greatly reduces the risks of collisions. + * @see @ref XXH64_family, @ref XXH3_family : Other xxHash families + * @see @ref XXH32_impl for implementation details + * @{ */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32 (const void* input, size_t length, XXH32_hash_t seed); -/******* Streaming *******/ +/*! + * @brief Calculates the 32-bit hash of @p input using xxHash32. + * + * Speed on Core 2 Duo @ 3 GHz (single thread, SMHasher benchmark): 5.4 GB/s + * + * See @ref single_shot_example "Single Shot Example" for an example. + * + * @param input The block of data to be hashed, at least @p length bytes in size. + * @param length The length of @p input, in bytes. + * @param seed The 32-bit seed to alter the hash's output predictably. + * + * @pre + * The memory between @p input and @p input + @p length must be valid, + * readable, contiguous memory. However, if @p length is `0`, @p input may be + * `NULL`. In C++, this also must be *TriviallyCopyable*. + * + * @return The calculated 32-bit hash value. + * + * @see + * XXH64(), XXH3_64bits_withSeed(), XXH3_128bits_withSeed(), XXH128(): + * Direct equivalents for the other variants of xxHash. + * @see + * XXH32_createState(), XXH32_update(), XXH32_digest(): Streaming version. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH32_hash_t XXH32 (const void* input, size_t length, XXH32_hash_t seed); -/* - * Streaming functions generate the xxHash value from an incrememtal input. +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM +/*! + * Streaming functions generate the xxHash value from an incremental input. * This method is slower than single-call functions, due to state management. * For small inputs, prefer `XXH32()` and `XXH64()`, which are better optimized. * @@ -319,16 +596,94 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32 (const void* input, size_t length, XXH32_hash_ * digest, and generate new hash values later on by invoking `XXH*_digest()`. * * When done, release the state using `XXH*_freeState()`. + * + * @see streaming_example at the top of @ref xxhash.h for an example. */ -typedef struct XXH32_state_s XXH32_state_t; /* incomplete type */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_state_t* XXH32_createState(void); +/*! + * @typedef struct XXH32_state_s XXH32_state_t + * @brief The opaque state struct for the XXH32 streaming API. + * + * @see XXH32_state_s for details. + */ +typedef struct XXH32_state_s XXH32_state_t; + +/*! + * @brief Allocates an @ref XXH32_state_t. + * + * Must be freed with XXH32_freeState(). + * @return An allocated XXH32_state_t on success, `NULL` on failure. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_MALLOCF XXH32_state_t* XXH32_createState(void); +/*! + * @brief Frees an @ref XXH32_state_t. + * + * Must be allocated with XXH32_createState(). + * @param statePtr A pointer to an @ref XXH32_state_t allocated with @ref XXH32_createState(). + * @return XXH_OK. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_freeState(XXH32_state_t* statePtr); +/*! + * @brief Copies one @ref XXH32_state_t to another. + * + * @param dst_state The state to copy to. + * @param src_state The state to copy from. + * @pre + * @p dst_state and @p src_state must not be `NULL` and must not overlap. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_copyState(XXH32_state_t* dst_state, const XXH32_state_t* src_state); +/*! + * @brief Resets an @ref XXH32_state_t to begin a new hash. + * + * This function resets and seeds a state. Call it before @ref XXH32_update(). + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to reset. + * @param seed The 32-bit seed to alter the hash result predictably. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_reset (XXH32_state_t* statePtr, XXH32_hash_t seed); + +/*! + * @brief Consumes a block of @p input to an @ref XXH32_state_t. + * + * Call this to incrementally consume blocks of data. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to update. + * @param input The block of data to be hashed, at least @p length bytes in size. + * @param length The length of @p input, in bytes. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * @pre + * The memory between @p input and @p input + @p length must be valid, + * readable, contiguous memory. However, if @p length is `0`, @p input may be + * `NULL`. In C++, this also must be *TriviallyCopyable*. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_update (XXH32_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_digest (const XXH32_state_t* statePtr); + +/*! + * @brief Returns the calculated hash value from an @ref XXH32_state_t. + * + * @note + * Calling XXH32_digest() will not affect @p statePtr, so you can update, + * digest, and update again. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to calculate the hash from. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return The calculated xxHash32 value from that state. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH32_hash_t XXH32_digest (const XXH32_state_t* statePtr); +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /******* Canonical representation *******/ @@ -351,62 +706,300 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_digest (const XXH32_state_t* statePtr); * canonical format. */ -typedef struct { unsigned char digest[4]; } XXH32_canonical_t; +/*! + * @brief Canonical (big endian) representation of @ref XXH32_hash_t. + */ +typedef struct { + unsigned char digest[4]; /*!< Hash bytes, big endian */ +} XXH32_canonical_t; + +/*! + * @brief Converts an @ref XXH32_hash_t to a big endian @ref XXH32_canonical_t. + * + * @param dst The @ref XXH32_canonical_t pointer to be stored to. + * @param hash The @ref XXH32_hash_t to be converted. + * + * @pre + * @p dst must not be `NULL`. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_canonicalFromHash(XXH32_canonical_t* dst, XXH32_hash_t hash); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_hashFromCanonical(const XXH32_canonical_t* src); +/*! + * @brief Converts an @ref XXH32_canonical_t to a native @ref XXH32_hash_t. + * + * @param src The @ref XXH32_canonical_t to convert. + * + * @pre + * @p src must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return The converted hash. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH32_hash_t XXH32_hashFromCanonical(const XXH32_canonical_t* src); + + +/*! @cond Doxygen ignores this part */ +#ifdef __has_attribute +# define XXH_HAS_ATTRIBUTE(x) __has_attribute(x) +#else +# define XXH_HAS_ATTRIBUTE(x) 0 +#endif +/*! @endcond */ + +/*! @cond Doxygen ignores this part */ +/* + * C23 __STDC_VERSION__ number hasn't been specified yet. For now + * leave as `201711L` (C17 + 1). + * TODO: Update to correct value when its been specified. + */ +#define XXH_C23_VN 201711L +/*! @endcond */ + +/*! @cond Doxygen ignores this part */ +/* C-language Attributes are added in C23. */ +#if defined(__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= XXH_C23_VN) && defined(__has_c_attribute) +# define XXH_HAS_C_ATTRIBUTE(x) __has_c_attribute(x) +#else +# define XXH_HAS_C_ATTRIBUTE(x) 0 +#endif +/*! @endcond */ + +/*! @cond Doxygen ignores this part */ +#if defined(__cplusplus) && defined(__has_cpp_attribute) +# define XXH_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(x) __has_cpp_attribute(x) +#else +# define XXH_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(x) 0 +#endif +/*! @endcond */ + +/*! @cond Doxygen ignores this part */ +/* + * Define XXH_FALLTHROUGH macro for annotating switch case with the 'fallthrough' attribute + * introduced in CPP17 and C23. + * CPP17 : https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/attributes/fallthrough + * C23 : https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/language/attributes/fallthrough + */ +#if XXH_HAS_C_ATTRIBUTE(fallthrough) || XXH_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(fallthrough) +# define XXH_FALLTHROUGH [[fallthrough]] +#elif XXH_HAS_ATTRIBUTE(__fallthrough__) +# define XXH_FALLTHROUGH __attribute__ ((__fallthrough__)) +#else +# define XXH_FALLTHROUGH /* fallthrough */ +#endif +/*! @endcond */ + +/*! @cond Doxygen ignores this part */ +/* + * Define XXH_NOESCAPE for annotated pointers in public API. + * https://clang.llvm.org/docs/AttributeReference.html#noescape + * As of writing this, only supported by clang. + */ +#if XXH_HAS_ATTRIBUTE(noescape) +# define XXH_NOESCAPE __attribute__((noescape)) +#else +# define XXH_NOESCAPE +#endif +/*! @endcond */ + + +/*! + * @} + * @ingroup public + * @{ + */ #ifndef XXH_NO_LONG_LONG /*-********************************************************************** * 64-bit hash ************************************************************************/ -#if !defined (__VMS) \ +#if defined(XXH_DOXYGEN) /* don't include <stdint.h> */ +/*! + * @brief An unsigned 64-bit integer. + * + * Not necessarily defined to `uint64_t` but functionally equivalent. + */ +typedef uint64_t XXH64_hash_t; +#elif !defined (__VMS) \ && (defined (__cplusplus) \ || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L) /* C99 */) ) -# include <stdint.h> - typedef uint64_t XXH64_hash_t; +# include <stdint.h> + typedef uint64_t XXH64_hash_t; #else - /* the following type must have a width of 64-bit */ - typedef unsigned long long XXH64_hash_t; +# include <limits.h> +# if defined(__LP64__) && ULONG_MAX == 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFULL + /* LP64 ABI says uint64_t is unsigned long */ + typedef unsigned long XXH64_hash_t; +# else + /* the following type must have a width of 64-bit */ + typedef unsigned long long XXH64_hash_t; +# endif #endif /*! - * XXH64(): - * Returns the 64-bit hash of sequence of length @length stored at memory - * address @input. - * @seed can be used to alter the result predictably. + * @} + * + * @defgroup XXH64_family XXH64 family + * @ingroup public + * @{ + * Contains functions used in the classic 64-bit xxHash algorithm. + * + * @note + * XXH3 provides competitive speed for both 32-bit and 64-bit systems, + * and offers true 64/128 bit hash results. + * It provides better speed for systems with vector processing capabilities. + */ + +/*! + * @brief Calculates the 64-bit hash of @p input using xxHash64. * * This function usually runs faster on 64-bit systems, but slower on 32-bit * systems (see benchmark). * - * Note: XXH3 provides competitive speed for both 32-bit and 64-bit systems, - * and offers true 64/128 bit hash results. It provides a superior level of - * dispersion, and greatly reduces the risks of collisions. + * @param input The block of data to be hashed, at least @p length bytes in size. + * @param length The length of @p input, in bytes. + * @param seed The 64-bit seed to alter the hash's output predictably. + * + * @pre + * The memory between @p input and @p input + @p length must be valid, + * readable, contiguous memory. However, if @p length is `0`, @p input may be + * `NULL`. In C++, this also must be *TriviallyCopyable*. + * + * @return The calculated 64-bit hash. + * + * @see + * XXH32(), XXH3_64bits_withSeed(), XXH3_128bits_withSeed(), XXH128(): + * Direct equivalents for the other variants of xxHash. + * @see + * XXH64_createState(), XXH64_update(), XXH64_digest(): Streaming version. */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64 (const void* input, size_t length, XXH64_hash_t seed); +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH64(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length, XXH64_hash_t seed); /******* Streaming *******/ +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM +/*! + * @brief The opaque state struct for the XXH64 streaming API. + * + * @see XXH64_state_s for details. + */ typedef struct XXH64_state_s XXH64_state_t; /* incomplete type */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_state_t* XXH64_createState(void); + +/*! + * @brief Allocates an @ref XXH64_state_t. + * + * Must be freed with XXH64_freeState(). + * @return An allocated XXH64_state_t on success, `NULL` on failure. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_MALLOCF XXH64_state_t* XXH64_createState(void); + +/*! + * @brief Frees an @ref XXH64_state_t. + * + * Must be allocated with XXH64_createState(). + * @param statePtr A pointer to an @ref XXH64_state_t allocated with @ref XXH64_createState(). + * @return XXH_OK. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_freeState(XXH64_state_t* statePtr); -XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_copyState(XXH64_state_t* dst_state, const XXH64_state_t* src_state); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_reset (XXH64_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_update (XXH64_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_digest (const XXH64_state_t* statePtr); +/*! + * @brief Copies one @ref XXH64_state_t to another. + * + * @param dst_state The state to copy to. + * @param src_state The state to copy from. + * @pre + * @p dst_state and @p src_state must not be `NULL` and must not overlap. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_copyState(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_state_t* dst_state, const XXH64_state_t* src_state); +/*! + * @brief Resets an @ref XXH64_state_t to begin a new hash. + * + * This function resets and seeds a state. Call it before @ref XXH64_update(). + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to reset. + * @param seed The 64-bit seed to alter the hash result predictably. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_reset (XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed); + +/*! + * @brief Consumes a block of @p input to an @ref XXH64_state_t. + * + * Call this to incrementally consume blocks of data. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to update. + * @param input The block of data to be hashed, at least @p length bytes in size. + * @param length The length of @p input, in bytes. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * @pre + * The memory between @p input and @p input + @p length must be valid, + * readable, contiguous memory. However, if @p length is `0`, @p input may be + * `NULL`. In C++, this also must be *TriviallyCopyable*. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_update (XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length); + +/*! + * @brief Returns the calculated hash value from an @ref XXH64_state_t. + * + * @note + * Calling XXH64_digest() will not affect @p statePtr, so you can update, + * digest, and update again. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to calculate the hash from. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return The calculated xxHash64 value from that state. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH64_digest (XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH64_state_t* statePtr); +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /******* Canonical representation *******/ + +/*! + * @brief Canonical (big endian) representation of @ref XXH64_hash_t. + */ typedef struct { unsigned char digest[sizeof(XXH64_hash_t)]; } XXH64_canonical_t; -XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_canonicalFromHash(XXH64_canonical_t* dst, XXH64_hash_t hash); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src); +/*! + * @brief Converts an @ref XXH64_hash_t to a big endian @ref XXH64_canonical_t. + * + * @param dst The @ref XXH64_canonical_t pointer to be stored to. + * @param hash The @ref XXH64_hash_t to be converted. + * + * @pre + * @p dst must not be `NULL`. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_canonicalFromHash(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_canonical_t* dst, XXH64_hash_t hash); -/*-********************************************************************** -* XXH3 64-bit variant -************************************************************************/ +/*! + * @brief Converts an @ref XXH64_canonical_t to a native @ref XXH64_hash_t. + * + * @param src The @ref XXH64_canonical_t to convert. + * + * @pre + * @p src must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return The converted hash. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH64_canonical_t* src); -/* ************************************************************************ - * XXH3 is a new hash algorithm featuring: +#ifndef XXH_NO_XXH3 + +/*! + * @} + * ************************************************************************ + * @defgroup XXH3_family XXH3 family + * @ingroup public + * @{ + * + * XXH3 is a more recent hash algorithm featuring: * - Improved speed for both small and large inputs * - True 64-bit and 128-bit outputs * - SIMD acceleration @@ -416,102 +1009,172 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src * * https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2019/03/presenting-xxh3.html * - * In general, expect XXH3 to run about ~2x faster on large inputs and >3x - * faster on small ones compared to XXH64, though exact differences depend on - * the platform. - * - * The algorithm is portable: Like XXH32 and XXH64, it generates the same hash - * on all platforms. + * Compared to XXH64, expect XXH3 to run approximately + * ~2x faster on large inputs and >3x faster on small ones, + * exact differences vary depending on platform. * - * It benefits greatly from SIMD and 64-bit arithmetic, but does not require it. - * - * Almost all 32-bit and 64-bit targets that can run XXH32 smoothly can run - * XXH3 at competitive speeds, even if XXH64 runs slowly. Further details are + * XXH3's speed benefits greatly from SIMD and 64-bit arithmetic, + * but does not require it. + * Most 32-bit and 64-bit targets that can run XXH32 smoothly can run XXH3 + * at competitive speeds, even without vector support. Further details are * explained in the implementation. * - * Optimized implementations are provided for AVX512, AVX2, SSE2, NEON, POWER8, - * ZVector and scalar targets. This can be controlled with the XXH_VECTOR macro. + * XXH3 has a fast scalar implementation, but it also includes accelerated SIMD + * implementations for many common platforms: + * - AVX512 + * - AVX2 + * - SSE2 + * - ARM NEON + * - WebAssembly SIMD128 + * - POWER8 VSX + * - s390x ZVector + * This can be controlled via the @ref XXH_VECTOR macro, but it automatically + * selects the best version according to predefined macros. For the x86 family, an + * automatic runtime dispatcher is included separately in @ref xxh_x86dispatch.c. + * + * XXH3 implementation is portable: + * it has a generic C90 formulation that can be compiled on any platform, + * all implementations generate exactly the same hash value on all platforms. + * Starting from v0.8.0, it's also labelled "stable", meaning that + * any future version will also generate the same hash value. * * XXH3 offers 2 variants, _64bits and _128bits. - * When only 64 bits are needed, prefer calling the _64bits variant, as it - * reduces the amount of mixing, resulting in faster speed on small inputs. * + * When only 64 bits are needed, prefer invoking the _64bits variant, as it + * reduces the amount of mixing, resulting in faster speed on small inputs. * It's also generally simpler to manipulate a scalar return type than a struct. * - * The 128-bit version adds additional strength, but it is slightly slower. - * - * The XXH3 algorithm is still in development. - * The results it produces may still change in future versions. + * The API supports one-shot hashing, streaming mode, and custom secrets. + */ +/*-********************************************************************** +* XXH3 64-bit variant +************************************************************************/ + +/*! + * @brief 64-bit unseeded variant of XXH3. + * + * This is equivalent to @ref XXH3_64bits_withSeed() with a seed of 0, however + * it may have slightly better performance due to constant propagation of the + * defaults. + * + * @see + * XXH32(), XXH64(), XXH3_128bits(): equivalent for the other xxHash algorithms + * @see + * XXH3_64bits_withSeed(), XXH3_64bits_withSecret(): other seeding variants + * @see + * XXH3_64bits_reset(), XXH3_64bits_update(), XXH3_64bits_digest(): Streaming version. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length); + +/*! + * @brief 64-bit seeded variant of XXH3 * - * Results produced by v0.7.x are not comparable with results from v0.7.y. - * However, the API is completely stable, and it can safely be used for - * ephemeral data (local sessions). + * This variant generates a custom secret on the fly based on default secret + * altered using the `seed` value. * - * Avoid storing values in long-term storage until the algorithm is finalized. - * XXH3's return values will be officially finalized upon reaching v0.8.0. + * While this operation is decently fast, note that it's not completely free. * - * After which, return values of XXH3 and XXH128 will no longer change in - * future versions. + * @note + * seed == 0 produces the same results as @ref XXH3_64bits(). * - * The API supports one-shot hashing, streaming mode, and custom secrets. + * @param input The data to hash + * @param length The length + * @param seed The 64-bit seed to alter the state. */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length, XXH64_hash_t seed); -/* XXH3_64bits(): - * default 64-bit variant, using default secret and default seed of 0. - * It's the fastest variant. */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits(const void* data, size_t len); - -/* - * XXH3_64bits_withSeed(): - * This variant generates a custom secret on the fly - * based on default secret altered using the `seed` value. - * While this operation is decently fast, note that it's not completely free. - * Note: seed==0 produces the same results as XXH3_64bits(). +/*! + * The bare minimum size for a custom secret. + * + * @see + * XXH3_64bits_withSecret(), XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(), + * XXH3_128bits_withSecret(), XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret(). */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_withSeed(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed); +#define XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN 136 -/* - * XXH3_64bits_withSecret(): +/*! + * @brief 64-bit variant of XXH3 with a custom "secret". + * * It's possible to provide any blob of bytes as a "secret" to generate the hash. * This makes it more difficult for an external actor to prepare an intentional collision. * The main condition is that secretSize *must* be large enough (>= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN). - * However, the quality of produced hash values depends on secret's entropy. - * Technically, the secret must look like a bunch of random bytes. + * However, the quality of the secret impacts the dispersion of the hash algorithm. + * Therefore, the secret _must_ look like a bunch of random bytes. * Avoid "trivial" or structured data such as repeated sequences or a text document. - * Whenever unsure about the "randomness" of the blob of bytes, - * consider relabelling it as a "custom seed" instead, - * and employ "XXH3_generateSecret()" (see below) - * to generate a high entropy secret derived from the custom seed. + * Whenever in doubt about the "randomness" of the blob of bytes, + * consider employing "XXH3_generateSecret()" instead (see below). + * It will generate a proper high entropy secret derived from the blob of bytes. + * Another advantage of using XXH3_generateSecret() is that + * it guarantees that all bits within the initial blob of bytes + * will impact every bit of the output. + * This is not necessarily the case when using the blob of bytes directly + * because, when hashing _small_ inputs, only a portion of the secret is employed. */ -#define XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN 136 -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_withSecret(const void* data, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize); +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* data, size_t len, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize); /******* Streaming *******/ +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM /* * Streaming requires state maintenance. * This operation costs memory and CPU. * As a consequence, streaming is slower than one-shot hashing. * For better performance, prefer one-shot functions whenever applicable. */ + +/*! + * @brief The state struct for the XXH3 streaming API. + * + * @see XXH3_state_s for details. + */ typedef struct XXH3_state_s XXH3_state_t; -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH3_state_t* XXH3_createState(void); +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_MALLOCF XXH3_state_t* XXH3_createState(void); XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_freeState(XXH3_state_t* statePtr); -XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH3_copyState(XXH3_state_t* dst_state, const XXH3_state_t* src_state); -/* - * XXH3_64bits_reset(): - * Initialize with default parameters. - * digest will be equivalent to `XXH3_64bits()`. +/*! + * @brief Copies one @ref XXH3_state_t to another. + * + * @param dst_state The state to copy to. + * @param src_state The state to copy from. + * @pre + * @p dst_state and @p src_state must not be `NULL` and must not overlap. */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr); -/* - * XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(): - * Generate a custom secret from `seed`, and store it into `statePtr`. - * digest will be equivalent to `XXH3_64bits_withSeed()`. +XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH3_copyState(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* dst_state, XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH3_state_t* src_state); + +/*! + * @brief Resets an @ref XXH3_state_t to begin a new hash. + * + * This function resets `statePtr` and generate a secret with default parameters. Call it before @ref XXH3_64bits_update(). + * Digest will be equivalent to `XXH3_64bits()`. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to reset. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + * */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed); -/* +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr); + +/*! + * @brief Resets an @ref XXH3_state_t with 64-bit seed to begin a new hash. + * + * This function resets `statePtr` and generate a secret from `seed`. Call it before @ref XXH3_64bits_update(). + * Digest will be equivalent to `XXH3_64bits_withSeed()`. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to reset. + * @param seed The 64-bit seed to alter the state. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + * + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed); + +/*! * XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(): * `secret` is referenced, it _must outlive_ the hash streaming session. * Similar to one-shot API, `secretSize` must be >= `XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN`, @@ -520,10 +1183,44 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, * When in doubt about the randomness of a candidate `secret`, * consider employing `XXH3_generateSecret()` instead (see below). */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize); +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_update (XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* statePtr); +/*! + * @brief Consumes a block of @p input to an @ref XXH3_state_t. + * + * Call this to incrementally consume blocks of data. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to update. + * @param input The block of data to be hashed, at least @p length bytes in size. + * @param length The length of @p input, in bytes. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * @pre + * The memory between @p input and @p input + @p length must be valid, + * readable, contiguous memory. However, if @p length is `0`, @p input may be + * `NULL`. In C++, this also must be *TriviallyCopyable*. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_update (XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length); + +/*! + * @brief Returns the calculated XXH3 64-bit hash value from an @ref XXH3_state_t. + * + * @note + * Calling XXH3_64bits_digest() will not affect @p statePtr, so you can update, + * digest, and update again. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to calculate the hash from. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return The calculated XXH3 64-bit hash value from that state. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH3_state_t* statePtr); +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /* note : canonical representation of XXH3 is the same as XXH64 * since they both produce XXH64_hash_t values */ @@ -533,16 +1230,42 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* statePtr); * XXH3 128-bit variant ************************************************************************/ +/*! + * @brief The return value from 128-bit hashes. + * + * Stored in little endian order, although the fields themselves are in native + * endianness. + */ typedef struct { - XXH64_hash_t low64; - XXH64_hash_t high64; + XXH64_hash_t low64; /*!< `value & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF` */ + XXH64_hash_t high64; /*!< `value >> 64` */ } XXH128_hash_t; -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits(const void* data, size_t len); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_withSeed(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_withSecret(const void* data, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize); +/*! + * @brief Unseeded 128-bit variant of XXH3 + * + * The 128-bit variant of XXH3 has more strength, but it has a bit of overhead + * for shorter inputs. + * + * This is equivalent to @ref XXH3_128bits_withSeed() with a seed of 0, however + * it may have slightly better performance due to constant propagation of the + * defaults. + * + * @see + * XXH32(), XXH64(), XXH3_64bits(): equivalent for the other xxHash algorithms + * @see + * XXH3_128bits_withSeed(), XXH3_128bits_withSecret(): other seeding variants + * @see + * XXH3_128bits_reset(), XXH3_128bits_update(), XXH3_128bits_digest(): Streaming version. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* data, size_t len); +/*! @brief Seeded 128-bit variant of XXH3. @see XXH3_64bits_withSeed(). */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed); +/*! @brief Custom secret 128-bit variant of XXH3. @see XXH3_64bits_withSecret(). */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* data, size_t len, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize); /******* Streaming *******/ +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM /* * Streaming requires state maintenance. * This operation costs memory and CPU. @@ -555,12 +1278,77 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_withSecret(const void* data, size_t le * All reset and streaming functions have same meaning as their 64-bit counterpart. */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize); +/*! + * @brief Resets an @ref XXH3_state_t to begin a new hash. + * + * This function resets `statePtr` and generate a secret with default parameters. Call it before @ref XXH3_128bits_update(). + * Digest will be equivalent to `XXH3_128bits()`. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to reset. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + * + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr); + +/*! + * @brief Resets an @ref XXH3_state_t with 64-bit seed to begin a new hash. + * + * This function resets `statePtr` and generate a secret from `seed`. Call it before @ref XXH3_128bits_update(). + * Digest will be equivalent to `XXH3_128bits_withSeed()`. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to reset. + * @param seed The 64-bit seed to alter the state. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + * + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed); +/*! @brief Custom secret 128-bit variant of XXH3. @see XXH_64bits_reset_withSecret(). */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_update (XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* statePtr); +/*! + * @brief Consumes a block of @p input to an @ref XXH3_state_t. + * + * Call this to incrementally consume blocks of data. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to update. + * @param input The block of data to be hashed, at least @p length bytes in size. + * @param length The length of @p input, in bytes. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * @pre + * The memory between @p input and @p input + @p length must be valid, + * readable, contiguous memory. However, if @p length is `0`, @p input may be + * `NULL`. In C++, this also must be *TriviallyCopyable*. + * + * @return @ref XXH_OK on success, @ref XXH_ERROR on failure. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_update (XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length); + +/*! + * @brief Returns the calculated XXH3 128-bit hash value from an @ref XXH3_state_t. + * + * @note + * Calling XXH3_128bits_digest() will not affect @p statePtr, so you can update, + * digest, and update again. + * + * @param statePtr The state struct to calculate the hash from. + * + * @pre + * @p statePtr must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return The calculated XXH3 128-bit hash value from that state. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH3_state_t* statePtr); +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /* Following helper functions make it possible to compare XXH128_hast_t values. * Since XXH128_hash_t is a structure, this capability is not offered by the language. @@ -570,28 +1358,53 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* statePtr); * XXH128_isEqual(): * Return: 1 if `h1` and `h2` are equal, 0 if they are not. */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_isEqual(XXH128_hash_t h1, XXH128_hash_t h2); +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF int XXH128_isEqual(XXH128_hash_t h1, XXH128_hash_t h2); /*! - * XXH128_cmp(): - * + * @brief Compares two @ref XXH128_hash_t * This comparator is compatible with stdlib's `qsort()`/`bsearch()`. * - * return: >0 if *h128_1 > *h128_2 - * =0 if *h128_1 == *h128_2 - * <0 if *h128_1 < *h128_2 + * @return: >0 if *h128_1 > *h128_2 + * =0 if *h128_1 == *h128_2 + * <0 if *h128_1 < *h128_2 */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_cmp(const void* h128_1, const void* h128_2); +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF int XXH128_cmp(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* h128_1, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* h128_2); /******* Canonical representation *******/ typedef struct { unsigned char digest[sizeof(XXH128_hash_t)]; } XXH128_canonical_t; -XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH128_canonicalFromHash(XXH128_canonical_t* dst, XXH128_hash_t hash); -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128_hashFromCanonical(const XXH128_canonical_t* src); +/*! + * @brief Converts an @ref XXH128_hash_t to a big endian @ref XXH128_canonical_t. + * + * @param dst The @ref XXH128_canonical_t pointer to be stored to. + * @param hash The @ref XXH128_hash_t to be converted. + * + * @pre + * @p dst must not be `NULL`. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH128_canonicalFromHash(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH128_canonical_t* dst, XXH128_hash_t hash); + +/*! + * @brief Converts an @ref XXH128_canonical_t to a native @ref XXH128_hash_t. + * + * @param src The @ref XXH128_canonical_t to convert. + * + * @pre + * @p src must not be `NULL`. + * + * @return The converted hash. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH128_hashFromCanonical(XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH128_canonical_t* src); + + +#endif /* !XXH_NO_XXH3 */ #endif /* XXH_NO_LONG_LONG */ +/*! + * @} + */ #endif /* XXHASH_H_5627135585666179 */ @@ -612,36 +1425,59 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128_hashFromCanonical(const XXH128_canonical_t* * Never **ever** access their members directly. */ +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Structure for XXH32 streaming API. + * + * @note This is only defined when @ref XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY, + * @ref XXH_INLINE_ALL, or @ref XXH_IMPLEMENTATION is defined. Otherwise it is + * an opaque type. This allows fields to safely be changed. + * + * Typedef'd to @ref XXH32_state_t. + * Do not access the members of this struct directly. + * @see XXH64_state_s, XXH3_state_s + */ struct XXH32_state_s { - XXH32_hash_t total_len_32; - XXH32_hash_t large_len; - XXH32_hash_t v1; - XXH32_hash_t v2; - XXH32_hash_t v3; - XXH32_hash_t v4; - XXH32_hash_t mem32[4]; - XXH32_hash_t memsize; - XXH32_hash_t reserved; /* never read nor write, might be removed in a future version */ + XXH32_hash_t total_len_32; /*!< Total length hashed, modulo 2^32 */ + XXH32_hash_t large_len; /*!< Whether the hash is >= 16 (handles @ref total_len_32 overflow) */ + XXH32_hash_t v[4]; /*!< Accumulator lanes */ + XXH32_hash_t mem32[4]; /*!< Internal buffer for partial reads. Treated as unsigned char[16]. */ + XXH32_hash_t memsize; /*!< Amount of data in @ref mem32 */ + XXH32_hash_t reserved; /*!< Reserved field. Do not read nor write to it. */ }; /* typedef'd to XXH32_state_t */ #ifndef XXH_NO_LONG_LONG /* defined when there is no 64-bit support */ +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Structure for XXH64 streaming API. + * + * @note This is only defined when @ref XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY, + * @ref XXH_INLINE_ALL, or @ref XXH_IMPLEMENTATION is defined. Otherwise it is + * an opaque type. This allows fields to safely be changed. + * + * Typedef'd to @ref XXH64_state_t. + * Do not access the members of this struct directly. + * @see XXH32_state_s, XXH3_state_s + */ struct XXH64_state_s { - XXH64_hash_t total_len; - XXH64_hash_t v1; - XXH64_hash_t v2; - XXH64_hash_t v3; - XXH64_hash_t v4; - XXH64_hash_t mem64[4]; - XXH32_hash_t memsize; - XXH32_hash_t reserved32; /* required for padding anyway */ - XXH64_hash_t reserved64; /* never read nor write, might be removed in a future version */ + XXH64_hash_t total_len; /*!< Total length hashed. This is always 64-bit. */ + XXH64_hash_t v[4]; /*!< Accumulator lanes */ + XXH64_hash_t mem64[4]; /*!< Internal buffer for partial reads. Treated as unsigned char[32]. */ + XXH32_hash_t memsize; /*!< Amount of data in @ref mem64 */ + XXH32_hash_t reserved32; /*!< Reserved field, needed for padding anyways*/ + XXH64_hash_t reserved64; /*!< Reserved field. Do not read or write to it. */ }; /* typedef'd to XXH64_state_t */ -#if defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L) /* C11+ */ +#ifndef XXH_NO_XXH3 + +#if defined(__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L) /* >= C11 */ # include <stdalign.h> # define XXH_ALIGN(n) alignas(n) +#elif defined(__cplusplus) && (__cplusplus >= 201103L) /* >= C++11 */ +/* In C++ alignas() is a keyword */ +# define XXH_ALIGN(n) alignas(n) #elif defined(__GNUC__) # define XXH_ALIGN(n) __attribute__ ((aligned(n))) #elif defined(_MSC_VER) @@ -652,35 +1488,89 @@ struct XXH64_state_s { /* Old GCC versions only accept the attribute after the type in structures. */ #if !(defined(__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L)) /* C11+ */ \ + && ! (defined(__cplusplus) && (__cplusplus >= 201103L)) /* >= C++11 */ \ && defined(__GNUC__) # define XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(align, type) type XXH_ALIGN(align) #else # define XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(align, type) XXH_ALIGN(align) type #endif +/*! + * @brief The size of the internal XXH3 buffer. + * + * This is the optimal update size for incremental hashing. + * + * @see XXH3_64b_update(), XXH3_128b_update(). + */ #define XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE 256 + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Default size of the secret buffer (and @ref XXH3_kSecret). + * + * This is the size used in @ref XXH3_kSecret and the seeded functions. + * + * Not to be confused with @ref XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN. + */ #define XXH3_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE 192 + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Structure for XXH3 streaming API. + * + * @note This is only defined when @ref XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY, + * @ref XXH_INLINE_ALL, or @ref XXH_IMPLEMENTATION is defined. + * Otherwise it is an opaque type. + * Never use this definition in combination with dynamic library. + * This allows fields to safely be changed in the future. + * + * @note ** This structure has a strict alignment requirement of 64 bytes!! ** + * Do not allocate this with `malloc()` or `new`, + * it will not be sufficiently aligned. + * Use @ref XXH3_createState() and @ref XXH3_freeState(), or stack allocation. + * + * Typedef'd to @ref XXH3_state_t. + * Do never access the members of this struct directly. + * + * @see XXH3_INITSTATE() for stack initialization. + * @see XXH3_createState(), XXH3_freeState(). + * @see XXH32_state_s, XXH64_state_s + */ struct XXH3_state_s { XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(64, XXH64_hash_t acc[8]); - /* used to store a custom secret generated from a seed */ + /*!< The 8 accumulators. See @ref XXH32_state_s::v and @ref XXH64_state_s::v */ XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(64, unsigned char customSecret[XXH3_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE]); + /*!< Used to store a custom secret generated from a seed. */ XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(64, unsigned char buffer[XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE]); + /*!< The internal buffer. @see XXH32_state_s::mem32 */ XXH32_hash_t bufferedSize; - XXH32_hash_t reserved32; + /*!< The amount of memory in @ref buffer, @see XXH32_state_s::memsize */ + XXH32_hash_t useSeed; + /*!< Reserved field. Needed for padding on 64-bit. */ size_t nbStripesSoFar; + /*!< Number or stripes processed. */ XXH64_hash_t totalLen; + /*!< Total length hashed. 64-bit even on 32-bit targets. */ size_t nbStripesPerBlock; + /*!< Number of stripes per block. */ size_t secretLimit; + /*!< Size of @ref customSecret or @ref extSecret */ XXH64_hash_t seed; + /*!< Seed for _withSeed variants. Must be zero otherwise, @see XXH3_INITSTATE() */ XXH64_hash_t reserved64; - const unsigned char* extSecret; /* reference to external secret; - * if == NULL, use .customSecret instead */ + /*!< Reserved field. */ + const unsigned char* extSecret; + /*!< Reference to an external secret for the _withSecret variants, NULL + * for other variants. */ /* note: there may be some padding at the end due to alignment on 64 bytes */ }; /* typedef'd to XXH3_state_t */ #undef XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER -/* When the XXH3_state_t structure is merely emplaced on stack, +/*! + * @brief Initializes a stack-allocated `XXH3_state_s`. + * + * When the @ref XXH3_state_t structure is merely emplaced on stack, * it should be initialized with XXH3_INITSTATE() or a memset() * in case its first reset uses XXH3_NNbits_reset_withSeed(). * This init can be omitted if the first reset uses default or _withSecret mode. @@ -688,51 +1578,165 @@ struct XXH3_state_s { * Note that this doesn't prepare the state for a streaming operation, * it's still necessary to use XXH3_NNbits_reset*() afterwards. */ -#define XXH3_INITSTATE(XXH3_state_ptr) { (XXH3_state_ptr)->seed = 0; } +#define XXH3_INITSTATE(XXH3_state_ptr) \ + do { \ + XXH3_state_t* tmp_xxh3_state_ptr = (XXH3_state_ptr); \ + tmp_xxh3_state_ptr->seed = 0; \ + tmp_xxh3_state_ptr->extSecret = NULL; \ + } while(0) + + +/*! + * simple alias to pre-selected XXH3_128bits variant + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH128(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed); /* === Experimental API === */ /* Symbols defined below must be considered tied to a specific library version. */ -/* +/*! * XXH3_generateSecret(): * * Derive a high-entropy secret from any user-defined content, named customSeed. * The generated secret can be used in combination with `*_withSecret()` functions. - * The `_withSecret()` variants are useful to provide a higher level of protection than 64-bit seed, - * as it becomes much more difficult for an external actor to guess how to impact the calculation logic. + * The `_withSecret()` variants are useful to provide a higher level of protection + * than 64-bit seed, as it becomes much more difficult for an external actor to + * guess how to impact the calculation logic. * * The function accepts as input a custom seed of any length and any content, - * and derives from it a high-entropy secret of length XXH3_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE - * into an already allocated buffer secretBuffer. - * The generated secret is _always_ XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE bytes long. + * and derives from it a high-entropy secret of length @p secretSize into an + * already allocated buffer @p secretBuffer. * * The generated secret can then be used with any `*_withSecret()` variant. - * Functions `XXH3_128bits_withSecret()`, `XXH3_64bits_withSecret()`, - * `XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret()` and `XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret()` + * The functions @ref XXH3_128bits_withSecret(), @ref XXH3_64bits_withSecret(), + * @ref XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret() and @ref XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret() * are part of this list. They all accept a `secret` parameter - * which must be very long for implementation reasons (>= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) + * which must be large enough for implementation reasons (>= @ref XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) * _and_ feature very high entropy (consist of random-looking bytes). - * These conditions can be a high bar to meet, so - * this function can be used to generate a secret of proper quality. - * - * customSeed can be anything. It can have any size, even small ones, - * and its content can be anything, even stupidly "low entropy" source such as a bunch of zeroes. - * The resulting `secret` will nonetheless provide all expected qualities. - * - * Supplying NULL as the customSeed copies the default secret into `secretBuffer`. - * When customSeedSize > 0, supplying NULL as customSeed is undefined behavior. + * These conditions can be a high bar to meet, so @ref XXH3_generateSecret() can + * be employed to ensure proper quality. + * + * @p customSeed can be anything. It can have any size, even small ones, + * and its content can be anything, even "poor entropy" sources such as a bunch + * of zeroes. The resulting `secret` will nonetheless provide all required qualities. + * + * @pre + * - @p secretSize must be >= @ref XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN + * - When @p customSeedSize > 0, supplying NULL as customSeed is undefined behavior. + * + * Example code: + * @code{.c} + * #include <stdio.h> + * #include <stdlib.h> + * #include <string.h> + * #define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY // expose unstable API + * #include "xxhash.h" + * // Hashes argv[2] using the entropy from argv[1]. + * int main(int argc, char* argv[]) + * { + * char secret[XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN]; + * if (argv != 3) { return 1; } + * XXH3_generateSecret(secret, sizeof(secret), argv[1], strlen(argv[1])); + * XXH64_hash_t h = XXH3_64bits_withSecret( + * argv[2], strlen(argv[2]), + * secret, sizeof(secret) + * ); + * printf("%016llx\n", (unsigned long long) h); + * } + * @endcode */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH3_generateSecret(void* secretBuffer, const void* customSeed, size_t customSeedSize); - +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_generateSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE void* secretBuffer, size_t secretSize, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* customSeed, size_t customSeedSize); -/* simple short-cut to pre-selected XXH3_128bits variant */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed); +/*! + * @brief Generate the same secret as the _withSeed() variants. + * + * The generated secret can be used in combination with + *`*_withSecret()` and `_withSecretandSeed()` variants. + * + * Example C++ `std::string` hash class: + * @code{.cpp} + * #include <string> + * #define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY // expose unstable API + * #include "xxhash.h" + * // Slow, seeds each time + * class HashSlow { + * XXH64_hash_t seed; + * public: + * HashSlow(XXH64_hash_t s) : seed{s} {} + * size_t operator()(const std::string& x) const { + * return size_t{XXH3_64bits_withSeed(x.c_str(), x.length(), seed)}; + * } + * }; + * // Fast, caches the seeded secret for future uses. + * class HashFast { + * unsigned char secret[XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN]; + * public: + * HashFast(XXH64_hash_t s) { + * XXH3_generateSecret_fromSeed(secret, seed); + * } + * size_t operator()(const std::string& x) const { + * return size_t{ + * XXH3_64bits_withSecret(x.c_str(), x.length(), secret, sizeof(secret)) + * }; + * } + * }; + * @endcode + * @param secretBuffer A writable buffer of @ref XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN bytes + * @param seed The seed to seed the state. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH3_generateSecret_fromSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE void* secretBuffer, XXH64_hash_t seed); +/*! + * These variants generate hash values using either + * @p seed for "short" keys (< XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX = 240 bytes) + * or @p secret for "large" keys (>= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX). + * + * This generally benefits speed, compared to `_withSeed()` or `_withSecret()`. + * `_withSeed()` has to generate the secret on the fly for "large" keys. + * It's fast, but can be perceptible for "not so large" keys (< 1 KB). + * `_withSecret()` has to generate the masks on the fly for "small" keys, + * which requires more instructions than _withSeed() variants. + * Therefore, _withSecretandSeed variant combines the best of both worlds. + * + * When @p secret has been generated by XXH3_generateSecret_fromSeed(), + * this variant produces *exactly* the same results as `_withSeed()` variant, + * hence offering only a pure speed benefit on "large" input, + * by skipping the need to regenerate the secret for every large input. + * + * Another usage scenario is to hash the secret to a 64-bit hash value, + * for example with XXH3_64bits(), which then becomes the seed, + * and then employ both the seed and the secret in _withSecretandSeed(). + * On top of speed, an added benefit is that each bit in the secret + * has a 50% chance to swap each bit in the output, via its impact to the seed. + * + * This is not guaranteed when using the secret directly in "small data" scenarios, + * because only portions of the secret are employed for small data. + */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t +XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* data, size_t len, + XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, + XXH64_hash_t seed); +/*! @copydoc XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed() */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t +XXH3_128bits_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length, + XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, + XXH64_hash_t seed64); +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM +/*! @copydoc XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed() */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode +XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, + XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, + XXH64_hash_t seed64); +/*! @copydoc XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed() */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode +XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, + XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, + XXH64_hash_t seed64); +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ +#endif /* !XXH_NO_XXH3 */ #endif /* XXH_NO_LONG_LONG */ - - #if defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) || defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API) # define XXH_IMPLEMENTATION #endif @@ -774,8 +1778,24 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t s /* ************************************* * Tuning parameters ***************************************/ + +/*! + * @defgroup tuning Tuning parameters + * @{ + * + * Various macros to control xxHash's behavior. + */ +#ifdef XXH_DOXYGEN /*! - * XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS: + * @brief Define this to disable 64-bit code. + * + * Useful if only using the @ref XXH32_family and you have a strict C90 compiler. + */ +# define XXH_NO_LONG_LONG +# undef XXH_NO_LONG_LONG /* don't actually */ +/*! + * @brief Controls how unaligned memory is accessed. + * * By default, access to unaligned memory is controlled by `memcpy()`, which is * safe and portable. * @@ -784,77 +1804,108 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t s * * The below switch allow selection of a different access method * in the search for improved performance. - * Method 0 (default): - * Use `memcpy()`. Safe and portable. Default. - * Method 1: - * `__attribute__((packed))` statement. It depends on compiler extensions - * and is therefore not portable. - * This method is safe if your compiler supports it, and *generally* as - * fast or faster than `memcpy`. - * Method 2: - * Direct access via cast. This method doesn't depend on the compiler but - * violates the C standard. - * It can generate buggy code on targets which do not support unaligned - * memory accesses. - * But in some circumstances, it's the only known way to get the most - * performance (example: GCC + ARMv6) - * Method 3: - * Byteshift. This can generate the best code on old compilers which don't + * + * @par Possible options: + * + * - `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS=0` (default): `memcpy` + * @par + * Use `memcpy()`. Safe and portable. Note that most modern compilers will + * eliminate the function call and treat it as an unaligned access. + * + * - `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS=1`: `__attribute__((aligned(1)))` + * @par + * Depends on compiler extensions and is therefore not portable. + * This method is safe _if_ your compiler supports it, + * and *generally* as fast or faster than `memcpy`. + * + * - `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS=2`: Direct cast + * @par + * Casts directly and dereferences. This method doesn't depend on the + * compiler, but it violates the C standard as it directly dereferences an + * unaligned pointer. It can generate buggy code on targets which do not + * support unaligned memory accesses, but in some circumstances, it's the + * only known way to get the most performance. + * + * - `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS=3`: Byteshift + * @par + * Also portable. This can generate the best code on old compilers which don't * inline small `memcpy()` calls, and it might also be faster on big-endian - * systems which lack a native byteswap instruction. - * See https://stackoverflow.com/a/32095106/646947 for details. - * Prefer these methods in priority order (0 > 1 > 2 > 3) + * systems which lack a native byteswap instruction. However, some compilers + * will emit literal byteshifts even if the target supports unaligned access. + * + * + * @warning + * Methods 1 and 2 rely on implementation-defined behavior. Use these with + * care, as what works on one compiler/platform/optimization level may cause + * another to read garbage data or even crash. + * + * See https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2015/08/accessing-unaligned-memory.html for details. + * + * Prefer these methods in priority order (0 > 3 > 1 > 2) */ -#ifndef XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS /* can be defined externally, on command line for example */ -# if !defined(__clang__) && defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__ARM_FEATURE_UNALIGNED) && defined(__ARM_ARCH) && (__ARM_ARCH == 6) -# define XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS 2 -# elif !defined(__clang__) && ((defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && !defined(_WIN32)) || \ - (defined(__GNUC__) && (defined(__ARM_ARCH) && __ARM_ARCH >= 7))) -# define XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS 1 -# endif -#endif +# define XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS 0 /*! - * XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER: - * If the input pointer is NULL, xxHash's default behavior is to dereference it, - * triggering a segfault. - * When this macro is enabled, xxHash actively checks the input for a null pointer. - * If it is, the result for null input pointers is the same as a zero-length input. - */ -#ifndef XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER /* can be defined externally */ -# define XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER 0 -#endif + * @def XXH_SIZE_OPT + * @brief Controls how much xxHash optimizes for size. + * + * xxHash, when compiled, tends to result in a rather large binary size. This + * is mostly due to heavy usage to forced inlining and constant folding of the + * @ref XXH3_family to increase performance. + * + * However, some developers prefer size over speed. This option can + * significantly reduce the size of the generated code. When using the `-Os` + * or `-Oz` options on GCC or Clang, this is defined to 1 by default, + * otherwise it is defined to 0. + * + * Most of these size optimizations can be controlled manually. + * + * This is a number from 0-2. + * - `XXH_SIZE_OPT` == 0: Default. xxHash makes no size optimizations. Speed + * comes first. + * - `XXH_SIZE_OPT` == 1: Default for `-Os` and `-Oz`. xxHash is more + * conservative and disables hacks that increase code size. It implies the + * options @ref XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS == 1, @ref XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK == 0, + * and @ref XXH3_NEON_LANES == 8 if they are not already defined. + * - `XXH_SIZE_OPT` == 2: xxHash tries to make itself as small as possible. + * Performance may cry. For example, the single shot functions just use the + * streaming API. + */ +# define XXH_SIZE_OPT 0 /*! - * XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK: - * This is an important performance trick - * for architectures without decent unaligned memory access performance. - * It checks for input alignment, and when conditions are met, - * uses a "fast path" employing direct 32-bit/64-bit read, - * resulting in _dramatically faster_ read speed. + * @def XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK + * @brief If defined to non-zero, adds a special path for aligned inputs (XXH32() + * and XXH64() only). + * + * This is an important performance trick for architectures without decent + * unaligned memory access performance. + * + * It checks for input alignment, and when conditions are met, uses a "fast + * path" employing direct 32-bit/64-bit reads, resulting in _dramatically + * faster_ read speed. * - * The check costs one initial branch per hash, which is generally negligible, but not zero. - * Moreover, it's not useful to generate binary for an additional code path - * if memory access uses same instruction for both aligned and unaligned adresses. + * The check costs one initial branch per hash, which is generally negligible, + * but not zero. + * + * Moreover, it's not useful to generate an additional code path if memory + * access uses the same instruction for both aligned and unaligned + * addresses (e.g. x86 and aarch64). * * In these cases, the alignment check can be removed by setting this macro to 0. * Then the code will always use unaligned memory access. - * Align check is automatically disabled on x86, x64 & arm64, + * Align check is automatically disabled on x86, x64, ARM64, and some ARM chips * which are platforms known to offer good unaligned memory accesses performance. * + * It is also disabled by default when @ref XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1. + * * This option does not affect XXH3 (only XXH32 and XXH64). */ -#ifndef XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK /* can be defined externally */ -# if defined(__i386) || defined(__x86_64__) || defined(__aarch64__) \ - || defined(_M_IX86) || defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_ARM64) /* visual */ -# define XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK 0 -# else -# define XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK 1 -# endif -#endif +# define XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK 0 /*! - * XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS: + * @def XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS + * @brief When non-zero, sets all functions to `static`. * * By default, xxHash tries to force the compiler to inline almost all internal * functions. @@ -869,48 +1920,169 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t s * XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS marks all internal functions as static, giving the * compiler full control on whether to inline or not. * - * When not optimizing (-O0), optimizing for size (-Os, -Oz), or using - * -fno-inline with GCC or Clang, this will automatically be defined. + * When not optimizing (-O0), using `-fno-inline` with GCC or Clang, or if + * @ref XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1, this will automatically be defined. + */ +# define XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS 0 + +/*! + * @def XXH3_INLINE_SECRET + * @brief Determines whether to inline the XXH3 withSecret code. + * + * When the secret size is known, the compiler can improve the performance + * of XXH3_64bits_withSecret() and XXH3_128bits_withSecret(). + * + * However, if the secret size is not known, it doesn't have any benefit. This + * happens when xxHash is compiled into a global symbol. Therefore, if + * @ref XXH_INLINE_ALL is *not* defined, this will be defined to 0. + * + * Additionally, this defaults to 0 on GCC 12+, which has an issue with function pointers + * that are *sometimes* force inline on -Og, and it is impossible to automatically + * detect this optimization level. */ +# define XXH3_INLINE_SECRET 0 + +/*! + * @def XXH32_ENDJMP + * @brief Whether to use a jump for `XXH32_finalize`. + * + * For performance, `XXH32_finalize` uses multiple branches in the finalizer. + * This is generally preferable for performance, + * but depending on exact architecture, a jmp may be preferable. + * + * This setting is only possibly making a difference for very small inputs. + */ +# define XXH32_ENDJMP 0 + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Redefines old internal names. + * + * For compatibility with code that uses xxHash's internals before the names + * were changed to improve namespacing. There is no other reason to use this. + */ +# define XXH_OLD_NAMES +# undef XXH_OLD_NAMES /* don't actually use, it is ugly. */ + +/*! + * @def XXH_NO_STREAM + * @brief Disables the streaming API. + * + * When xxHash is not inlined and the streaming functions are not used, disabling + * the streaming functions can improve code size significantly, especially with + * the @ref XXH3_family which tends to make constant folded copies of itself. + */ +# define XXH_NO_STREAM +# undef XXH_NO_STREAM /* don't actually */ +#endif /* XXH_DOXYGEN */ +/*! + * @} + */ + +#ifndef XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS /* can be defined externally, on command line for example */ + /* prefer __packed__ structures (method 1) for GCC + * < ARMv7 with unaligned access (e.g. Raspbian armhf) still uses byte shifting, so we use memcpy + * which for some reason does unaligned loads. */ +# if defined(__GNUC__) && !(defined(__ARM_ARCH) && __ARM_ARCH < 7 && defined(__ARM_FEATURE_UNALIGNED)) +# define XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS 1 +# endif +#endif + +#ifndef XXH_SIZE_OPT + /* default to 1 for -Os or -Oz */ +# if (defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)) && defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) +# define XXH_SIZE_OPT 1 +# else +# define XXH_SIZE_OPT 0 +# endif +#endif + +#ifndef XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK /* can be defined externally */ + /* don't check on sizeopt, x86, aarch64, or arm when unaligned access is available */ +# if XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1 || \ + defined(__i386) || defined(__x86_64__) || defined(__aarch64__) || defined(__ARM_FEATURE_UNALIGNED) \ + || defined(_M_IX86) || defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_ARM64) || defined(_M_ARM) /* visual */ +# define XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK 0 +# else +# define XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK 1 +# endif +#endif + #ifndef XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS -# if defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) /* -Os, -Oz */ \ - || defined(__NO_INLINE__) /* -O0, -fno-inline */ +# if XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1 || defined(__NO_INLINE__) /* -O0, -fno-inline */ # define XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS 1 # else # define XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS 0 # endif #endif -/*! - * XXH_REROLL: - * Whether to reroll XXH32_finalize, and XXH64_finalize, - * instead of using an unrolled jump table/if statement loop. - * - * This is automatically defined on -Os/-Oz on GCC and Clang. - */ -#ifndef XXH_REROLL -# if defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) -# define XXH_REROLL 1 +#ifndef XXH3_INLINE_SECRET +# if (defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) && __GNUC__ >= 12) \ + || !defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) +# define XXH3_INLINE_SECRET 0 # else -# define XXH_REROLL 0 +# define XXH3_INLINE_SECRET 1 # endif #endif +#ifndef XXH32_ENDJMP +/* generally preferable for performance */ +# define XXH32_ENDJMP 0 +#endif + +/*! + * @defgroup impl Implementation + * @{ + */ + /* ************************************* * Includes & Memory related functions ***************************************/ -/*! +#if defined(XXH_NO_STREAM) +/* nothing */ +#elif defined(XXH_NO_STDLIB) + +/* When requesting to disable any mention of stdlib, + * the library loses the ability to invoked malloc / free. + * In practice, it means that functions like `XXH*_createState()` + * will always fail, and return NULL. + * This flag is useful in situations where + * xxhash.h is integrated into some kernel, embedded or limited environment + * without access to dynamic allocation. + */ + +static XXH_CONSTF void* XXH_malloc(size_t s) { (void)s; return NULL; } +static void XXH_free(void* p) { (void)p; } + +#else + +/* * Modify the local functions below should you wish to use * different memory routines for malloc() and free() */ #include <stdlib.h> -static void* XXH_malloc(size_t s) { return malloc(s); } +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Modify this function to use a different routine than malloc(). + */ +static XXH_MALLOCF void* XXH_malloc(size_t s) { return malloc(s); } + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Modify this function to use a different routine than free(). + */ static void XXH_free(void* p) { free(p); } -/*! and for memcpy() */ +#endif /* XXH_NO_STDLIB */ + #include <string.h> + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Modify this function to use a different routine than memcpy(). + */ static void* XXH_memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t size) { return memcpy(dest,src,size); @@ -927,19 +2099,19 @@ static void* XXH_memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t size) #endif #if XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS /* disable inlining hints */ -# if defined(__GNUC__) +# if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__) # define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static __attribute__((unused)) # else # define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static # endif # define XXH_NO_INLINE static /* enable inlining hints */ +#elif defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__) +# define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static __inline__ __attribute__((always_inline, unused)) +# define XXH_NO_INLINE static __attribute__((noinline)) #elif defined(_MSC_VER) /* Visual Studio */ # define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static __forceinline # define XXH_NO_INLINE static __declspec(noinline) -#elif defined(__GNUC__) -# define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static __inline__ __attribute__((always_inline, unused)) -# define XXH_NO_INLINE static __attribute__((noinline)) #elif defined (__cplusplus) \ || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L)) /* C99 */ # define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static inline @@ -949,12 +2121,21 @@ static void* XXH_memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t size) # define XXH_NO_INLINE static #endif +#if XXH3_INLINE_SECRET +# define XXH3_WITH_SECRET_INLINE XXH_FORCE_INLINE +#else +# define XXH3_WITH_SECRET_INLINE XXH_NO_INLINE +#endif /* ************************************* * Debug ***************************************/ -/* +/*! + * @ingroup tuning + * @def XXH_DEBUGLEVEL + * @brief Sets the debugging level. + * * XXH_DEBUGLEVEL is expected to be defined externally, typically via the * compiler's command line options. The value must be a number. */ @@ -970,12 +2151,54 @@ static void* XXH_memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t size) # include <assert.h> /* note: can still be disabled with NDEBUG */ # define XXH_ASSERT(c) assert(c) #else -# define XXH_ASSERT(c) ((void)0) +# if defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) +# define XXH_ASSERT(c) XXH_ASSUME((unsigned char) (c)) +# else +# define XXH_ASSERT(c) XXH_ASSUME(c) +# endif #endif /* note: use after variable declarations */ -#define XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(c) do { enum { XXH_sa = 1/(int)(!!(c)) }; } while (0) +#ifndef XXH_STATIC_ASSERT +# if defined(__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L) /* C11 */ +# define XXH_STATIC_ASSERT_WITH_MESSAGE(c,m) do { _Static_assert((c),m); } while(0) +# elif defined(__cplusplus) && (__cplusplus >= 201103L) /* C++11 */ +# define XXH_STATIC_ASSERT_WITH_MESSAGE(c,m) do { static_assert((c),m); } while(0) +# else +# define XXH_STATIC_ASSERT_WITH_MESSAGE(c,m) do { struct xxh_sa { char x[(c) ? 1 : -1]; }; } while(0) +# endif +# define XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(c) XXH_STATIC_ASSERT_WITH_MESSAGE((c),#c) +#endif +/*! + * @internal + * @def XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(var) + * @brief Used to prevent unwanted optimizations for @p var. + * + * It uses an empty GCC inline assembly statement with a register constraint + * which forces @p var into a general purpose register (eg eax, ebx, ecx + * on x86) and marks it as modified. + * + * This is used in a few places to avoid unwanted autovectorization (e.g. + * XXH32_round()). All vectorization we want is explicit via intrinsics, + * and _usually_ isn't wanted elsewhere. + * + * We also use it to prevent unwanted constant folding for AArch64 in + * XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar(). + */ +#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__) +# define XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(var) __asm__("" : "+r" (var)) +#else +# define XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(var) ((void)0) +#endif + +/* Specifically for NEON vectors which use the "w" constraint, on + * Clang. */ +#if defined(__clang__) && defined(__ARM_ARCH) && !defined(__wasm__) +# define XXH_COMPILER_GUARD_CLANG_NEON(var) __asm__("" : "+w" (var)) +#else +# define XXH_COMPILER_GUARD_CLANG_NEON(var) ((void)0) +#endif /* ************************************* * Basic Types @@ -991,6 +2214,7 @@ static void* XXH_memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t size) typedef XXH32_hash_t xxh_u32; #ifdef XXH_OLD_NAMES +# warning "XXH_OLD_NAMES is planned to be removed starting v0.9. If the program depends on it, consider moving away from it by employing newer type names directly" # define BYTE xxh_u8 # define U8 xxh_u8 # define U32 xxh_u32 @@ -998,6 +2222,56 @@ typedef XXH32_hash_t xxh_u32; /* *** Memory access *** */ +/*! + * @internal + * @fn xxh_u32 XXH_read32(const void* ptr) + * @brief Reads an unaligned 32-bit integer from @p ptr in native endianness. + * + * Affected by @ref XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS. + * + * @param ptr The pointer to read from. + * @return The 32-bit native endian integer from the bytes at @p ptr. + */ + +/*! + * @internal + * @fn xxh_u32 XXH_readLE32(const void* ptr) + * @brief Reads an unaligned 32-bit little endian integer from @p ptr. + * + * Affected by @ref XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS. + * + * @param ptr The pointer to read from. + * @return The 32-bit little endian integer from the bytes at @p ptr. + */ + +/*! + * @internal + * @fn xxh_u32 XXH_readBE32(const void* ptr) + * @brief Reads an unaligned 32-bit big endian integer from @p ptr. + * + * Affected by @ref XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS. + * + * @param ptr The pointer to read from. + * @return The 32-bit big endian integer from the bytes at @p ptr. + */ + +/*! + * @internal + * @fn xxh_u32 XXH_readLE32_align(const void* ptr, XXH_alignment align) + * @brief Like @ref XXH_readLE32(), but has an option for aligned reads. + * + * Affected by @ref XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS. + * Note that when @ref XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK == 0, the @p align parameter is + * always @ref XXH_alignment::XXH_unaligned. + * + * @param ptr The pointer to read from. + * @param align Whether @p ptr is aligned. + * @pre + * If @p align == @ref XXH_alignment::XXH_aligned, @p ptr must be 4 byte + * aligned. + * @return The 32-bit little endian integer from the bytes at @p ptr. + */ + #if (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3)) /* * Manual byteshift. Best for old compilers which don't inline memcpy. @@ -1014,46 +2288,54 @@ static xxh_u32 XXH_read32(const void* memPtr) { return *(const xxh_u32*) memPtr; #elif (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==1)) /* - * __pack instructions are safer but compiler specific, hence potentially - * problematic for some compilers. - * - * Currently only defined for GCC and ICC. + * __attribute__((aligned(1))) is supported by gcc and clang. Originally the + * documentation claimed that it only increased the alignment, but actually it + * can decrease it on gcc, clang, and icc: + * https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=69502, + * https://gcc.godbolt.org/z/xYez1j67Y. */ #ifdef XXH_OLD_NAMES typedef union { xxh_u32 u32; } __attribute__((packed)) unalign; #endif static xxh_u32 XXH_read32(const void* ptr) { - typedef union { xxh_u32 u32; } __attribute__((packed)) xxh_unalign; - return ((const xxh_unalign*)ptr)->u32; + typedef __attribute__((aligned(1))) xxh_u32 xxh_unalign32; + return *((const xxh_unalign32*)ptr); } #else /* * Portable and safe solution. Generally efficient. - * see: https://stackoverflow.com/a/32095106/646947 + * see: https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2015/08/accessing-unaligned-memory.html */ static xxh_u32 XXH_read32(const void* memPtr) { xxh_u32 val; - memcpy(&val, memPtr, sizeof(val)); + XXH_memcpy(&val, memPtr, sizeof(val)); return val; } #endif /* XXH_FORCE_DIRECT_MEMORY_ACCESS */ -/* *** Endianess *** */ -typedef enum { XXH_bigEndian=0, XXH_littleEndian=1 } XXH_endianess; +/* *** Endianness *** */ /*! - * XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN: + * @ingroup tuning + * @def XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN + * @brief Whether the target is little endian. + * * Defined to 1 if the target is little endian, or 0 if it is big endian. * It can be defined externally, for example on the compiler command line. * - * If it is not defined, a runtime check (which is usually constant folded) - * is used instead. + * If it is not defined, + * a runtime check (which is usually constant folded) is used instead. + * + * @note + * This is not necessarily defined to an integer constant. + * + * @see XXH_isLittleEndian() for the runtime check. */ #ifndef XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN /* @@ -1068,8 +2350,11 @@ typedef enum { XXH_bigEndian=0, XXH_littleEndian=1 } XXH_endianess; || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__) # define XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN 0 # else -/* - * runtime test, presumed to simplify to a constant by compiler +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Runtime check for @ref XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN. + * + * Most compilers will constant fold this. */ static int XXH_isLittleEndian(void) { @@ -1098,6 +2383,64 @@ static int XXH_isLittleEndian(void) # define XXH_HAS_BUILTIN(x) 0 #endif + + +/* + * C23 and future versions have standard "unreachable()". + * Once it has been implemented reliably we can add it as an + * additional case: + * + * ``` + * #if defined(__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= XXH_C23_VN) + * # include <stddef.h> + * # ifdef unreachable + * # define XXH_UNREACHABLE() unreachable() + * # endif + * #endif + * ``` + * + * Note C++23 also has std::unreachable() which can be detected + * as follows: + * ``` + * #if defined(__cpp_lib_unreachable) && (__cpp_lib_unreachable >= 202202L) + * # include <utility> + * # define XXH_UNREACHABLE() std::unreachable() + * #endif + * ``` + * NB: `__cpp_lib_unreachable` is defined in the `<version>` header. + * We don't use that as including `<utility>` in `extern "C"` blocks + * doesn't work on GCC12 + */ + +#if XXH_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_unreachable) +# define XXH_UNREACHABLE() __builtin_unreachable() + +#elif defined(_MSC_VER) +# define XXH_UNREACHABLE() __assume(0) + +#else +# define XXH_UNREACHABLE() +#endif + +#if XXH_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_assume) +# define XXH_ASSUME(c) __builtin_assume(c) +#else +# define XXH_ASSUME(c) if (!(c)) { XXH_UNREACHABLE(); } +#endif + +/*! + * @internal + * @def XXH_rotl32(x,r) + * @brief 32-bit rotate left. + * + * @param x The 32-bit integer to be rotated. + * @param r The number of bits to rotate. + * @pre + * @p r > 0 && @p r < 32 + * @note + * @p x and @p r may be evaluated multiple times. + * @return The rotated result. + */ #if !defined(NO_CLANG_BUILTIN) && XXH_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_rotateleft32) \ && XXH_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_rotateleft64) # define XXH_rotl32 __builtin_rotateleft32 @@ -1111,6 +2454,14 @@ static int XXH_isLittleEndian(void) # define XXH_rotl64(x,r) (((x) << (r)) | ((x) >> (64 - (r)))) #endif +/*! + * @internal + * @fn xxh_u32 XXH_swap32(xxh_u32 x) + * @brief A 32-bit byteswap. + * + * @param x The 32-bit integer to byteswap. + * @return @p x, byteswapped. + */ #if defined(_MSC_VER) /* Visual Studio */ # define XXH_swap32 _byteswap_ulong #elif XXH_GCC_VERSION >= 403 @@ -1129,7 +2480,15 @@ static xxh_u32 XXH_swap32 (xxh_u32 x) /* *************************** * Memory reads *****************************/ -typedef enum { XXH_aligned, XXH_unaligned } XXH_alignment; + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Enum to indicate whether a pointer is aligned. + */ +typedef enum { + XXH_aligned, /*!< Aligned */ + XXH_unaligned /*!< Possibly unaligned */ +} XXH_alignment; /* * XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3 is an endian-independent byteshift load. @@ -1182,17 +2541,27 @@ XXH_readLE32_align(const void* ptr, XXH_alignment align) /* ************************************* * Misc ***************************************/ +/*! @ingroup public */ XXH_PUBLIC_API unsigned XXH_versionNumber (void) { return XXH_VERSION_NUMBER; } /* ******************************************************************* * 32-bit hash functions *********************************************************************/ -static const xxh_u32 XXH_PRIME32_1 = 0x9E3779B1U; /* 0b10011110001101110111100110110001 */ -static const xxh_u32 XXH_PRIME32_2 = 0x85EBCA77U; /* 0b10000101111010111100101001110111 */ -static const xxh_u32 XXH_PRIME32_3 = 0xC2B2AE3DU; /* 0b11000010101100101010111000111101 */ -static const xxh_u32 XXH_PRIME32_4 = 0x27D4EB2FU; /* 0b00100111110101001110101100101111 */ -static const xxh_u32 XXH_PRIME32_5 = 0x165667B1U; /* 0b00010110010101100110011110110001 */ +/*! + * @} + * @defgroup XXH32_impl XXH32 implementation + * @ingroup impl + * + * Details on the XXH32 implementation. + * @{ + */ + /* #define instead of static const, to be used as initializers */ +#define XXH_PRIME32_1 0x9E3779B1U /*!< 0b10011110001101110111100110110001 */ +#define XXH_PRIME32_2 0x85EBCA77U /*!< 0b10000101111010111100101001110111 */ +#define XXH_PRIME32_3 0xC2B2AE3DU /*!< 0b11000010101100101010111000111101 */ +#define XXH_PRIME32_4 0x27D4EB2FU /*!< 0b00100111110101001110101100101111 */ +#define XXH_PRIME32_5 0x165667B1U /*!< 0b00010110010101100110011110110001 */ #ifdef XXH_OLD_NAMES # define PRIME32_1 XXH_PRIME32_1 @@ -1202,18 +2571,28 @@ static const xxh_u32 XXH_PRIME32_5 = 0x165667B1U; /* 0b00010110010101100110011 # define PRIME32_5 XXH_PRIME32_5 #endif +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Normal stripe processing routine. + * + * This shuffles the bits so that any bit from @p input impacts several bits in + * @p acc. + * + * @param acc The accumulator lane. + * @param input The stripe of input to mix. + * @return The mixed accumulator lane. + */ static xxh_u32 XXH32_round(xxh_u32 acc, xxh_u32 input) { acc += input * XXH_PRIME32_2; acc = XXH_rotl32(acc, 13); acc *= XXH_PRIME32_1; -#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__SSE4_1__) && !defined(XXH_ENABLE_AUTOVECTORIZE) +#if (defined(__SSE4_1__) || defined(__aarch64__) || defined(__wasm_simd128__)) && !defined(XXH_ENABLE_AUTOVECTORIZE) /* * UGLY HACK: - * This inline assembly hack forces acc into a normal register. This is the - * only thing that prevents GCC and Clang from autovectorizing the XXH32 - * loop (pragmas and attributes don't work for some resason) without globally - * disabling SSE4.1. + * A compiler fence is the only thing that prevents GCC and Clang from + * autovectorizing the XXH32 loop (pragmas and attributes don't work for some + * reason) without globally disabling SSE4.1. * * The reason we want to avoid vectorization is because despite working on * 4 integers at a time, there are multiple factors slowing XXH32 down on @@ -1238,55 +2617,73 @@ static xxh_u32 XXH32_round(xxh_u32 acc, xxh_u32 input) * can load data, while v3 can multiply. SSE forces them to operate * together. * - * How this hack works: - * __asm__("" // Declare an assembly block but don't declare any instructions - * : // However, as an Input/Output Operand, - * "+r" // constrain a read/write operand (+) as a general purpose register (r). - * (acc) // and set acc as the operand - * ); + * This is also enabled on AArch64, as Clang is *very aggressive* in vectorizing + * the loop. NEON is only faster on the A53, and with the newer cores, it is less + * than half the speed. * - * Because of the 'r', the compiler has promised that seed will be in a - * general purpose register and the '+' says that it will be 'read/write', - * so it has to assume it has changed. It is like volatile without all the - * loads and stores. - * - * Since the argument has to be in a normal register (not an SSE register), - * each time XXH32_round is called, it is impossible to vectorize. + * Additionally, this is used on WASM SIMD128 because it JITs to the same + * SIMD instructions and has the same issue. */ - __asm__("" : "+r" (acc)); + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(acc); #endif return acc; } -/* mix all bits */ -static xxh_u32 XXH32_avalanche(xxh_u32 h32) +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Mixes all bits to finalize the hash. + * + * The final mix ensures that all input bits have a chance to impact any bit in + * the output digest, resulting in an unbiased distribution. + * + * @param hash The hash to avalanche. + * @return The avalanched hash. + */ +static xxh_u32 XXH32_avalanche(xxh_u32 hash) { - h32 ^= h32 >> 15; - h32 *= XXH_PRIME32_2; - h32 ^= h32 >> 13; - h32 *= XXH_PRIME32_3; - h32 ^= h32 >> 16; - return(h32); + hash ^= hash >> 15; + hash *= XXH_PRIME32_2; + hash ^= hash >> 13; + hash *= XXH_PRIME32_3; + hash ^= hash >> 16; + return hash; } #define XXH_get32bits(p) XXH_readLE32_align(p, align) -static xxh_u32 -XXH32_finalize(xxh_u32 h32, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align) +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Processes the last 0-15 bytes of @p ptr. + * + * There may be up to 15 bytes remaining to consume from the input. + * This final stage will digest them to ensure that all input bytes are present + * in the final mix. + * + * @param hash The hash to finalize. + * @param ptr The pointer to the remaining input. + * @param len The remaining length, modulo 16. + * @param align Whether @p ptr is aligned. + * @return The finalized hash. + * @see XXH64_finalize(). + */ +static XXH_PUREF xxh_u32 +XXH32_finalize(xxh_u32 hash, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align) { -#define XXH_PROCESS1 do { \ - h32 += (*ptr++) * XXH_PRIME32_5; \ - h32 = XXH_rotl32(h32, 11) * XXH_PRIME32_1; \ +#define XXH_PROCESS1 do { \ + hash += (*ptr++) * XXH_PRIME32_5; \ + hash = XXH_rotl32(hash, 11) * XXH_PRIME32_1; \ } while (0) -#define XXH_PROCESS4 do { \ - h32 += XXH_get32bits(ptr) * XXH_PRIME32_3; \ - ptr += 4; \ - h32 = XXH_rotl32(h32, 17) * XXH_PRIME32_4; \ +#define XXH_PROCESS4 do { \ + hash += XXH_get32bits(ptr) * XXH_PRIME32_3; \ + ptr += 4; \ + hash = XXH_rotl32(hash, 17) * XXH_PRIME32_4; \ } while (0) - /* Compact rerolled version */ - if (XXH_REROLL) { + if (ptr==NULL) XXH_ASSERT(len == 0); + + /* Compact rerolled version; generally faster */ + if (!XXH32_ENDJMP) { len &= 15; while (len >= 4) { XXH_PROCESS4; @@ -1296,49 +2693,49 @@ XXH32_finalize(xxh_u32 h32, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align) XXH_PROCESS1; --len; } - return XXH32_avalanche(h32); + return XXH32_avalanche(hash); } else { switch(len&15) /* or switch(bEnd - p) */ { case 12: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 8: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 4: XXH_PROCESS4; - return XXH32_avalanche(h32); + return XXH32_avalanche(hash); case 13: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 9: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 5: XXH_PROCESS4; XXH_PROCESS1; - return XXH32_avalanche(h32); + return XXH32_avalanche(hash); case 14: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 10: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 6: XXH_PROCESS4; XXH_PROCESS1; XXH_PROCESS1; - return XXH32_avalanche(h32); + return XXH32_avalanche(hash); case 15: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 11: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 7: XXH_PROCESS4; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 3: XXH_PROCESS1; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 2: XXH_PROCESS1; - /* fallthrough */ + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ case 1: XXH_PROCESS1; - /* fallthrough */ - case 0: return XXH32_avalanche(h32); + XXH_FALLTHROUGH; /* fallthrough */ + case 0: return XXH32_avalanche(hash); } XXH_ASSERT(0); - return h32; /* reaching this point is deemed impossible */ + return hash; /* reaching this point is deemed impossible */ } } @@ -1350,20 +2747,23 @@ XXH32_finalize(xxh_u32 h32, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align) # undef XXH_PROCESS4 #endif -XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u32 +/*! + * @internal + * @brief The implementation for @ref XXH32(). + * + * @param input , len , seed Directly passed from @ref XXH32(). + * @param align Whether @p input is aligned. + * @return The calculated hash. + */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF xxh_u32 XXH32_endian_align(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, xxh_u32 seed, XXH_alignment align) { - const xxh_u8* bEnd = input + len; xxh_u32 h32; -#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1) - if (input==NULL) { - len=0; - bEnd=input=(const xxh_u8*)(size_t)16; - } -#endif + if (input==NULL) XXH_ASSERT(len == 0); if (len>=16) { + const xxh_u8* const bEnd = input + len; const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 15; xxh_u32 v1 = seed + XXH_PRIME32_1 + XXH_PRIME32_2; xxh_u32 v2 = seed + XXH_PRIME32_2; @@ -1388,18 +2788,16 @@ XXH32_endian_align(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, xxh_u32 seed, XXH_alignment return XXH32_finalize(h32, input, len&15, align); } - +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32 (const void* input, size_t len, XXH32_hash_t seed) { -#if 0 +#if !defined(XXH_NO_STREAM) && XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 2 /* Simple version, good for code maintenance, but unfortunately slow for small inputs */ XXH32_state_t state; XXH32_reset(&state, seed); XXH32_update(&state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len); return XXH32_digest(&state); - #else - if (XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK) { if ((((size_t)input) & 3) == 0) { /* Input is 4-bytes aligned, leverage the speed benefit */ return XXH32_endian_align((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed, XXH_aligned); @@ -1412,45 +2810,46 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32 (const void* input, size_t len, XXH32_hash_t s /******* Hash streaming *******/ - +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_state_t* XXH32_createState(void) { return (XXH32_state_t*)XXH_malloc(sizeof(XXH32_state_t)); } +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_freeState(XXH32_state_t* statePtr) { XXH_free(statePtr); return XXH_OK; } +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_copyState(XXH32_state_t* dstState, const XXH32_state_t* srcState) { - memcpy(dstState, srcState, sizeof(*dstState)); + XXH_memcpy(dstState, srcState, sizeof(*dstState)); } +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_reset(XXH32_state_t* statePtr, XXH32_hash_t seed) { - XXH32_state_t state; /* using a local state to memcpy() in order to avoid strict-aliasing warnings */ - memset(&state, 0, sizeof(state)); - state.v1 = seed + XXH_PRIME32_1 + XXH_PRIME32_2; - state.v2 = seed + XXH_PRIME32_2; - state.v3 = seed + 0; - state.v4 = seed - XXH_PRIME32_1; - /* do not write into reserved, planned to be removed in a future version */ - memcpy(statePtr, &state, sizeof(state) - sizeof(state.reserved)); + XXH_ASSERT(statePtr != NULL); + memset(statePtr, 0, sizeof(*statePtr)); + statePtr->v[0] = seed + XXH_PRIME32_1 + XXH_PRIME32_2; + statePtr->v[1] = seed + XXH_PRIME32_2; + statePtr->v[2] = seed + 0; + statePtr->v[3] = seed - XXH_PRIME32_1; return XXH_OK; } +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_update(XXH32_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) { - if (input==NULL) -#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1) + if (input==NULL) { + XXH_ASSERT(len == 0); return XXH_OK; -#else - return XXH_ERROR; -#endif + } { const xxh_u8* p = (const xxh_u8*)input; const xxh_u8* const bEnd = p + len; @@ -1467,10 +2866,10 @@ XXH32_update(XXH32_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) if (state->memsize) { /* some data left from previous update */ XXH_memcpy((xxh_u8*)(state->mem32) + state->memsize, input, 16-state->memsize); { const xxh_u32* p32 = state->mem32; - state->v1 = XXH32_round(state->v1, XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++; - state->v2 = XXH32_round(state->v2, XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++; - state->v3 = XXH32_round(state->v3, XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++; - state->v4 = XXH32_round(state->v4, XXH_readLE32(p32)); + state->v[0] = XXH32_round(state->v[0], XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++; + state->v[1] = XXH32_round(state->v[1], XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++; + state->v[2] = XXH32_round(state->v[2], XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++; + state->v[3] = XXH32_round(state->v[3], XXH_readLE32(p32)); } p += 16-state->memsize; state->memsize = 0; @@ -1478,22 +2877,14 @@ XXH32_update(XXH32_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) if (p <= bEnd-16) { const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 16; - xxh_u32 v1 = state->v1; - xxh_u32 v2 = state->v2; - xxh_u32 v3 = state->v3; - xxh_u32 v4 = state->v4; do { - v1 = XXH32_round(v1, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; - v2 = XXH32_round(v2, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; - v3 = XXH32_round(v3, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; - v4 = XXH32_round(v4, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; + state->v[0] = XXH32_round(state->v[0], XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; + state->v[1] = XXH32_round(state->v[1], XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; + state->v[2] = XXH32_round(state->v[2], XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; + state->v[3] = XXH32_round(state->v[3], XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4; } while (p<=limit); - state->v1 = v1; - state->v2 = v2; - state->v3 = v3; - state->v4 = v4; } if (p < bEnd) { @@ -1506,28 +2897,30 @@ XXH32_update(XXH32_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) } -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_digest (const XXH32_state_t* state) +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_digest(const XXH32_state_t* state) { xxh_u32 h32; if (state->large_len) { - h32 = XXH_rotl32(state->v1, 1) - + XXH_rotl32(state->v2, 7) - + XXH_rotl32(state->v3, 12) - + XXH_rotl32(state->v4, 18); + h32 = XXH_rotl32(state->v[0], 1) + + XXH_rotl32(state->v[1], 7) + + XXH_rotl32(state->v[2], 12) + + XXH_rotl32(state->v[3], 18); } else { - h32 = state->v3 /* == seed */ + XXH_PRIME32_5; + h32 = state->v[2] /* == seed */ + XXH_PRIME32_5; } h32 += state->total_len_32; return XXH32_finalize(h32, (const xxh_u8*)state->mem32, state->memsize, XXH_aligned); } - +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /******* Canonical representation *******/ -/* +/*! + * @ingroup XXH32_family * The default return values from XXH functions are unsigned 32 and 64 bit * integers. * @@ -1544,9 +2937,9 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_canonicalFromHash(XXH32_canonical_t* dst, XXH32_hash_t { XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(XXH32_canonical_t) == sizeof(XXH32_hash_t)); if (XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) hash = XXH_swap32(hash); - memcpy(dst, &hash, sizeof(*dst)); + XXH_memcpy(dst, &hash, sizeof(*dst)); } - +/*! @ingroup XXH32_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_hashFromCanonical(const XXH32_canonical_t* src) { return XXH_readBE32(src); @@ -1558,7 +2951,11 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_hashFromCanonical(const XXH32_canonical_t* src /* ******************************************************************* * 64-bit hash functions *********************************************************************/ - +/*! + * @} + * @ingroup impl + * @{ + */ /******* Memory access *******/ typedef XXH64_hash_t xxh_u64; @@ -1567,35 +2964,6 @@ typedef XXH64_hash_t xxh_u64; # define U64 xxh_u64 #endif -/*! - * XXH_REROLL_XXH64: - * Whether to reroll the XXH64_finalize() loop. - * - * Just like XXH32, we can unroll the XXH64_finalize() loop. This can be a - * performance gain on 64-bit hosts, as only one jump is required. - * - * However, on 32-bit hosts, because arithmetic needs to be done with two 32-bit - * registers, and 64-bit arithmetic needs to be simulated, it isn't beneficial - * to unroll. The code becomes ridiculously large (the largest function in the - * binary on i386!), and rerolling it saves anywhere from 3kB to 20kB. It is - * also slightly faster because it fits into cache better and is more likely - * to be inlined by the compiler. - * - * If XXH_REROLL is defined, this is ignored and the loop is always rerolled. - */ -#ifndef XXH_REROLL_XXH64 -# if (defined(__ILP32__) || defined(_ILP32)) /* ILP32 is often defined on 32-bit GCC family */ \ - || !(defined(__x86_64__) || defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_AMD64) /* x86-64 */ \ - || defined(_M_ARM64) || defined(__aarch64__) || defined(__arm64__) /* aarch64 */ \ - || defined(__PPC64__) || defined(__PPC64LE__) || defined(__ppc64__) || defined(__powerpc64__) /* ppc64 */ \ - || defined(__mips64__) || defined(__mips64)) /* mips64 */ \ - || (!defined(SIZE_MAX) || SIZE_MAX < ULLONG_MAX) /* check limits */ -# define XXH_REROLL_XXH64 1 -# else -# define XXH_REROLL_XXH64 0 -# endif -#endif /* !defined(XXH_REROLL_XXH64) */ - #if (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3)) /* * Manual byteshift. Best for old compilers which don't inline memcpy. @@ -1604,35 +2972,39 @@ typedef XXH64_hash_t xxh_u64; #elif (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==2)) /* Force direct memory access. Only works on CPU which support unaligned memory access in hardware */ -static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* memPtr) { return *(const xxh_u64*) memPtr; } +static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* memPtr) +{ + return *(const xxh_u64*) memPtr; +} #elif (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==1)) /* - * __pack instructions are safer, but compiler specific, hence potentially - * problematic for some compilers. - * - * Currently only defined for GCC and ICC. + * __attribute__((aligned(1))) is supported by gcc and clang. Originally the + * documentation claimed that it only increased the alignment, but actually it + * can decrease it on gcc, clang, and icc: + * https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=69502, + * https://gcc.godbolt.org/z/xYez1j67Y. */ #ifdef XXH_OLD_NAMES typedef union { xxh_u32 u32; xxh_u64 u64; } __attribute__((packed)) unalign64; #endif static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* ptr) { - typedef union { xxh_u32 u32; xxh_u64 u64; } __attribute__((packed)) xxh_unalign64; - return ((const xxh_unalign64*)ptr)->u64; + typedef __attribute__((aligned(1))) xxh_u64 xxh_unalign64; + return *((const xxh_unalign64*)ptr); } #else /* * Portable and safe solution. Generally efficient. - * see: https://stackoverflow.com/a/32095106/646947 + * see: https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2015/08/accessing-unaligned-memory.html */ static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* memPtr) { xxh_u64 val; - memcpy(&val, memPtr, sizeof(val)); + XXH_memcpy(&val, memPtr, sizeof(val)); return val; } @@ -1643,7 +3015,7 @@ static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* memPtr) #elif XXH_GCC_VERSION >= 403 # define XXH_swap64 __builtin_bswap64 #else -static xxh_u64 XXH_swap64 (xxh_u64 x) +static xxh_u64 XXH_swap64(xxh_u64 x) { return ((x << 56) & 0xff00000000000000ULL) | ((x << 40) & 0x00ff000000000000ULL) | @@ -1709,12 +3081,20 @@ XXH_readLE64_align(const void* ptr, XXH_alignment align) /******* xxh64 *******/ - -static const xxh_u64 XXH_PRIME64_1 = 0x9E3779B185EBCA87ULL; /* 0b1001111000110111011110011011000110000101111010111100101010000111 */ -static const xxh_u64 XXH_PRIME64_2 = 0xC2B2AE3D27D4EB4FULL; /* 0b1100001010110010101011100011110100100111110101001110101101001111 */ -static const xxh_u64 XXH_PRIME64_3 = 0x165667B19E3779F9ULL; /* 0b0001011001010110011001111011000110011110001101110111100111111001 */ -static const xxh_u64 XXH_PRIME64_4 = 0x85EBCA77C2B2AE63ULL; /* 0b1000010111101011110010100111011111000010101100101010111001100011 */ -static const xxh_u64 XXH_PRIME64_5 = 0x27D4EB2F165667C5ULL; /* 0b0010011111010100111010110010111100010110010101100110011111000101 */ +/*! + * @} + * @defgroup XXH64_impl XXH64 implementation + * @ingroup impl + * + * Details on the XXH64 implementation. + * @{ + */ +/* #define rather that static const, to be used as initializers */ +#define XXH_PRIME64_1 0x9E3779B185EBCA87ULL /*!< 0b1001111000110111011110011011000110000101111010111100101010000111 */ +#define XXH_PRIME64_2 0xC2B2AE3D27D4EB4FULL /*!< 0b1100001010110010101011100011110100100111110101001110101101001111 */ +#define XXH_PRIME64_3 0x165667B19E3779F9ULL /*!< 0b0001011001010110011001111011000110011110001101110111100111111001 */ +#define XXH_PRIME64_4 0x85EBCA77C2B2AE63ULL /*!< 0b1000010111101011110010100111011111000010101100101010111001100011 */ +#define XXH_PRIME64_5 0x27D4EB2F165667C5ULL /*!< 0b0010011111010100111010110010111100010110010101100110011111000101 */ #ifdef XXH_OLD_NAMES # define PRIME64_1 XXH_PRIME64_1 @@ -1724,6 +3104,7 @@ static const xxh_u64 XXH_PRIME64_5 = 0x27D4EB2F165667C5ULL; /* 0b0010011111010 # define PRIME64_5 XXH_PRIME64_5 #endif +/*! @copydoc XXH32_round */ static xxh_u64 XXH64_round(xxh_u64 acc, xxh_u64 input) { acc += input * XXH_PRIME64_2; @@ -1740,142 +3121,59 @@ static xxh_u64 XXH64_mergeRound(xxh_u64 acc, xxh_u64 val) return acc; } -static xxh_u64 XXH64_avalanche(xxh_u64 h64) +/*! @copydoc XXH32_avalanche */ +static xxh_u64 XXH64_avalanche(xxh_u64 hash) { - h64 ^= h64 >> 33; - h64 *= XXH_PRIME64_2; - h64 ^= h64 >> 29; - h64 *= XXH_PRIME64_3; - h64 ^= h64 >> 32; - return h64; + hash ^= hash >> 33; + hash *= XXH_PRIME64_2; + hash ^= hash >> 29; + hash *= XXH_PRIME64_3; + hash ^= hash >> 32; + return hash; } #define XXH_get64bits(p) XXH_readLE64_align(p, align) -static xxh_u64 -XXH64_finalize(xxh_u64 h64, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align) -{ -#define XXH_PROCESS1_64 do { \ - h64 ^= (*ptr++) * XXH_PRIME64_5; \ - h64 = XXH_rotl64(h64, 11) * XXH_PRIME64_1; \ -} while (0) - -#define XXH_PROCESS4_64 do { \ - h64 ^= (xxh_u64)(XXH_get32bits(ptr)) * XXH_PRIME64_1; \ - ptr += 4; \ - h64 = XXH_rotl64(h64, 23) * XXH_PRIME64_2 + XXH_PRIME64_3; \ -} while (0) - -#define XXH_PROCESS8_64 do { \ - xxh_u64 const k1 = XXH64_round(0, XXH_get64bits(ptr)); \ - ptr += 8; \ - h64 ^= k1; \ - h64 = XXH_rotl64(h64,27) * XXH_PRIME64_1 + XXH_PRIME64_4; \ -} while (0) - - /* Rerolled version for 32-bit targets is faster and much smaller. */ - if (XXH_REROLL || XXH_REROLL_XXH64) { - len &= 31; - while (len >= 8) { - XXH_PROCESS8_64; - len -= 8; - } - if (len >= 4) { - XXH_PROCESS4_64; - len -= 4; - } - while (len > 0) { - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - --len; - } - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - } else { - switch(len & 31) { - case 24: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 16: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 8: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - - case 28: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 20: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 12: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 4: XXH_PROCESS4_64; - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - - case 25: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 17: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 9: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - - case 29: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 21: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 13: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 5: XXH_PROCESS4_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - - case 26: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 18: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 10: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - - case 30: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 22: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 14: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 6: XXH_PROCESS4_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - - case 27: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 19: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 11: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - XXH_PROCESS1_64; - return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - - case 31: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 23: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 15: XXH_PROCESS8_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 7: XXH_PROCESS4_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 3: XXH_PROCESS1_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 2: XXH_PROCESS1_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 1: XXH_PROCESS1_64; - /* fallthrough */ - case 0: return XXH64_avalanche(h64); - } +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Processes the last 0-31 bytes of @p ptr. + * + * There may be up to 31 bytes remaining to consume from the input. + * This final stage will digest them to ensure that all input bytes are present + * in the final mix. + * + * @param hash The hash to finalize. + * @param ptr The pointer to the remaining input. + * @param len The remaining length, modulo 32. + * @param align Whether @p ptr is aligned. + * @return The finalized hash + * @see XXH32_finalize(). + */ +static XXH_PUREF xxh_u64 +XXH64_finalize(xxh_u64 hash, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align) +{ + if (ptr==NULL) XXH_ASSERT(len == 0); + len &= 31; + while (len >= 8) { + xxh_u64 const k1 = XXH64_round(0, XXH_get64bits(ptr)); + ptr += 8; + hash ^= k1; + hash = XXH_rotl64(hash,27) * XXH_PRIME64_1 + XXH_PRIME64_4; + len -= 8; + } + if (len >= 4) { + hash ^= (xxh_u64)(XXH_get32bits(ptr)) * XXH_PRIME64_1; + ptr += 4; + hash = XXH_rotl64(hash, 23) * XXH_PRIME64_2 + XXH_PRIME64_3; + len -= 4; } - /* impossible to reach */ - XXH_ASSERT(0); - return 0; /* unreachable, but some compilers complain without it */ + while (len > 0) { + hash ^= (*ptr++) * XXH_PRIME64_5; + hash = XXH_rotl64(hash, 11) * XXH_PRIME64_1; + --len; + } + return XXH64_avalanche(hash); } #ifdef XXH_OLD_NAMES @@ -1888,21 +3186,23 @@ XXH64_finalize(xxh_u64 h64, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align) # undef XXH_PROCESS8_64 #endif -XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 +/*! + * @internal + * @brief The implementation for @ref XXH64(). + * + * @param input , len , seed Directly passed from @ref XXH64(). + * @param align Whether @p input is aligned. + * @return The calculated hash. + */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF xxh_u64 XXH64_endian_align(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, xxh_u64 seed, XXH_alignment align) { - const xxh_u8* bEnd = input + len; xxh_u64 h64; - -#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1) - if (input==NULL) { - len=0; - bEnd=input=(const xxh_u8*)(size_t)32; - } -#endif + if (input==NULL) XXH_ASSERT(len == 0); if (len>=32) { - const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 32; + const xxh_u8* const bEnd = input + len; + const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 31; xxh_u64 v1 = seed + XXH_PRIME64_1 + XXH_PRIME64_2; xxh_u64 v2 = seed + XXH_PRIME64_2; xxh_u64 v3 = seed + 0; @@ -1913,7 +3213,7 @@ XXH64_endian_align(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, xxh_u64 seed, XXH_alignment v2 = XXH64_round(v2, XXH_get64bits(input)); input+=8; v3 = XXH64_round(v3, XXH_get64bits(input)); input+=8; v4 = XXH64_round(v4, XXH_get64bits(input)); input+=8; - } while (input<=limit); + } while (input<limit); h64 = XXH_rotl64(v1, 1) + XXH_rotl64(v2, 7) + XXH_rotl64(v3, 12) + XXH_rotl64(v4, 18); h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v1); @@ -1931,17 +3231,16 @@ XXH64_endian_align(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, xxh_u64 seed, XXH_alignment } -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64 (const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64 (XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) { -#if 0 +#if !defined(XXH_NO_STREAM) && XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 2 /* Simple version, good for code maintenance, but unfortunately slow for small inputs */ XXH64_state_t state; XXH64_reset(&state, seed); XXH64_update(&state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len); return XXH64_digest(&state); - #else - if (XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK) { if ((((size_t)input) & 7)==0) { /* Input is aligned, let's leverage the speed advantage */ return XXH64_endian_align((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed, XXH_aligned); @@ -1953,44 +3252,45 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64 (const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t s } /******* Hash Streaming *******/ - +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family*/ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_state_t* XXH64_createState(void) { return (XXH64_state_t*)XXH_malloc(sizeof(XXH64_state_t)); } +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_freeState(XXH64_state_t* statePtr) { XXH_free(statePtr); return XXH_OK; } -XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_copyState(XXH64_state_t* dstState, const XXH64_state_t* srcState) +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_copyState(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_state_t* dstState, const XXH64_state_t* srcState) { - memcpy(dstState, srcState, sizeof(*dstState)); + XXH_memcpy(dstState, srcState, sizeof(*dstState)); } -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_reset(XXH64_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed) +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_reset(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed) { - XXH64_state_t state; /* use a local state to memcpy() in order to avoid strict-aliasing warnings */ - memset(&state, 0, sizeof(state)); - state.v1 = seed + XXH_PRIME64_1 + XXH_PRIME64_2; - state.v2 = seed + XXH_PRIME64_2; - state.v3 = seed + 0; - state.v4 = seed - XXH_PRIME64_1; - /* do not write into reserved64, might be removed in a future version */ - memcpy(statePtr, &state, sizeof(state) - sizeof(state.reserved64)); + XXH_ASSERT(statePtr != NULL); + memset(statePtr, 0, sizeof(*statePtr)); + statePtr->v[0] = seed + XXH_PRIME64_1 + XXH_PRIME64_2; + statePtr->v[1] = seed + XXH_PRIME64_2; + statePtr->v[2] = seed + 0; + statePtr->v[3] = seed - XXH_PRIME64_1; return XXH_OK; } +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH64_update (XXH64_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) +XXH64_update (XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_state_t* state, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len) { - if (input==NULL) -#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1) + if (input==NULL) { + XXH_ASSERT(len == 0); return XXH_OK; -#else - return XXH_ERROR; -#endif + } { const xxh_u8* p = (const xxh_u8*)input; const xxh_u8* const bEnd = p + len; @@ -2005,32 +3305,24 @@ XXH64_update (XXH64_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) if (state->memsize) { /* tmp buffer is full */ XXH_memcpy(((xxh_u8*)state->mem64) + state->memsize, input, 32-state->memsize); - state->v1 = XXH64_round(state->v1, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+0)); - state->v2 = XXH64_round(state->v2, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+1)); - state->v3 = XXH64_round(state->v3, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+2)); - state->v4 = XXH64_round(state->v4, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+3)); - p += 32-state->memsize; + state->v[0] = XXH64_round(state->v[0], XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+0)); + state->v[1] = XXH64_round(state->v[1], XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+1)); + state->v[2] = XXH64_round(state->v[2], XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+2)); + state->v[3] = XXH64_round(state->v[3], XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+3)); + p += 32 - state->memsize; state->memsize = 0; } if (p+32 <= bEnd) { const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 32; - xxh_u64 v1 = state->v1; - xxh_u64 v2 = state->v2; - xxh_u64 v3 = state->v3; - xxh_u64 v4 = state->v4; do { - v1 = XXH64_round(v1, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; - v2 = XXH64_round(v2, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; - v3 = XXH64_round(v3, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; - v4 = XXH64_round(v4, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; + state->v[0] = XXH64_round(state->v[0], XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; + state->v[1] = XXH64_round(state->v[1], XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; + state->v[2] = XXH64_round(state->v[2], XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; + state->v[3] = XXH64_round(state->v[3], XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8; } while (p<=limit); - state->v1 = v1; - state->v2 = v2; - state->v3 = v3; - state->v4 = v4; } if (p < bEnd) { @@ -2043,58 +3335,72 @@ XXH64_update (XXH64_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) } -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_digest (const XXH64_state_t* state) +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_digest(XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH64_state_t* state) { xxh_u64 h64; if (state->total_len >= 32) { - xxh_u64 const v1 = state->v1; - xxh_u64 const v2 = state->v2; - xxh_u64 const v3 = state->v3; - xxh_u64 const v4 = state->v4; - - h64 = XXH_rotl64(v1, 1) + XXH_rotl64(v2, 7) + XXH_rotl64(v3, 12) + XXH_rotl64(v4, 18); - h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v1); - h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v2); - h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v3); - h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v4); + h64 = XXH_rotl64(state->v[0], 1) + XXH_rotl64(state->v[1], 7) + XXH_rotl64(state->v[2], 12) + XXH_rotl64(state->v[3], 18); + h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, state->v[0]); + h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, state->v[1]); + h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, state->v[2]); + h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, state->v[3]); } else { - h64 = state->v3 /*seed*/ + XXH_PRIME64_5; + h64 = state->v[2] /*seed*/ + XXH_PRIME64_5; } h64 += (xxh_u64) state->total_len; return XXH64_finalize(h64, (const xxh_u8*)state->mem64, (size_t)state->total_len, XXH_aligned); } - +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /******* Canonical representation *******/ -XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_canonicalFromHash(XXH64_canonical_t* dst, XXH64_hash_t hash) +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_canonicalFromHash(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH64_canonical_t* dst, XXH64_hash_t hash) { XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(XXH64_canonical_t) == sizeof(XXH64_hash_t)); if (XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) hash = XXH_swap64(hash); - memcpy(dst, &hash, sizeof(*dst)); + XXH_memcpy(dst, &hash, sizeof(*dst)); } -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src) +/*! @ingroup XXH64_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH64_canonical_t* src) { return XXH_readBE64(src); } - +#ifndef XXH_NO_XXH3 /* ********************************************************************* * XXH3 * New generation hash designed for speed on small keys and vectorization ************************************************************************ */ +/*! + * @} + * @defgroup XXH3_impl XXH3 implementation + * @ingroup impl + * @{ + */ /* === Compiler specifics === */ -#if defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L /* >= C99 */ +#if ((defined(sun) || defined(__sun)) && __cplusplus) /* Solaris includes __STDC_VERSION__ with C++. Tested with GCC 5.5 */ +# define XXH_RESTRICT /* disable */ +#elif defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L /* >= C99 */ # define XXH_RESTRICT restrict +#elif (defined (__GNUC__) && ((__GNUC__ > 3) || (__GNUC__ == 3 && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= 1))) \ + || (defined (__clang__)) \ + || (defined (_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER >= 1400)) \ + || (defined (__INTEL_COMPILER) && (__INTEL_COMPILER >= 1300)) +/* + * There are a LOT more compilers that recognize __restrict but this + * covers the major ones. + */ +# define XXH_RESTRICT __restrict #else -/* Note: it might be useful to define __restrict or __restrict__ for some C++ compilers */ # define XXH_RESTRICT /* disable */ #endif @@ -2108,17 +3414,33 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src # define XXH_unlikely(x) (x) #endif -#if defined(__GNUC__) -# if defined(__AVX2__) -# include <immintrin.h> -# elif defined(__SSE2__) -# include <emmintrin.h> -# elif defined(__ARM_NEON__) || defined(__ARM_NEON) +#ifndef XXH_HAS_INCLUDE +# ifdef __has_include +# define XXH_HAS_INCLUDE(x) __has_include(x) +# else +# define XXH_HAS_INCLUDE(x) 0 +# endif +#endif + +#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__) +# if defined(__ARM_FEATURE_SVE) +# error #include <arm_sve.h> +# endif +# if defined(__ARM_NEON__) || defined(__ARM_NEON) \ + || (defined(_M_ARM) && _M_ARM >= 7) \ + || defined(_M_ARM64) || defined(_M_ARM64EC) \ + || (defined(__wasm_simd128__) && XXH_HAS_INCLUDE(<arm_neon.h>)) /* WASM SIMD128 via SIMDe */ # define inline __inline__ /* circumvent a clang bug */ # include <arm_neon.h> # undef inline +# elif defined(__AVX2__) +# include <immintrin.h> +# elif defined(__SSE2__) +# include <emmintrin.h> # endif -#elif defined(_MSC_VER) +#endif + +#if defined(_MSC_VER) # include <intrin.h> #endif @@ -2198,25 +3520,87 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src /* ========================================== * Vectorization detection * ========================================== */ -#define XXH_SCALAR 0 /* Portable scalar version */ -#define XXH_SSE2 1 /* SSE2 for Pentium 4 and all x86_64 */ -#define XXH_AVX2 2 /* AVX2 for Haswell and Bulldozer */ -#define XXH_AVX512 3 /* AVX512 for Skylake and Icelake */ -#define XXH_NEON 4 /* NEON for most ARMv7-A and all AArch64 */ -#define XXH_VSX 5 /* VSX and ZVector for POWER8/z13 */ + +#ifdef XXH_DOXYGEN +/*! + * @ingroup tuning + * @brief Overrides the vectorization implementation chosen for XXH3. + * + * Can be defined to 0 to disable SIMD or any of the values mentioned in + * @ref XXH_VECTOR_TYPE. + * + * If this is not defined, it uses predefined macros to determine the best + * implementation. + */ +# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_SCALAR +/*! + * @ingroup tuning + * @brief Possible values for @ref XXH_VECTOR. + * + * Note that these are actually implemented as macros. + * + * If this is not defined, it is detected automatically. + * internal macro XXH_X86DISPATCH overrides this. + */ +enum XXH_VECTOR_TYPE /* fake enum */ { + XXH_SCALAR = 0, /*!< Portable scalar version */ + XXH_SSE2 = 1, /*!< + * SSE2 for Pentium 4, Opteron, all x86_64. + * + * @note SSE2 is also guaranteed on Windows 10, macOS, and + * Android x86. + */ + XXH_AVX2 = 2, /*!< AVX2 for Haswell and Bulldozer */ + XXH_AVX512 = 3, /*!< AVX512 for Skylake and Icelake */ + XXH_NEON = 4, /*!< + * NEON for most ARMv7-A, all AArch64, and WASM SIMD128 + * via the SIMDeverywhere polyfill provided with the + * Emscripten SDK. + */ + XXH_VSX = 5, /*!< VSX and ZVector for POWER8/z13 (64-bit) */ + XXH_SVE = 6, /*!< SVE for some ARMv8-A and ARMv9-A */ +}; +/*! + * @ingroup tuning + * @brief Selects the minimum alignment for XXH3's accumulators. + * + * When using SIMD, this should match the alignment required for said vector + * type, so, for example, 32 for AVX2. + * + * Default: Auto detected. + */ +# define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 8 +#endif + +/* Actual definition */ +#ifndef XXH_DOXYGEN +# define XXH_SCALAR 0 +# define XXH_SSE2 1 +# define XXH_AVX2 2 +# define XXH_AVX512 3 +# define XXH_NEON 4 +# define XXH_VSX 5 +# define XXH_SVE 6 +#endif #ifndef XXH_VECTOR /* can be defined on command line */ -# if defined(__AVX512F__) +# if defined(__ARM_FEATURE_SVE) +# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_SVE +# elif ( \ + defined(__ARM_NEON__) || defined(__ARM_NEON) /* gcc */ \ + || defined(_M_ARM) || defined(_M_ARM64) || defined(_M_ARM64EC) /* msvc */ \ + || (defined(__wasm_simd128__) && XXH_HAS_INCLUDE(<arm_neon.h>)) /* wasm simd128 via SIMDe */ \ + ) && ( \ + defined(_WIN32) || defined(__LITTLE_ENDIAN__) /* little endian only */ \ + || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_LITTLE_ENDIAN__) \ + ) +# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_NEON +# elif defined(__AVX512F__) # define XXH_VECTOR XXH_AVX512 # elif defined(__AVX2__) # define XXH_VECTOR XXH_AVX2 # elif defined(__SSE2__) || defined(_M_AMD64) || defined(_M_X64) || (defined(_M_IX86_FP) && (_M_IX86_FP == 2)) # define XXH_VECTOR XXH_SSE2 -# elif defined(__GNUC__) /* msvc support maybe later */ \ - && (defined(__ARM_NEON__) || defined(__ARM_NEON)) \ - && (defined(__LITTLE_ENDIAN__) /* We only support little endian NEON */ \ - || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_LITTLE_ENDIAN__)) -# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_NEON # elif (defined(__PPC64__) && defined(__POWER8_VECTOR__)) \ || (defined(__s390x__) && defined(__VEC__)) \ && defined(__GNUC__) /* TODO: IBM XL */ @@ -2226,6 +3610,17 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src # endif #endif +/* __ARM_FEATURE_SVE is only supported by GCC & Clang. */ +#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SVE) && !defined(__ARM_FEATURE_SVE) +# ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(once : 4606) +# else +# warning "__ARM_FEATURE_SVE isn't supported. Use SCALAR instead." +# endif +# undef XXH_VECTOR +# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_SCALAR +#endif + /* * Controls the alignment of the accumulator, * for compatibility with aligned vector loads, which are usually faster. @@ -2245,16 +3640,26 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src # define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 16 # elif XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX512 /* avx512 */ # define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 64 +# elif XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SVE /* sve */ +# define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 64 # endif #endif #if defined(XXH_X86DISPATCH) || XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SSE2 \ || XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2 || XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX512 # define XXH_SEC_ALIGN XXH_ACC_ALIGN +#elif XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SVE +# define XXH_SEC_ALIGN XXH_ACC_ALIGN #else # define XXH_SEC_ALIGN 8 #endif +#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__) +# define XXH_ALIASING __attribute__((may_alias)) +#else +# define XXH_ALIASING /* nothing */ +#endif + /* * UGLY HACK: * GCC usually generates the best code with -O3 for xxHash. @@ -2278,111 +3683,130 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src */ #if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2 /* AVX2 */ \ && defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) /* GCC, not Clang */ \ - && defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && !defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) /* respect -O0 and -Os */ + && defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && XXH_SIZE_OPT <= 0 /* respect -O0 and -Os */ # pragma GCC push_options # pragma GCC optimize("-O2") #endif - #if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON + /* - * NEON's setup for vmlal_u32 is a little more complicated than it is on - * SSE2, AVX2, and VSX. - * - * While PMULUDQ and VMULEUW both perform a mask, VMLAL.U32 performs an upcast. - * - * To do the same operation, the 128-bit 'Q' register needs to be split into - * two 64-bit 'D' registers, performing this operation:: - * - * [ a | b ] - * | '---------. .--------' | - * | x | - * | .---------' '--------. | - * [ a & 0xFFFFFFFF | b & 0xFFFFFFFF ],[ a >> 32 | b >> 32 ] + * UGLY HACK: While AArch64 GCC on Linux does not seem to care, on macOS, GCC -O3 + * optimizes out the entire hashLong loop because of the aliasing violation. * - * Due to significant changes in aarch64, the fastest method for aarch64 is - * completely different than the fastest method for ARMv7-A. - * - * ARMv7-A treats D registers as unions overlaying Q registers, so modifying - * D11 will modify the high half of Q5. This is similar to how modifying AH - * will only affect bits 8-15 of AX on x86. - * - * VZIP takes two registers, and puts even lanes in one register and odd lanes - * in the other. + * However, GCC is also inefficient at load-store optimization with vld1q/vst1q, + * so the only option is to mark it as aliasing. + */ +typedef uint64x2_t xxh_aliasing_uint64x2_t XXH_ALIASING; + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief `vld1q_u64` but faster and alignment-safe. * - * On ARMv7-A, this strangely modifies both parameters in place instead of - * taking the usual 3-operand form. + * On AArch64, unaligned access is always safe, but on ARMv7-a, it is only + * *conditionally* safe (`vld1` has an alignment bit like `movdq[ua]` in x86). * - * Therefore, if we want to do this, we can simply use a D-form VZIP.32 on the - * lower and upper halves of the Q register to end up with the high and low - * halves where we want - all in one instruction. + * GCC for AArch64 sees `vld1q_u8` as an intrinsic instead of a load, so it + * prohibits load-store optimizations. Therefore, a direct dereference is used. * - * vzip.32 d10, d11 @ d10 = { d10[0], d11[0] }; d11 = { d10[1], d11[1] } + * Otherwise, `vld1q_u8` is used with `vreinterpretq_u8_u64` to do a safe + * unaligned load. + */ +#if defined(__aarch64__) && defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) +XXH_FORCE_INLINE uint64x2_t XXH_vld1q_u64(void const* ptr) /* silence -Wcast-align */ +{ + return *(xxh_aliasing_uint64x2_t const *)ptr; +} +#else +XXH_FORCE_INLINE uint64x2_t XXH_vld1q_u64(void const* ptr) +{ + return vreinterpretq_u64_u8(vld1q_u8((uint8_t const*)ptr)); +} +#endif + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief `vmlal_u32` on low and high halves of a vector. * - * Unfortunately we need inline assembly for this: Instructions modifying two - * registers at once is not possible in GCC or Clang's IR, and they have to - * create a copy. + * This is a workaround for AArch64 GCC < 11 which implemented arm_neon.h with + * inline assembly and were therefore incapable of merging the `vget_{low, high}_u32` + * with `vmlal_u32`. + */ +#if defined(__aarch64__) && defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) && __GNUC__ < 11 +XXH_FORCE_INLINE uint64x2_t +XXH_vmlal_low_u32(uint64x2_t acc, uint32x4_t lhs, uint32x4_t rhs) +{ + /* Inline assembly is the only way */ + __asm__("umlal %0.2d, %1.2s, %2.2s" : "+w" (acc) : "w" (lhs), "w" (rhs)); + return acc; +} +XXH_FORCE_INLINE uint64x2_t +XXH_vmlal_high_u32(uint64x2_t acc, uint32x4_t lhs, uint32x4_t rhs) +{ + /* This intrinsic works as expected */ + return vmlal_high_u32(acc, lhs, rhs); +} +#else +/* Portable intrinsic versions */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE uint64x2_t +XXH_vmlal_low_u32(uint64x2_t acc, uint32x4_t lhs, uint32x4_t rhs) +{ + return vmlal_u32(acc, vget_low_u32(lhs), vget_low_u32(rhs)); +} +/*! @copydoc XXH_vmlal_low_u32 + * Assume the compiler converts this to vmlal_high_u32 on aarch64 */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE uint64x2_t +XXH_vmlal_high_u32(uint64x2_t acc, uint32x4_t lhs, uint32x4_t rhs) +{ + return vmlal_u32(acc, vget_high_u32(lhs), vget_high_u32(rhs)); +} +#endif + +/*! + * @ingroup tuning + * @brief Controls the NEON to scalar ratio for XXH3 * - * aarch64 requires a different approach. + * This can be set to 2, 4, 6, or 8. * - * In order to make it easier to write a decent compiler for aarch64, many - * quirks were removed, such as conditional execution. + * ARM Cortex CPUs are _very_ sensitive to how their pipelines are used. * - * NEON was also affected by this. + * For example, the Cortex-A73 can dispatch 3 micro-ops per cycle, but only 2 of those + * can be NEON. If you are only using NEON instructions, you are only using 2/3 of the CPU + * bandwidth. * - * aarch64 cannot access the high bits of a Q-form register, and writes to a - * D-form register zero the high bits, similar to how writes to W-form scalar - * registers (or DWORD registers on x86_64) work. + * This is even more noticeable on the more advanced cores like the Cortex-A76 which + * can dispatch 8 micro-ops per cycle, but still only 2 NEON micro-ops at once. * - * The formerly free vget_high intrinsics now require a vext (with a few - * exceptions) + * Therefore, to make the most out of the pipeline, it is beneficial to run 6 NEON lanes + * and 2 scalar lanes, which is chosen by default. * - * Additionally, VZIP was replaced by ZIP1 and ZIP2, which are the equivalent - * of PUNPCKL* and PUNPCKH* in SSE, respectively, in order to only modify one - * operand. + * This does not apply to Apple processors or 32-bit processors, which run better with + * full NEON. These will default to 8. Additionally, size-optimized builds run 8 lanes. * - * The equivalent of the VZIP.32 on the lower and upper halves would be this - * mess: + * This change benefits CPUs with large micro-op buffers without negatively affecting + * most other CPUs: * - * ext v2.4s, v0.4s, v0.4s, #2 // v2 = { v0[2], v0[3], v0[0], v0[1] } - * zip1 v1.2s, v0.2s, v2.2s // v1 = { v0[0], v2[0] } - * zip2 v0.2s, v0.2s, v1.2s // v0 = { v0[1], v2[1] } + * | Chipset | Dispatch type | NEON only | 6:2 hybrid | Diff. | + * |:----------------------|:--------------------|----------:|-----------:|------:| + * | Snapdragon 730 (A76) | 2 NEON/8 micro-ops | 8.8 GB/s | 10.1 GB/s | ~16% | + * | Snapdragon 835 (A73) | 2 NEON/3 micro-ops | 5.1 GB/s | 5.3 GB/s | ~5% | + * | Marvell PXA1928 (A53) | In-order dual-issue | 1.9 GB/s | 1.9 GB/s | 0% | + * | Apple M1 | 4 NEON/8 micro-ops | 37.3 GB/s | 36.1 GB/s | ~-3% | * - * Instead, we use a literal downcast, vmovn_u64 (XTN), and vshrn_n_u64 (SHRN): + * It also seems to fix some bad codegen on GCC, making it almost as fast as clang. * - * shrn v1.2s, v0.2d, #32 // v1 = (uint32x2_t)(v0 >> 32); - * xtn v0.2s, v0.2d // v0 = (uint32x2_t)(v0 & 0xFFFFFFFF); + * When using WASM SIMD128, if this is 2 or 6, SIMDe will scalarize 2 of the lanes meaning + * it effectively becomes worse 4. * - * This is available on ARMv7-A, but is less efficient than a single VZIP.32. + * @see XXH3_accumulate_512_neon() */ - -/* - * Function-like macro: - * void XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(uint64x2_t &in, uint32x2_t &outLo, uint32x2_t &outHi) - * { - * outLo = (uint32x2_t)(in & 0xFFFFFFFF); - * outHi = (uint32x2_t)(in >> 32); - * in = UNDEFINED; - * } - */ -# if !defined(XXH_NO_VZIP_HACK) /* define to disable */ \ - && defined(__GNUC__) \ - && !defined(__aarch64__) && !defined(__arm64__) -# define XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(in, outLo, outHi) \ - do { \ - /* Undocumented GCC/Clang operand modifier: %e0 = lower D half, %f0 = upper D half */ \ - /* https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/38cf91e5/gcc/config/arm/arm.c#L22486 */ \ - /* https://github.com/llvm-mirror/llvm/blob/2c4ca683/lib/Target/ARM/ARMAsmPrinter.cpp#L399 */ \ - __asm__("vzip.32 %e0, %f0" : "+w" (in)); \ - (outLo) = vget_low_u32 (vreinterpretq_u32_u64(in)); \ - (outHi) = vget_high_u32(vreinterpretq_u32_u64(in)); \ - } while (0) -# else -# define XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(in, outLo, outHi) \ - do { \ - (outLo) = vmovn_u64 (in); \ - (outHi) = vshrn_n_u64 ((in), 32); \ - } while (0) +# ifndef XXH3_NEON_LANES +# if (defined(__aarch64__) || defined(__arm64__) || defined(_M_ARM64) || defined(_M_ARM64EC)) \ + && !defined(__APPLE__) && XXH_SIZE_OPT <= 0 +# define XXH3_NEON_LANES 6 +# else +# define XXH3_NEON_LANES XXH_ACC_NB +# endif # endif #endif /* XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON */ @@ -2395,27 +3819,42 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src * inconsistent intrinsics, spotty coverage, and multiple endiannesses. */ #if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX +/* Annoyingly, these headers _may_ define three macros: `bool`, `vector`, + * and `pixel`. This is a problem for obvious reasons. + * + * These keywords are unnecessary; the spec literally says they are + * equivalent to `__bool`, `__vector`, and `__pixel` and may be undef'd + * after including the header. + * + * We use pragma push_macro/pop_macro to keep the namespace clean. */ +# pragma push_macro("bool") +# pragma push_macro("vector") +# pragma push_macro("pixel") +/* silence potential macro redefined warnings */ +# undef bool +# undef vector +# undef pixel + # if defined(__s390x__) # include <s390intrin.h> # else -/* gcc's altivec.h can have the unwanted consequence to unconditionally - * #define bool, vector, and pixel keywords, - * with bad consequences for programs already using these keywords for other purposes. - * The paragraph defining these macros is skipped when __APPLE_ALTIVEC__ is defined. - * __APPLE_ALTIVEC__ is _generally_ defined automatically by the compiler, - * but it seems that, in some cases, it isn't. - * Force the build macro to be defined, so that keywords are not altered. - */ -# if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__APPLE_ALTIVEC__) -# define __APPLE_ALTIVEC__ -# endif # include <altivec.h> # endif +/* Restore the original macro values, if applicable. */ +# pragma pop_macro("pixel") +# pragma pop_macro("vector") +# pragma pop_macro("bool") + typedef __vector unsigned long long xxh_u64x2; typedef __vector unsigned char xxh_u8x16; typedef __vector unsigned xxh_u32x4; +/* + * UGLY HACK: Similar to aarch64 macOS GCC, s390x GCC has the same aliasing issue. + */ +typedef xxh_u64x2 xxh_aliasing_u64x2 XXH_ALIASING; + # ifndef XXH_VSX_BE # if defined(__BIG_ENDIAN__) \ || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__) @@ -2429,10 +3868,12 @@ typedef __vector unsigned xxh_u32x4; # endif /* !defined(XXH_VSX_BE) */ # if XXH_VSX_BE -/* A wrapper for POWER9's vec_revb. */ # if defined(__POWER9_VECTOR__) || (defined(__clang__) && defined(__s390x__)) # define XXH_vec_revb vec_revb # else +/*! + * A polyfill for POWER9's vec_revb(). + */ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_revb(xxh_u64x2 val) { xxh_u8x16 const vByteSwap = { 0x07, 0x06, 0x05, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x01, 0x00, @@ -2442,13 +3883,13 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_revb(xxh_u64x2 val) # endif # endif /* XXH_VSX_BE */ -/* - * Performs an unaligned load and byte swaps it on big endian. +/*! + * Performs an unaligned vector load and byte swaps it on big endian. */ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_loadu(const void *ptr) { xxh_u64x2 ret; - memcpy(&ret, ptr, sizeof(xxh_u64x2)); + XXH_memcpy(&ret, ptr, sizeof(xxh_u64x2)); # if XXH_VSX_BE ret = XXH_vec_revb(ret); # endif @@ -2465,8 +3906,9 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_loadu(const void *ptr) /* s390x is always big endian, no issue on this platform */ # define XXH_vec_mulo vec_mulo # define XXH_vec_mule vec_mule -# elif defined(__clang__) && XXH_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_altivec_vmuleuw) +# elif defined(__clang__) && XXH_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_altivec_vmuleuw) && !defined(__ibmxl__) /* Clang has a better way to control this, we can just use the builtin which doesn't swap. */ + /* The IBM XL Compiler (which defined __clang__) only implements the vec_* operations */ # define XXH_vec_mulo __builtin_altivec_vmulouw # define XXH_vec_mule __builtin_altivec_vmuleuw # else @@ -2487,13 +3929,28 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_mule(xxh_u32x4 a, xxh_u32x4 b) # endif /* XXH_vec_mulo, XXH_vec_mule */ #endif /* XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX */ +#if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SVE +#define ACCRND(acc, offset) \ +do { \ + svuint64_t input_vec = svld1_u64(mask, xinput + offset); \ + svuint64_t secret_vec = svld1_u64(mask, xsecret + offset); \ + svuint64_t mixed = sveor_u64_x(mask, secret_vec, input_vec); \ + svuint64_t swapped = svtbl_u64(input_vec, kSwap); \ + svuint64_t mixed_lo = svextw_u64_x(mask, mixed); \ + svuint64_t mixed_hi = svlsr_n_u64_x(mask, mixed, 32); \ + svuint64_t mul = svmad_u64_x(mask, mixed_lo, mixed_hi, swapped); \ + acc = svadd_u64_x(mask, acc, mul); \ +} while (0) +#endif /* XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SVE */ /* prefetch * can be disabled, by declaring XXH_NO_PREFETCH build macro */ #if defined(XXH_NO_PREFETCH) # define XXH_PREFETCH(ptr) (void)(ptr) /* disabled */ #else -# if defined(_MSC_VER) && (defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_I86)) /* _mm_prefetch() is not defined outside of x86/x64 */ +# if XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1 +# define XXH_PREFETCH(ptr) (void)(ptr) +# elif defined(_MSC_VER) && (defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_IX86)) /* _mm_prefetch() not defined outside of x86/x64 */ # include <mmintrin.h> /* https://msdn.microsoft.com/fr-fr/library/84szxsww(v=vs.90).aspx */ # define XXH_PREFETCH(ptr) _mm_prefetch((const char*)(ptr), _MM_HINT_T0) # elif defined(__GNUC__) && ( (__GNUC__ >= 4) || ( (__GNUC__ == 3) && (__GNUC_MINOR__ >= 1) ) ) @@ -2514,7 +3971,7 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_mule(xxh_u32x4 a, xxh_u32x4 b) # error "default keyset is not large enough" #endif -/* Pseudorandom secret taken directly from FARSH */ +/*! Pseudorandom secret taken directly from FARSH. */ XXH_ALIGN(64) static const xxh_u8 XXH3_kSecret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE] = { 0xb8, 0xfe, 0x6c, 0x39, 0x23, 0xa4, 0x4b, 0xbe, 0x7c, 0x01, 0x81, 0x2c, 0xf7, 0x21, 0xad, 0x1c, 0xde, 0xd4, 0x6d, 0xe9, 0x83, 0x90, 0x97, 0xdb, 0x72, 0x40, 0xa4, 0xa4, 0xb7, 0xb3, 0x67, 0x1f, @@ -2530,29 +3987,36 @@ XXH_ALIGN(64) static const xxh_u8 XXH3_kSecret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE] = { 0x45, 0xcb, 0x3a, 0x8f, 0x95, 0x16, 0x04, 0x28, 0xaf, 0xd7, 0xfb, 0xca, 0xbb, 0x4b, 0x40, 0x7e, }; +static const xxh_u64 PRIME_MX1 = 0x165667919E3779F9ULL; /*!< 0b0001011001010110011001111001000110011110001101110111100111111001 */ +static const xxh_u64 PRIME_MX2 = 0x9FB21C651E98DF25ULL; /*!< 0b1001111110110010000111000110010100011110100110001101111100100101 */ #ifdef XXH_OLD_NAMES # define kSecret XXH3_kSecret #endif -/* - * Calculates a 32-bit to 64-bit long multiply. +#ifdef XXH_DOXYGEN +/*! + * @brief Calculates a 32-bit to 64-bit long multiply. + * + * Implemented as a macro. * - * Wraps __emulu on MSVC x86 because it tends to call __allmul when it doesn't + * Wraps `__emulu` on MSVC x86 because it tends to call `__allmul` when it doesn't * need to (but it shouldn't need to anyways, it is about 7 instructions to do - * a 64x64 multiply...). Since we know that this will _always_ emit MULL, we + * a 64x64 multiply...). Since we know that this will _always_ emit `MULL`, we * use that instead of the normal method. * * If you are compiling for platforms like Thumb-1 and don't have a better option, * you may also want to write your own long multiply routine here. * - * XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_mult32to64(xxh_u64 x, xxh_u64 y) - * { - * return (x & 0xFFFFFFFF) * (y & 0xFFFFFFFF); - * } + * @param x, y Numbers to be multiplied + * @return 64-bit product of the low 32 bits of @p x and @p y. */ -#if defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_IX86) -# include <intrin.h> +XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 +XXH_mult32to64(xxh_u64 x, xxh_u64 y) +{ + return (x & 0xFFFFFFFF) * (y & 0xFFFFFFFF); +} +#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_IX86) # define XXH_mult32to64(x, y) __emulu((unsigned)(x), (unsigned)(y)) #else /* @@ -2565,10 +4029,14 @@ XXH_ALIGN(64) static const xxh_u8 XXH3_kSecret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE] = { # define XXH_mult32to64(x, y) ((xxh_u64)(xxh_u32)(x) * (xxh_u64)(xxh_u32)(y)) #endif -/* - * Calculates a 64->128-bit long multiply. +/*! + * @brief Calculates a 64->128-bit long multiply. + * + * Uses `__uint128_t` and `_umul128` if available, otherwise uses a scalar + * version. * - * Uses __uint128_t and _umul128 if available, otherwise uses a scalar version. + * @param lhs , rhs The 64-bit integers to be multiplied + * @return The 128-bit result represented in an @ref XXH128_hash_t. */ static XXH128_hash_t XXH_mult64to128(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs) @@ -2588,7 +4056,7 @@ XXH_mult64to128(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs) * In that case it is best to use the portable one. * https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/issues/211#issuecomment-515575677 */ -#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__wasm__) \ +#if (defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)) && !defined(__wasm__) \ && defined(__SIZEOF_INT128__) \ || (defined(_INTEGRAL_MAX_BITS) && _INTEGRAL_MAX_BITS >= 128) @@ -2605,7 +4073,7 @@ XXH_mult64to128(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs) * * This compiles to single operand MUL on x64. */ -#elif defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_IA64) +#elif (defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_IA64)) && !defined(_M_ARM64EC) #ifndef _MSC_VER # pragma intrinsic(_umul128) @@ -2617,6 +4085,21 @@ XXH_mult64to128(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs) r128.high64 = product_high; return r128; + /* + * MSVC for ARM64's __umulh method. + * + * This compiles to the same MUL + UMULH as GCC/Clang's __uint128_t method. + */ +#elif defined(_M_ARM64) || defined(_M_ARM64EC) + +#ifndef _MSC_VER +# pragma intrinsic(__umulh) +#endif + XXH128_hash_t r128; + r128.low64 = lhs * rhs; + r128.high64 = __umulh(lhs, rhs); + return r128; + #else /* * Portable scalar method. Optimized for 32-bit and 64-bit ALUs. @@ -2679,11 +4162,15 @@ XXH_mult64to128(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs) #endif } -/* - * Does a 64-bit to 128-bit multiply, then XOR folds it. +/*! + * @brief Calculates a 64-bit to 128-bit multiply, then XOR folds it. * * The reason for the separate function is to prevent passing too many structs * around by value. This will hopefully inline the multiply, but we don't force it. + * + * @param lhs , rhs The 64-bit integers to multiply + * @return The low 64 bits of the product XOR'd by the high 64 bits. + * @see XXH_mult64to128() */ static xxh_u64 XXH3_mul128_fold64(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs) @@ -2692,8 +4179,8 @@ XXH3_mul128_fold64(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs) return product.low64 ^ product.high64; } -/* Seems to produce slightly better code on GCC for some reason. */ -XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_xorshift64(xxh_u64 v64, int shift) +/*! Seems to produce slightly better code on GCC for some reason. */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_CONSTF xxh_u64 XXH_xorshift64(xxh_u64 v64, int shift) { XXH_ASSERT(0 <= shift && shift < 64); return v64 ^ (v64 >> shift); @@ -2706,7 +4193,7 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_xorshift64(xxh_u64 v64, int shift) static XXH64_hash_t XXH3_avalanche(xxh_u64 h64) { h64 = XXH_xorshift64(h64, 37); - h64 *= 0x165667919E3779F9ULL; + h64 *= PRIME_MX1; h64 = XXH_xorshift64(h64, 32); return h64; } @@ -2720,9 +4207,9 @@ static XXH64_hash_t XXH3_rrmxmx(xxh_u64 h64, xxh_u64 len) { /* this mix is inspired by Pelle Evensen's rrmxmx */ h64 ^= XXH_rotl64(h64, 49) ^ XXH_rotl64(h64, 24); - h64 *= 0x9FB21C651E98DF25ULL; + h64 *= PRIME_MX2; h64 ^= (h64 >> 35) + len ; - h64 *= 0x9FB21C651E98DF25ULL; + h64 *= PRIME_MX2; return XXH_xorshift64(h64, 28); } @@ -2760,7 +4247,7 @@ static XXH64_hash_t XXH3_rrmxmx(xxh_u64 h64, xxh_u64 len) * * This adds an extra layer of strength for custom secrets. */ -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_len_1to3_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL); @@ -2782,12 +4269,12 @@ XXH3_len_1to3_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_h } } -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_len_4to8_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL); XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL); - XXH_ASSERT(4 <= len && len < 8); + XXH_ASSERT(4 <= len && len <= 8); seed ^= (xxh_u64)XXH_swap32((xxh_u32)seed) << 32; { xxh_u32 const input1 = XXH_readLE32(input); xxh_u32 const input2 = XXH_readLE32(input + len - 4); @@ -2798,12 +4285,12 @@ XXH3_len_4to8_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_h } } -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_len_9to16_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL); XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL); - XXH_ASSERT(8 <= len && len <= 16); + XXH_ASSERT(9 <= len && len <= 16); { xxh_u64 const bitflip1 = (XXH_readLE64(secret+24) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+32)) + seed; xxh_u64 const bitflip2 = (XXH_readLE64(secret+40) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+48)) - seed; xxh_u64 const input_lo = XXH_readLE64(input) ^ bitflip1; @@ -2815,7 +4302,7 @@ XXH3_len_9to16_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_ } } -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_len_0to16_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { XXH_ASSERT(len <= 16); @@ -2873,7 +4360,7 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH3_mix16B(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, * GCC generates much better scalar code than Clang for the rest of XXH3, * which is why finding a more optimal codepath is an interest. */ - __asm__ ("" : "+r" (seed64)); + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(seed64); #endif { xxh_u64 const input_lo = XXH_readLE64(input); xxh_u64 const input_hi = XXH_readLE64(input+8); @@ -2885,7 +4372,7 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH3_mix16B(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, } /* For mid range keys, XXH3 uses a Mum-hash variant. */ -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_len_17to128_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed) @@ -2894,6 +4381,14 @@ XXH3_len_17to128_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH_ASSERT(16 < len && len <= 128); { xxh_u64 acc = len * XXH_PRIME64_1; +#if XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1 + /* Smaller and cleaner, but slightly slower. */ + unsigned int i = (unsigned int)(len - 1) / 32; + do { + acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+16 * i, secret+32*i, seed); + acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+len-16*(i+1), secret+32*i+16, seed); + } while (i-- != 0); +#else if (len > 32) { if (len > 64) { if (len > 96) { @@ -2908,14 +4403,14 @@ XXH3_len_17to128_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, } acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+0, secret+0, seed); acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+len-16, secret+16, seed); - +#endif return XXH3_avalanche(acc); } } #define XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX 240 -XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH_NO_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_len_129to240_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed) @@ -2927,13 +4422,17 @@ XXH3_len_129to240_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, #define XXH3_MIDSIZE_LASTOFFSET 17 { xxh_u64 acc = len * XXH_PRIME64_1; - int const nbRounds = (int)len / 16; - int i; + xxh_u64 acc_end; + unsigned int const nbRounds = (unsigned int)len / 16; + unsigned int i; + XXH_ASSERT(128 < len && len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX); for (i=0; i<8; i++) { acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+(16*i), secret+(16*i), seed); } - acc = XXH3_avalanche(acc); + /* last bytes */ + acc_end = XXH3_mix16B(input + len - 16, secret + XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN - XXH3_MIDSIZE_LASTOFFSET, seed); XXH_ASSERT(nbRounds >= 8); + acc = XXH3_avalanche(acc); #if defined(__clang__) /* Clang */ \ && (defined(__ARM_NEON) || defined(__ARM_NEON__)) /* NEON */ \ && !defined(XXH_ENABLE_AUTOVECTORIZE) /* Define to disable */ @@ -2960,11 +4459,13 @@ XXH3_len_129to240_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, #pragma clang loop vectorize(disable) #endif for (i=8 ; i < nbRounds; i++) { - acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+(16*i), secret+(16*(i-8)) + XXH3_MIDSIZE_STARTOFFSET, seed); + /* + * Prevents clang for unrolling the acc loop and interleaving with this one. + */ + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(acc); + acc_end += XXH3_mix16B(input+(16*i), secret+(16*(i-8)) + XXH3_MIDSIZE_STARTOFFSET, seed); } - /* last bytes */ - acc += XXH3_mix16B(input + len - 16, secret + XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN - XXH3_MIDSIZE_LASTOFFSET, seed); - return XXH3_avalanche(acc); + return XXH3_avalanche(acc + acc_end); } } @@ -2980,10 +4481,51 @@ XXH3_len_129to240_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, # define ACC_NB XXH_ACC_NB #endif +#ifndef XXH_PREFETCH_DIST +# ifdef __clang__ +# define XXH_PREFETCH_DIST 320 +# else +# if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX512) +# define XXH_PREFETCH_DIST 512 +# else +# define XXH_PREFETCH_DIST 384 +# endif +# endif /* __clang__ */ +#endif /* XXH_PREFETCH_DIST */ + +/* + * These macros are to generate an XXH3_accumulate() function. + * The two arguments select the name suffix and target attribute. + * + * The name of this symbol is XXH3_accumulate_<name>() and it calls + * XXH3_accumulate_512_<name>(). + * + * It may be useful to hand implement this function if the compiler fails to + * optimize the inline function. + */ +#define XXH3_ACCUMULATE_TEMPLATE(name) \ +void \ +XXH3_accumulate_##name(xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, \ + const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, \ + const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, \ + size_t nbStripes) \ +{ \ + size_t n; \ + for (n = 0; n < nbStripes; n++ ) { \ + const xxh_u8* const in = input + n*XXH_STRIPE_LEN; \ + XXH_PREFETCH(in + XXH_PREFETCH_DIST); \ + XXH3_accumulate_512_##name( \ + acc, \ + in, \ + secret + n*XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE); \ + } \ +} + + XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH_writeLE64(void* dst, xxh_u64 v64) { if (!XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) v64 = XXH_swap64(v64); - memcpy(dst, &v64, sizeof(v64)); + XXH_memcpy(dst, &v64, sizeof(v64)); } /* Several intrinsic functions below are supposed to accept __int64 as argument, @@ -3000,6 +4542,7 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH_writeLE64(void* dst, xxh_u64 v64) typedef long long xxh_i64; #endif + /* * XXH3_accumulate_512 is the tightest loop for long inputs, and it is the most optimized. * @@ -3023,7 +4566,8 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH_writeLE64(void* dst, xxh_u64 v64) * Both XXH3_64bits and XXH3_128bits use this subroutine. */ -#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX512) || defined(XXH_X86DISPATCH) +#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX512) \ + || (defined(XXH_DISPATCH_AVX512) && XXH_DISPATCH_AVX512 != 0) #ifndef XXH_TARGET_AVX512 # define XXH_TARGET_AVX512 /* disable attribute target */ @@ -3034,7 +4578,7 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_avx512(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { - XXH_ALIGN(64) __m512i* const xacc = (__m512i *) acc; + __m512i* const xacc = (__m512i *) acc; XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 63) == 0); XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(XXH_STRIPE_LEN == sizeof(__m512i)); @@ -3046,7 +4590,7 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_avx512(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, /* data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; */ __m512i const data_key = _mm512_xor_si512 (data_vec, key_vec); /* data_key_lo = data_key >> 32; */ - __m512i const data_key_lo = _mm512_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, (_MM_PERM_ENUM)_MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1)); + __m512i const data_key_lo = _mm512_srli_epi64 (data_key, 32); /* product = (data_key & 0xffffffff) * (data_key_lo & 0xffffffff); */ __m512i const product = _mm512_mul_epu32 (data_key, data_key_lo); /* xacc[0] += swap(data_vec); */ @@ -3056,6 +4600,7 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_avx512(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, *xacc = _mm512_add_epi64(product, sum); } } +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_AVX512 XXH3_ACCUMULATE_TEMPLATE(avx512) /* * XXH3_scrambleAcc: Scrambles the accumulators to improve mixing. @@ -3083,19 +4628,18 @@ XXH3_scrambleAcc_avx512(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 63) == 0); XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(XXH_STRIPE_LEN == sizeof(__m512i)); - { XXH_ALIGN(64) __m512i* const xacc = (__m512i*) acc; + { __m512i* const xacc = (__m512i*) acc; const __m512i prime32 = _mm512_set1_epi32((int)XXH_PRIME32_1); /* xacc[0] ^= (xacc[0] >> 47) */ __m512i const acc_vec = *xacc; __m512i const shifted = _mm512_srli_epi64 (acc_vec, 47); - __m512i const data_vec = _mm512_xor_si512 (acc_vec, shifted); /* xacc[0] ^= secret; */ __m512i const key_vec = _mm512_loadu_si512 (secret); - __m512i const data_key = _mm512_xor_si512 (data_vec, key_vec); + __m512i const data_key = _mm512_ternarylogic_epi32(key_vec, acc_vec, shifted, 0x96 /* key_vec ^ acc_vec ^ shifted */); /* xacc[0] *= XXH_PRIME32_1; */ - __m512i const data_key_hi = _mm512_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, (_MM_PERM_ENUM)_MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1)); + __m512i const data_key_hi = _mm512_srli_epi64 (data_key, 32); __m512i const prod_lo = _mm512_mul_epu32 (data_key, prime32); __m512i const prod_hi = _mm512_mul_epu32 (data_key_hi, prime32); *xacc = _mm512_add_epi64(prod_lo, _mm512_slli_epi64(prod_hi, 32)); @@ -3110,26 +4654,23 @@ XXH3_initCustomSecret_avx512(void* XXH_RESTRICT customSecret, xxh_u64 seed64) XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)customSecret & 63) == 0); (void)(&XXH_writeLE64); { int const nbRounds = XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE / sizeof(__m512i); - __m512i const seed = _mm512_mask_set1_epi64(_mm512_set1_epi64((xxh_i64)seed64), 0xAA, -(xxh_i64)seed64); + __m512i const seed_pos = _mm512_set1_epi64((xxh_i64)seed64); + __m512i const seed = _mm512_mask_sub_epi64(seed_pos, 0xAA, _mm512_set1_epi8(0), seed_pos); - XXH_ALIGN(64) const __m512i* const src = (const __m512i*) XXH3_kSecret; - XXH_ALIGN(64) __m512i* const dest = ( __m512i*) customSecret; + const __m512i* const src = (const __m512i*) ((const void*) XXH3_kSecret); + __m512i* const dest = ( __m512i*) customSecret; int i; + XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)src & 63) == 0); /* control alignment */ + XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)dest & 63) == 0); for (i=0; i < nbRounds; ++i) { - /* GCC has a bug, _mm512_stream_load_si512 accepts 'void*', not 'void const*', - * this will warn "discards ‘const’ qualifier". */ - union { - XXH_ALIGN(64) const __m512i* cp; - XXH_ALIGN(64) void* p; - } remote_const_void; - remote_const_void.cp = src + i; - dest[i] = _mm512_add_epi64(_mm512_stream_load_si512(remote_const_void.p), seed); + dest[i] = _mm512_add_epi64(_mm512_load_si512(src + i), seed); } } } #endif -#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2) || defined(XXH_X86DISPATCH) +#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2) \ + || (defined(XXH_DISPATCH_AVX2) && XXH_DISPATCH_AVX2 != 0) #ifndef XXH_TARGET_AVX2 # define XXH_TARGET_AVX2 /* disable attribute target */ @@ -3141,7 +4682,7 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_avx2( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 31) == 0); - { XXH_ALIGN(32) __m256i* const xacc = (__m256i *) acc; + { __m256i* const xacc = (__m256i *) acc; /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because * _mm256_loadu_si256 requires a const __m256i * pointer for some reason. */ const __m256i* const xinput = (const __m256i *) input; @@ -3158,7 +4699,7 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_avx2( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, /* data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; */ __m256i const data_key = _mm256_xor_si256 (data_vec, key_vec); /* data_key_lo = data_key >> 32; */ - __m256i const data_key_lo = _mm256_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, _MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1)); + __m256i const data_key_lo = _mm256_srli_epi64 (data_key, 32); /* product = (data_key & 0xffffffff) * (data_key_lo & 0xffffffff); */ __m256i const product = _mm256_mul_epu32 (data_key, data_key_lo); /* xacc[i] += swap(data_vec); */ @@ -3168,12 +4709,13 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_avx2( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, xacc[i] = _mm256_add_epi64(product, sum); } } } +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_AVX2 XXH3_ACCUMULATE_TEMPLATE(avx2) XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_AVX2 void XXH3_scrambleAcc_avx2(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 31) == 0); - { XXH_ALIGN(32) __m256i* const xacc = (__m256i*) acc; + { __m256i* const xacc = (__m256i*) acc; /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because * _mm256_loadu_si256 requires a const __m256i * pointer for some reason. */ const __m256i* const xsecret = (const __m256i *) secret; @@ -3190,7 +4732,7 @@ XXH3_scrambleAcc_avx2(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) __m256i const data_key = _mm256_xor_si256 (data_vec, key_vec); /* xacc[i] *= XXH_PRIME32_1; */ - __m256i const data_key_hi = _mm256_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, _MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1)); + __m256i const data_key_hi = _mm256_srli_epi64 (data_key, 32); __m256i const prod_lo = _mm256_mul_epu32 (data_key, prime32); __m256i const prod_hi = _mm256_mul_epu32 (data_key_hi, prime32); xacc[i] = _mm256_add_epi64(prod_lo, _mm256_slli_epi64(prod_hi, 32)); @@ -3205,36 +4747,35 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_AVX2 void XXH3_initCustomSecret_avx2(void* XXH_RESTR XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(XXH_SEC_ALIGN <= 64); (void)(&XXH_writeLE64); XXH_PREFETCH(customSecret); - { __m256i const seed = _mm256_set_epi64x(-(xxh_i64)seed64, (xxh_i64)seed64, -(xxh_i64)seed64, (xxh_i64)seed64); + { __m256i const seed = _mm256_set_epi64x((xxh_i64)(0U - seed64), (xxh_i64)seed64, (xxh_i64)(0U - seed64), (xxh_i64)seed64); - XXH_ALIGN(64) const __m256i* const src = (const __m256i*) XXH3_kSecret; - XXH_ALIGN(64) __m256i* dest = ( __m256i*) customSecret; + const __m256i* const src = (const __m256i*) ((const void*) XXH3_kSecret); + __m256i* dest = ( __m256i*) customSecret; # if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__) /* * On GCC & Clang, marking 'dest' as modified will cause the compiler: * - do not extract the secret from sse registers in the internal loop * - use less common registers, and avoid pushing these reg into stack - * The asm hack causes Clang to assume that XXH3_kSecretPtr aliases with - * customSecret, and on aarch64, this prevented LDP from merging two - * loads together for free. Putting the loads together before the stores - * properly generates LDP. */ - __asm__("" : "+r" (dest)); + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(dest); # endif + XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)src & 31) == 0); /* control alignment */ + XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)dest & 31) == 0); /* GCC -O2 need unroll loop manually */ - dest[0] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_stream_load_si256(src+0), seed); - dest[1] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_stream_load_si256(src+1), seed); - dest[2] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_stream_load_si256(src+2), seed); - dest[3] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_stream_load_si256(src+3), seed); - dest[4] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_stream_load_si256(src+4), seed); - dest[5] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_stream_load_si256(src+5), seed); + dest[0] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_load_si256(src+0), seed); + dest[1] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_load_si256(src+1), seed); + dest[2] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_load_si256(src+2), seed); + dest[3] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_load_si256(src+3), seed); + dest[4] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_load_si256(src+4), seed); + dest[5] = _mm256_add_epi64(_mm256_load_si256(src+5), seed); } } #endif +/* x86dispatch always generates SSE2 */ #if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SSE2) || defined(XXH_X86DISPATCH) #ifndef XXH_TARGET_SSE2 @@ -3248,7 +4789,7 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_sse2( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, { /* SSE2 is just a half-scale version of the AVX2 version. */ XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0); - { XXH_ALIGN(16) __m128i* const xacc = (__m128i *) acc; + { __m128i* const xacc = (__m128i *) acc; /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because * _mm_loadu_si128 requires a const __m128i * pointer for some reason. */ const __m128i* const xinput = (const __m128i *) input; @@ -3275,12 +4816,13 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_sse2( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, xacc[i] = _mm_add_epi64(product, sum); } } } +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_SSE2 XXH3_ACCUMULATE_TEMPLATE(sse2) XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_SSE2 void XXH3_scrambleAcc_sse2(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0); - { XXH_ALIGN(16) __m128i* const xacc = (__m128i*) acc; + { __m128i* const xacc = (__m128i*) acc; /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because * _mm_loadu_si128 requires a const __m128i * pointer for some reason. */ const __m128i* const xsecret = (const __m128i *) secret; @@ -3312,27 +4854,29 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_SSE2 void XXH3_initCustomSecret_sse2(void* XXH_RESTR { int const nbRounds = XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE / sizeof(__m128i); # if defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_IX86) && _MSC_VER < 1900 - // MSVC 32bit mode does not support _mm_set_epi64x before 2015 - XXH_ALIGN(16) const xxh_i64 seed64x2[2] = { (xxh_i64)seed64, -(xxh_i64)seed64 }; + /* MSVC 32bit mode does not support _mm_set_epi64x before 2015 */ + XXH_ALIGN(16) const xxh_i64 seed64x2[2] = { (xxh_i64)seed64, (xxh_i64)(0U - seed64) }; __m128i const seed = _mm_load_si128((__m128i const*)seed64x2); # else - __m128i const seed = _mm_set_epi64x(-(xxh_i64)seed64, (xxh_i64)seed64); + __m128i const seed = _mm_set_epi64x((xxh_i64)(0U - seed64), (xxh_i64)seed64); # endif int i; - XXH_ALIGN(64) const float* const src = (float const*) XXH3_kSecret; - XXH_ALIGN(XXH_SEC_ALIGN) __m128i* dest = (__m128i*) customSecret; + const void* const src16 = XXH3_kSecret; + __m128i* dst16 = (__m128i*) customSecret; # if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__) /* * On GCC & Clang, marking 'dest' as modified will cause the compiler: * - do not extract the secret from sse registers in the internal loop * - use less common registers, and avoid pushing these reg into stack */ - __asm__("" : "+r" (dest)); + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(dst16); # endif + XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)src16 & 15) == 0); /* control alignment */ + XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)dst16 & 15) == 0); for (i=0; i < nbRounds; ++i) { - dest[i] = _mm_add_epi64(_mm_castps_si128(_mm_load_ps(src+i*4)), seed); + dst16[i] = _mm_add_epi64(_mm_load_si128((const __m128i *)src16+i), seed); } } } @@ -3340,96 +4884,222 @@ XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_TARGET_SSE2 void XXH3_initCustomSecret_sse2(void* XXH_RESTR #if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON) +/* forward declarations for the scalar routines */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE void +XXH3_scalarRound(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, void const* XXH_RESTRICT input, + void const* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t lane); + +XXH_FORCE_INLINE void +XXH3_scalarScrambleRound(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, + void const* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t lane); + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief The bulk processing loop for NEON and WASM SIMD128. + * + * The NEON code path is actually partially scalar when running on AArch64. This + * is to optimize the pipelining and can have up to 15% speedup depending on the + * CPU, and it also mitigates some GCC codegen issues. + * + * @see XXH3_NEON_LANES for configuring this and details about this optimization. + * + * NEON's 32-bit to 64-bit long multiply takes a half vector of 32-bit + * integers instead of the other platforms which mask full 64-bit vectors, + * so the setup is more complicated than just shifting right. + * + * Additionally, there is an optimization for 4 lanes at once noted below. + * + * Since, as stated, the most optimal amount of lanes for Cortexes is 6, + * there needs to be *three* versions of the accumulate operation used + * for the remaining 2 lanes. + * + * WASM's SIMD128 uses SIMDe's arm_neon.h polyfill because the intrinsics overlap + * nearly perfectly. + */ + XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH3_accumulate_512_neon( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0); - { - XXH_ALIGN(16) uint64x2_t* const xacc = (uint64x2_t *) acc; + XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(XXH3_NEON_LANES > 0 && XXH3_NEON_LANES <= XXH_ACC_NB && XXH3_NEON_LANES % 2 == 0); + { /* GCC for darwin arm64 does not like aliasing here */ + xxh_aliasing_uint64x2_t* const xacc = (xxh_aliasing_uint64x2_t*) acc; /* We don't use a uint32x4_t pointer because it causes bus errors on ARMv7. */ - uint8_t const* const xinput = (const uint8_t *) input; - uint8_t const* const xsecret = (const uint8_t *) secret; + uint8_t const* xinput = (const uint8_t *) input; + uint8_t const* xsecret = (const uint8_t *) secret; size_t i; - for (i=0; i < XXH_STRIPE_LEN / sizeof(uint64x2_t); i++) { +#ifdef __wasm_simd128__ + /* + * On WASM SIMD128, Clang emits direct address loads when XXH3_kSecret + * is constant propagated, which results in it converting it to this + * inside the loop: + * + * a = v128.load(XXH3_kSecret + 0 + $secret_offset, offset = 0) + * b = v128.load(XXH3_kSecret + 16 + $secret_offset, offset = 0) + * ... + * + * This requires a full 32-bit address immediate (and therefore a 6 byte + * instruction) as well as an add for each offset. + * + * Putting an asm guard prevents it from folding (at the cost of losing + * the alignment hint), and uses the free offset in `v128.load` instead + * of adding secret_offset each time which overall reduces code size by + * about a kilobyte and improves performance. + */ + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(xsecret); +#endif + /* Scalar lanes use the normal scalarRound routine */ + for (i = XXH3_NEON_LANES; i < XXH_ACC_NB; i++) { + XXH3_scalarRound(acc, input, secret, i); + } + i = 0; + /* 4 NEON lanes at a time. */ + for (; i+1 < XXH3_NEON_LANES / 2; i+=2) { /* data_vec = xinput[i]; */ - uint8x16_t data_vec = vld1q_u8(xinput + (i * 16)); + uint64x2_t data_vec_1 = XXH_vld1q_u64(xinput + (i * 16)); + uint64x2_t data_vec_2 = XXH_vld1q_u64(xinput + ((i+1) * 16)); /* key_vec = xsecret[i]; */ - uint8x16_t key_vec = vld1q_u8(xsecret + (i * 16)); - uint64x2_t data_key; - uint32x2_t data_key_lo, data_key_hi; - /* xacc[i] += swap(data_vec); */ - uint64x2_t const data64 = vreinterpretq_u64_u8(data_vec); - uint64x2_t const swapped = vextq_u64(data64, data64, 1); - xacc[i] = vaddq_u64 (xacc[i], swapped); + uint64x2_t key_vec_1 = XXH_vld1q_u64(xsecret + (i * 16)); + uint64x2_t key_vec_2 = XXH_vld1q_u64(xsecret + ((i+1) * 16)); + /* data_swap = swap(data_vec) */ + uint64x2_t data_swap_1 = vextq_u64(data_vec_1, data_vec_1, 1); + uint64x2_t data_swap_2 = vextq_u64(data_vec_2, data_vec_2, 1); /* data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; */ - data_key = vreinterpretq_u64_u8(veorq_u8(data_vec, key_vec)); - /* data_key_lo = (uint32x2_t) (data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF); - * data_key_hi = (uint32x2_t) (data_key >> 32); - * data_key = UNDEFINED; */ - XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(data_key, data_key_lo, data_key_hi); - /* xacc[i] += (uint64x2_t) data_key_lo * (uint64x2_t) data_key_hi; */ - xacc[i] = vmlal_u32 (xacc[i], data_key_lo, data_key_hi); + uint64x2_t data_key_1 = veorq_u64(data_vec_1, key_vec_1); + uint64x2_t data_key_2 = veorq_u64(data_vec_2, key_vec_2); + /* + * If we reinterpret the 64x2 vectors as 32x4 vectors, we can use a + * de-interleave operation for 4 lanes in 1 step with `vuzpq_u32` to + * get one vector with the low 32 bits of each lane, and one vector + * with the high 32 bits of each lane. + * + * The intrinsic returns a double vector because the original ARMv7-a + * instruction modified both arguments in place. AArch64 and SIMD128 emit + * two instructions from this intrinsic. + * + * [ dk11L | dk11H | dk12L | dk12H ] -> [ dk11L | dk12L | dk21L | dk22L ] + * [ dk21L | dk21H | dk22L | dk22H ] -> [ dk11H | dk12H | dk21H | dk22H ] + */ + uint32x4x2_t unzipped = vuzpq_u32( + vreinterpretq_u32_u64(data_key_1), + vreinterpretq_u32_u64(data_key_2) + ); + /* data_key_lo = data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF */ + uint32x4_t data_key_lo = unzipped.val[0]; + /* data_key_hi = data_key >> 32 */ + uint32x4_t data_key_hi = unzipped.val[1]; + /* + * Then, we can split the vectors horizontally and multiply which, as for most + * widening intrinsics, have a variant that works on both high half vectors + * for free on AArch64. A similar instruction is available on SIMD128. + * + * sum = data_swap + (u64x2) data_key_lo * (u64x2) data_key_hi + */ + uint64x2_t sum_1 = XXH_vmlal_low_u32(data_swap_1, data_key_lo, data_key_hi); + uint64x2_t sum_2 = XXH_vmlal_high_u32(data_swap_2, data_key_lo, data_key_hi); + /* + * Clang reorders + * a += b * c; // umlal swap.2d, dkl.2s, dkh.2s + * c += a; // add acc.2d, acc.2d, swap.2d + * to + * c += a; // add acc.2d, acc.2d, swap.2d + * c += b * c; // umlal acc.2d, dkl.2s, dkh.2s + * + * While it would make sense in theory since the addition is faster, + * for reasons likely related to umlal being limited to certain NEON + * pipelines, this is worse. A compiler guard fixes this. + */ + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD_CLANG_NEON(sum_1); + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD_CLANG_NEON(sum_2); + /* xacc[i] = acc_vec + sum; */ + xacc[i] = vaddq_u64(xacc[i], sum_1); + xacc[i+1] = vaddq_u64(xacc[i+1], sum_2); + } + /* Operate on the remaining NEON lanes 2 at a time. */ + for (; i < XXH3_NEON_LANES / 2; i++) { + /* data_vec = xinput[i]; */ + uint64x2_t data_vec = XXH_vld1q_u64(xinput + (i * 16)); + /* key_vec = xsecret[i]; */ + uint64x2_t key_vec = XXH_vld1q_u64(xsecret + (i * 16)); + /* acc_vec_2 = swap(data_vec) */ + uint64x2_t data_swap = vextq_u64(data_vec, data_vec, 1); + /* data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; */ + uint64x2_t data_key = veorq_u64(data_vec, key_vec); + /* For two lanes, just use VMOVN and VSHRN. */ + /* data_key_lo = data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF; */ + uint32x2_t data_key_lo = vmovn_u64(data_key); + /* data_key_hi = data_key >> 32; */ + uint32x2_t data_key_hi = vshrn_n_u64(data_key, 32); + /* sum = data_swap + (u64x2) data_key_lo * (u64x2) data_key_hi; */ + uint64x2_t sum = vmlal_u32(data_swap, data_key_lo, data_key_hi); + /* Same Clang workaround as before */ + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD_CLANG_NEON(sum); + /* xacc[i] = acc_vec + sum; */ + xacc[i] = vaddq_u64 (xacc[i], sum); } } } +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH3_ACCUMULATE_TEMPLATE(neon) XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH3_scrambleAcc_neon(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0); - { uint64x2_t* xacc = (uint64x2_t*) acc; + { xxh_aliasing_uint64x2_t* xacc = (xxh_aliasing_uint64x2_t*) acc; uint8_t const* xsecret = (uint8_t const*) secret; - uint32x2_t prime = vdup_n_u32 (XXH_PRIME32_1); size_t i; - for (i=0; i < XXH_STRIPE_LEN/sizeof(uint64x2_t); i++) { + /* WASM uses operator overloads and doesn't need these. */ +#ifndef __wasm_simd128__ + /* { prime32_1, prime32_1 } */ + uint32x2_t const kPrimeLo = vdup_n_u32(XXH_PRIME32_1); + /* { 0, prime32_1, 0, prime32_1 } */ + uint32x4_t const kPrimeHi = vreinterpretq_u32_u64(vdupq_n_u64((xxh_u64)XXH_PRIME32_1 << 32)); +#endif + + /* AArch64 uses both scalar and neon at the same time */ + for (i = XXH3_NEON_LANES; i < XXH_ACC_NB; i++) { + XXH3_scalarScrambleRound(acc, secret, i); + } + for (i=0; i < XXH3_NEON_LANES / 2; i++) { /* xacc[i] ^= (xacc[i] >> 47); */ uint64x2_t acc_vec = xacc[i]; - uint64x2_t shifted = vshrq_n_u64 (acc_vec, 47); - uint64x2_t data_vec = veorq_u64 (acc_vec, shifted); + uint64x2_t shifted = vshrq_n_u64(acc_vec, 47); + uint64x2_t data_vec = veorq_u64(acc_vec, shifted); /* xacc[i] ^= xsecret[i]; */ - uint8x16_t key_vec = vld1q_u8(xsecret + (i * 16)); - uint64x2_t data_key = veorq_u64(data_vec, vreinterpretq_u64_u8(key_vec)); - + uint64x2_t key_vec = XXH_vld1q_u64(xsecret + (i * 16)); + uint64x2_t data_key = veorq_u64(data_vec, key_vec); /* xacc[i] *= XXH_PRIME32_1 */ - uint32x2_t data_key_lo, data_key_hi; - /* data_key_lo = (uint32x2_t) (xacc[i] & 0xFFFFFFFF); - * data_key_hi = (uint32x2_t) (xacc[i] >> 32); - * xacc[i] = UNDEFINED; */ - XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(data_key, data_key_lo, data_key_hi); - { /* - * prod_hi = (data_key >> 32) * XXH_PRIME32_1; - * - * Avoid vmul_u32 + vshll_n_u32 since Clang 6 and 7 will - * incorrectly "optimize" this: - * tmp = vmul_u32(vmovn_u64(a), vmovn_u64(b)); - * shifted = vshll_n_u32(tmp, 32); - * to this: - * tmp = "vmulq_u64"(a, b); // no such thing! - * shifted = vshlq_n_u64(tmp, 32); - * - * However, unlike SSE, Clang lacks a 64-bit multiply routine - * for NEON, and it scalarizes two 64-bit multiplies instead. - * - * vmull_u32 has the same timing as vmul_u32, and it avoids - * this bug completely. - * See https://bugs.llvm.org/show_bug.cgi?id=39967 - */ - uint64x2_t prod_hi = vmull_u32 (data_key_hi, prime); - /* xacc[i] = prod_hi << 32; */ - xacc[i] = vshlq_n_u64(prod_hi, 32); - /* xacc[i] += (prod_hi & 0xFFFFFFFF) * XXH_PRIME32_1; */ - xacc[i] = vmlal_u32(xacc[i], data_key_lo, prime); - } - } } +#ifdef __wasm_simd128__ + /* SIMD128 has multiply by u64x2, use it instead of expanding and scalarizing */ + xacc[i] = data_key * XXH_PRIME32_1; +#else + /* + * Expanded version with portable NEON intrinsics + * + * lo(x) * lo(y) + (hi(x) * lo(y) << 32) + * + * prod_hi = hi(data_key) * lo(prime) << 32 + * + * Since we only need 32 bits of this multiply a trick can be used, reinterpreting the vector + * as a uint32x4_t and multiplying by { 0, prime, 0, prime } to cancel out the unwanted bits + * and avoid the shift. + */ + uint32x4_t prod_hi = vmulq_u32 (vreinterpretq_u32_u64(data_key), kPrimeHi); + /* Extract low bits for vmlal_u32 */ + uint32x2_t data_key_lo = vmovn_u64(data_key); + /* xacc[i] = prod_hi + lo(data_key) * XXH_PRIME32_1; */ + xacc[i] = vmlal_u32(vreinterpretq_u64_u32(prod_hi), data_key_lo, kPrimeLo); +#endif + } + } } - #endif #if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX) @@ -3439,39 +5109,44 @@ XXH3_accumulate_512_vsx( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { - xxh_u64x2* const xacc = (xxh_u64x2*) acc; /* presumed aligned */ - xxh_u64x2 const* const xinput = (xxh_u64x2 const*) input; /* no alignment restriction */ - xxh_u64x2 const* const xsecret = (xxh_u64x2 const*) secret; /* no alignment restriction */ + /* presumed aligned */ + xxh_aliasing_u64x2* const xacc = (xxh_aliasing_u64x2*) acc; + xxh_u8 const* const xinput = (xxh_u8 const*) input; /* no alignment restriction */ + xxh_u8 const* const xsecret = (xxh_u8 const*) secret; /* no alignment restriction */ xxh_u64x2 const v32 = { 32, 32 }; size_t i; for (i = 0; i < XXH_STRIPE_LEN / sizeof(xxh_u64x2); i++) { /* data_vec = xinput[i]; */ - xxh_u64x2 const data_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xinput + i); + xxh_u64x2 const data_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xinput + 16*i); /* key_vec = xsecret[i]; */ - xxh_u64x2 const key_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xsecret + i); + xxh_u64x2 const key_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xsecret + 16*i); xxh_u64x2 const data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; /* shuffled = (data_key << 32) | (data_key >> 32); */ xxh_u32x4 const shuffled = (xxh_u32x4)vec_rl(data_key, v32); /* product = ((xxh_u64x2)data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF) * ((xxh_u64x2)shuffled & 0xFFFFFFFF); */ xxh_u64x2 const product = XXH_vec_mulo((xxh_u32x4)data_key, shuffled); - xacc[i] += product; + /* acc_vec = xacc[i]; */ + xxh_u64x2 acc_vec = xacc[i]; + acc_vec += product; /* swap high and low halves */ #ifdef __s390x__ - xacc[i] += vec_permi(data_vec, data_vec, 2); + acc_vec += vec_permi(data_vec, data_vec, 2); #else - xacc[i] += vec_xxpermdi(data_vec, data_vec, 2); + acc_vec += vec_xxpermdi(data_vec, data_vec, 2); #endif + xacc[i] = acc_vec; } } +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH3_ACCUMULATE_TEMPLATE(vsx) XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH3_scrambleAcc_vsx(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0); - { xxh_u64x2* const xacc = (xxh_u64x2*) acc; - const xxh_u64x2* const xsecret = (const xxh_u64x2*) secret; + { xxh_aliasing_u64x2* const xacc = (xxh_aliasing_u64x2*) acc; + const xxh_u8* const xsecret = (const xxh_u8*) secret; /* constants */ xxh_u64x2 const v32 = { 32, 32 }; xxh_u64x2 const v47 = { 47, 47 }; @@ -3483,7 +5158,7 @@ XXH3_scrambleAcc_vsx(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) xxh_u64x2 const data_vec = acc_vec ^ (acc_vec >> v47); /* xacc[i] ^= xsecret[i]; */ - xxh_u64x2 const key_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xsecret + i); + xxh_u64x2 const key_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xsecret + 16*i); xxh_u64x2 const data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; /* xacc[i] *= XXH_PRIME32_1 */ @@ -3497,40 +5172,233 @@ XXH3_scrambleAcc_vsx(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) #endif +#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SVE) + +XXH_FORCE_INLINE void +XXH3_accumulate_512_sve( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, + const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, + const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) +{ + uint64_t *xacc = (uint64_t *)acc; + const uint64_t *xinput = (const uint64_t *)(const void *)input; + const uint64_t *xsecret = (const uint64_t *)(const void *)secret; + svuint64_t kSwap = sveor_n_u64_z(svptrue_b64(), svindex_u64(0, 1), 1); + uint64_t element_count = svcntd(); + if (element_count >= 8) { + svbool_t mask = svptrue_pat_b64(SV_VL8); + svuint64_t vacc = svld1_u64(mask, xacc); + ACCRND(vacc, 0); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc, vacc); + } else if (element_count == 2) { /* sve128 */ + svbool_t mask = svptrue_pat_b64(SV_VL2); + svuint64_t acc0 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 0); + svuint64_t acc1 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 2); + svuint64_t acc2 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 4); + svuint64_t acc3 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 6); + ACCRND(acc0, 0); + ACCRND(acc1, 2); + ACCRND(acc2, 4); + ACCRND(acc3, 6); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 0, acc0); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 2, acc1); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 4, acc2); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 6, acc3); + } else { + svbool_t mask = svptrue_pat_b64(SV_VL4); + svuint64_t acc0 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 0); + svuint64_t acc1 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 4); + ACCRND(acc0, 0); + ACCRND(acc1, 4); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 0, acc0); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 4, acc1); + } +} + +XXH_FORCE_INLINE void +XXH3_accumulate_sve(xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, + const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, + const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, + size_t nbStripes) +{ + if (nbStripes != 0) { + uint64_t *xacc = (uint64_t *)acc; + const uint64_t *xinput = (const uint64_t *)(const void *)input; + const uint64_t *xsecret = (const uint64_t *)(const void *)secret; + svuint64_t kSwap = sveor_n_u64_z(svptrue_b64(), svindex_u64(0, 1), 1); + uint64_t element_count = svcntd(); + if (element_count >= 8) { + svbool_t mask = svptrue_pat_b64(SV_VL8); + svuint64_t vacc = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 0); + do { + /* svprfd(svbool_t, void *, enum svfprop); */ + svprfd(mask, xinput + 128, SV_PLDL1STRM); + ACCRND(vacc, 0); + xinput += 8; + xsecret += 1; + nbStripes--; + } while (nbStripes != 0); + + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 0, vacc); + } else if (element_count == 2) { /* sve128 */ + svbool_t mask = svptrue_pat_b64(SV_VL2); + svuint64_t acc0 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 0); + svuint64_t acc1 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 2); + svuint64_t acc2 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 4); + svuint64_t acc3 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 6); + do { + svprfd(mask, xinput + 128, SV_PLDL1STRM); + ACCRND(acc0, 0); + ACCRND(acc1, 2); + ACCRND(acc2, 4); + ACCRND(acc3, 6); + xinput += 8; + xsecret += 1; + nbStripes--; + } while (nbStripes != 0); + + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 0, acc0); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 2, acc1); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 4, acc2); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 6, acc3); + } else { + svbool_t mask = svptrue_pat_b64(SV_VL4); + svuint64_t acc0 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 0); + svuint64_t acc1 = svld1_u64(mask, xacc + 4); + do { + svprfd(mask, xinput + 128, SV_PLDL1STRM); + ACCRND(acc0, 0); + ACCRND(acc1, 4); + xinput += 8; + xsecret += 1; + nbStripes--; + } while (nbStripes != 0); + + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 0, acc0); + svst1_u64(mask, xacc + 4, acc1); + } + } +} + +#endif + /* scalar variants - universal */ +#if defined(__aarch64__) && (defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)) +/* + * In XXH3_scalarRound(), GCC and Clang have a similar codegen issue, where they + * emit an excess mask and a full 64-bit multiply-add (MADD X-form). + * + * While this might not seem like much, as AArch64 is a 64-bit architecture, only + * big Cortex designs have a full 64-bit multiplier. + * + * On the little cores, the smaller 32-bit multiplier is used, and full 64-bit + * multiplies expand to 2-3 multiplies in microcode. This has a major penalty + * of up to 4 latency cycles and 2 stall cycles in the multiply pipeline. + * + * Thankfully, AArch64 still provides the 32-bit long multiply-add (UMADDL) which does + * not have this penalty and does the mask automatically. + */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 +XXH_mult32to64_add64(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs, xxh_u64 acc) +{ + xxh_u64 ret; + /* note: %x = 64-bit register, %w = 32-bit register */ + __asm__("umaddl %x0, %w1, %w2, %x3" : "=r" (ret) : "r" (lhs), "r" (rhs), "r" (acc)); + return ret; +} +#else +XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 +XXH_mult32to64_add64(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs, xxh_u64 acc) +{ + return XXH_mult32to64((xxh_u32)lhs, (xxh_u32)rhs) + acc; +} +#endif + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Scalar round for @ref XXH3_accumulate_512_scalar(). + * + * This is extracted to its own function because the NEON path uses a combination + * of NEON and scalar. + */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE void +XXH3_scalarRound(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, + void const* XXH_RESTRICT input, + void const* XXH_RESTRICT secret, + size_t lane) +{ + xxh_u64* xacc = (xxh_u64*) acc; + xxh_u8 const* xinput = (xxh_u8 const*) input; + xxh_u8 const* xsecret = (xxh_u8 const*) secret; + XXH_ASSERT(lane < XXH_ACC_NB); + XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)acc & (XXH_ACC_ALIGN-1)) == 0); + { + xxh_u64 const data_val = XXH_readLE64(xinput + lane * 8); + xxh_u64 const data_key = data_val ^ XXH_readLE64(xsecret + lane * 8); + xacc[lane ^ 1] += data_val; /* swap adjacent lanes */ + xacc[lane] = XXH_mult32to64_add64(data_key /* & 0xFFFFFFFF */, data_key >> 32, xacc[lane]); + } +} + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Processes a 64 byte block of data using the scalar path. + */ XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH3_accumulate_512_scalar(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) { - XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64* const xacc = (xxh_u64*) acc; /* presumed aligned */ - const xxh_u8* const xinput = (const xxh_u8*) input; /* no alignment restriction */ - const xxh_u8* const xsecret = (const xxh_u8*) secret; /* no alignment restriction */ size_t i; - XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)acc & (XXH_ACC_ALIGN-1)) == 0); + /* ARM GCC refuses to unroll this loop, resulting in a 24% slowdown on ARMv6. */ +#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) \ + && (defined(__arm__) || defined(__thumb2__)) \ + && defined(__ARM_FEATURE_UNALIGNED) /* no unaligned access just wastes bytes */ \ + && XXH_SIZE_OPT <= 0 +# pragma GCC unroll 8 +#endif for (i=0; i < XXH_ACC_NB; i++) { - xxh_u64 const data_val = XXH_readLE64(xinput + 8*i); - xxh_u64 const data_key = data_val ^ XXH_readLE64(xsecret + i*8); - xacc[i ^ 1] += data_val; /* swap adjacent lanes */ - xacc[i] += XXH_mult32to64(data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF, data_key >> 32); + XXH3_scalarRound(acc, input, secret, i); } } +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH3_ACCUMULATE_TEMPLATE(scalar) +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Scalar scramble step for @ref XXH3_scrambleAcc_scalar(). + * + * This is extracted to its own function because the NEON path uses a combination + * of NEON and scalar. + */ XXH_FORCE_INLINE void -XXH3_scrambleAcc_scalar(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) +XXH3_scalarScrambleRound(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, + void const* XXH_RESTRICT secret, + size_t lane) { - XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64* const xacc = (xxh_u64*) acc; /* presumed aligned */ + xxh_u64* const xacc = (xxh_u64*) acc; /* presumed aligned */ const xxh_u8* const xsecret = (const xxh_u8*) secret; /* no alignment restriction */ - size_t i; XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & (XXH_ACC_ALIGN-1)) == 0); - for (i=0; i < XXH_ACC_NB; i++) { - xxh_u64 const key64 = XXH_readLE64(xsecret + 8*i); - xxh_u64 acc64 = xacc[i]; + XXH_ASSERT(lane < XXH_ACC_NB); + { + xxh_u64 const key64 = XXH_readLE64(xsecret + lane * 8); + xxh_u64 acc64 = xacc[lane]; acc64 = XXH_xorshift64(acc64, 47); acc64 ^= key64; acc64 *= XXH_PRIME32_1; - xacc[i] = acc64; + xacc[lane] = acc64; + } +} + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Scrambles the accumulators after a large chunk has been read + */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE void +XXH3_scrambleAcc_scalar(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret) +{ + size_t i; + for (i=0; i < XXH_ACC_NB; i++) { + XXH3_scalarScrambleRound(acc, secret, i); } } @@ -3545,15 +5413,16 @@ XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar(void* XXH_RESTRICT customSecret, xxh_u64 seed64) const xxh_u8* kSecretPtr = XXH3_kSecret; XXH_STATIC_ASSERT((XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE & 15) == 0); -#if defined(__clang__) && defined(__aarch64__) +#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__aarch64__) /* * UGLY HACK: - * Clang generates a bunch of MOV/MOVK pairs for aarch64, and they are + * GCC and Clang generate a bunch of MOV/MOVK pairs for aarch64, and they are * placed sequentially, in order, at the top of the unrolled loop. * * While MOVK is great for generating constants (2 cycles for a 64-bit - * constant compared to 4 cycles for LDR), long MOVK chains stall the - * integer pipelines: + * constant compared to 4 cycles for LDR), it fights for bandwidth with + * the arithmetic instructions. + * * I L S * MOVK * MOVK @@ -3562,7 +5431,7 @@ XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar(void* XXH_RESTRICT customSecret, xxh_u64 seed64) * ADD * SUB STR * STR - * By forcing loads from memory (as the asm line causes Clang to assume + * By forcing loads from memory (as the asm line causes the compiler to assume * that XXH3_kSecretPtr has been changed), the pipelines are used more * efficiently: * I L S @@ -3570,23 +5439,20 @@ XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar(void* XXH_RESTRICT customSecret, xxh_u64 seed64) * ADD LDR * SUB STR * STR + * + * See XXH3_NEON_LANES for details on the pipsline. + * * XXH3_64bits_withSeed, len == 256, Snapdragon 835 * without hack: 2654.4 MB/s * with hack: 3202.9 MB/s */ - __asm__("" : "+r" (kSecretPtr)); + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(kSecretPtr); #endif - /* - * Note: in debug mode, this overrides the asm optimization - * and Clang will emit MOVK chains again. - */ - XXH_ASSERT(kSecretPtr == XXH3_kSecret); - { int const nbRounds = XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE / 16; int i; for (i=0; i < nbRounds; i++) { /* - * The asm hack causes Clang to assume that kSecretPtr aliases with + * The asm hack causes the compiler to assume that kSecretPtr aliases with * customSecret, and on aarch64, this prevented LDP from merging two * loads together for free. Putting the loads together before the stores * properly generates LDP. @@ -3599,7 +5465,7 @@ XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar(void* XXH_RESTRICT customSecret, xxh_u64 seed64) } -typedef void (*XXH3_f_accumulate_512)(void* XXH_RESTRICT, const void*, const void*); +typedef void (*XXH3_f_accumulate)(xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT, size_t); typedef void (*XXH3_f_scrambleAcc)(void* XXH_RESTRICT, const void*); typedef void (*XXH3_f_initCustomSecret)(void* XXH_RESTRICT, xxh_u64); @@ -3607,82 +5473,63 @@ typedef void (*XXH3_f_initCustomSecret)(void* XXH_RESTRICT, xxh_u64); #if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX512) #define XXH3_accumulate_512 XXH3_accumulate_512_avx512 +#define XXH3_accumulate XXH3_accumulate_avx512 #define XXH3_scrambleAcc XXH3_scrambleAcc_avx512 #define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_avx512 #elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2) #define XXH3_accumulate_512 XXH3_accumulate_512_avx2 +#define XXH3_accumulate XXH3_accumulate_avx2 #define XXH3_scrambleAcc XXH3_scrambleAcc_avx2 #define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_avx2 #elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SSE2) #define XXH3_accumulate_512 XXH3_accumulate_512_sse2 +#define XXH3_accumulate XXH3_accumulate_sse2 #define XXH3_scrambleAcc XXH3_scrambleAcc_sse2 #define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_sse2 #elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON) #define XXH3_accumulate_512 XXH3_accumulate_512_neon +#define XXH3_accumulate XXH3_accumulate_neon #define XXH3_scrambleAcc XXH3_scrambleAcc_neon #define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar #elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX) #define XXH3_accumulate_512 XXH3_accumulate_512_vsx +#define XXH3_accumulate XXH3_accumulate_vsx #define XXH3_scrambleAcc XXH3_scrambleAcc_vsx #define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar +#elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SVE) +#define XXH3_accumulate_512 XXH3_accumulate_512_sve +#define XXH3_accumulate XXH3_accumulate_sve +#define XXH3_scrambleAcc XXH3_scrambleAcc_scalar +#define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar + #else /* scalar */ #define XXH3_accumulate_512 XXH3_accumulate_512_scalar +#define XXH3_accumulate XXH3_accumulate_scalar #define XXH3_scrambleAcc XXH3_scrambleAcc_scalar #define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar #endif - - -#ifndef XXH_PREFETCH_DIST -# ifdef __clang__ -# define XXH_PREFETCH_DIST 320 -# else -# if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX512) -# define XXH_PREFETCH_DIST 512 -# else -# define XXH_PREFETCH_DIST 384 -# endif -# endif /* __clang__ */ -#endif /* XXH_PREFETCH_DIST */ - -/* - * XXH3_accumulate() - * Loops over XXH3_accumulate_512(). - * Assumption: nbStripes will not overflow the secret size - */ -XXH_FORCE_INLINE void -XXH3_accumulate( xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, - const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, - const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, - size_t nbStripes, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512) -{ - size_t n; - for (n = 0; n < nbStripes; n++ ) { - const xxh_u8* const in = input + n*XXH_STRIPE_LEN; - XXH_PREFETCH(in + XXH_PREFETCH_DIST); - f_acc512(acc, - in, - secret + n*XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE); - } -} +#if XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1 /* don't do SIMD for initialization */ +# undef XXH3_initCustomSecret +# define XXH3_initCustomSecret XXH3_initCustomSecret_scalar +#endif XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512, + XXH3_f_accumulate f_acc, XXH3_f_scrambleAcc f_scramble) { size_t const nbStripesPerBlock = (secretSize - XXH_STRIPE_LEN) / XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE; @@ -3694,7 +5541,7 @@ XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN); for (n = 0; n < nb_blocks; n++) { - XXH3_accumulate(acc, input + n*block_len, secret, nbStripesPerBlock, f_acc512); + f_acc(acc, input + n*block_len, secret, nbStripesPerBlock); f_scramble(acc, secret + secretSize - XXH_STRIPE_LEN); } @@ -3702,12 +5549,12 @@ XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, XXH_ASSERT(len > XXH_STRIPE_LEN); { size_t const nbStripes = ((len - 1) - (block_len * nb_blocks)) / XXH_STRIPE_LEN; XXH_ASSERT(nbStripes <= (secretSize / XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE)); - XXH3_accumulate(acc, input + nb_blocks*block_len, secret, nbStripes, f_acc512); + f_acc(acc, input + nb_blocks*block_len, secret, nbStripes); /* last stripe */ { const xxh_u8* const p = input + len - XXH_STRIPE_LEN; #define XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START 7 /* not aligned on 8, last secret is different from acc & scrambler */ - f_acc512(acc, p, secret + secretSize - XXH_STRIPE_LEN - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START); + XXH3_accumulate_512(acc, p, secret + secretSize - XXH_STRIPE_LEN - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START); } } } @@ -3739,7 +5586,7 @@ XXH3_mergeAccs(const xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secre * without hack: 2063.7 MB/s * with hack: 2560.7 MB/s */ - __asm__("" : "+r" (result64)); + XXH_COMPILER_GUARD(result64); #endif } @@ -3752,12 +5599,12 @@ XXH3_mergeAccs(const xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secre XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512, + XXH3_f_accumulate f_acc, XXH3_f_scrambleAcc f_scramble) { XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64 acc[XXH_ACC_NB] = XXH3_INIT_ACC; - XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(acc, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize, f_acc512, f_scramble); + XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(acc, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize, f_acc, f_scramble); /* converge into final hash */ XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(acc) == 64); @@ -3768,29 +5615,32 @@ XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, } /* - * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. + * It's important for performance to transmit secret's size (when it's static) + * so that the compiler can properly optimize the vectorized loop. + * This makes a big performance difference for "medium" keys (<1 KB) when using AVX instruction set. + * When the secret size is unknown, or on GCC 12 where the mix of NO_INLINE and FORCE_INLINE + * breaks -Og, this is XXH_NO_INLINE. */ -XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH3_WITH_SECRET_INLINE XXH64_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSecret(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed64, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretLen) { (void)seed64; - return XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(input, len, secret, secretLen, XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc); + return XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(input, len, secret, secretLen, XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc); } /* - * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. - * Since the function is not inlined, the compiler may not be able to understand that, - * in some scenarios, its `secret` argument is actually a compile time constant. - * This variant enforces that the compiler can detect that, - * and uses this opportunity to streamline the generated code for better performance. + * It's preferable for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined, + * as it results in a smaller function for small data, easier to the instruction cache. + * Note that inside this no_inline function, we do inline the internal loop, + * and provide a statically defined secret size to allow optimization of vector loop. */ -XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t +XXH_NO_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH64_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_64b_default(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed64, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretLen) { (void)seed64; (void)secret; (void)secretLen; - return XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(input, len, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc); + return XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(input, len, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc); } /* @@ -3807,18 +5657,20 @@ XXH3_hashLong_64b_default(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed_internal(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512, + XXH3_f_accumulate f_acc, XXH3_f_scrambleAcc f_scramble, XXH3_f_initCustomSecret f_initSec) { +#if XXH_SIZE_OPT <= 0 if (seed == 0) return XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(input, len, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), - f_acc512, f_scramble); + f_acc, f_scramble); +#endif { XXH_ALIGN(XXH_SEC_ALIGN) xxh_u8 secret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE]; f_initSec(secret, seed); return XXH3_hashLong_64b_internal(input, len, secret, sizeof(secret), - f_acc512, f_scramble); + f_acc, f_scramble); } } @@ -3826,12 +5678,12 @@ XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed_internal(const void* input, size_t len, * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. */ XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t -XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed(const void* input, size_t len, - XXH64_hash_t seed, const xxh_u8* secret, size_t secretLen) +XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, + XXH64_hash_t seed, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretLen) { (void)secret; (void)secretLen; return XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed_internal(input, len, seed, - XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc, XXH3_initCustomSecret); + XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc, XXH3_initCustomSecret); } @@ -3863,26 +5715,37 @@ XXH3_64bits_internal(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, /* === Public entry point === */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits(const void* input, size_t len) +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length) +{ + return XXH3_64bits_internal(input, length, 0, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_hashLong_64b_default); +} + +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t +XXH3_64bits_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize) { - return XXH3_64bits_internal(input, len, 0, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_hashLong_64b_default); + return XXH3_64bits_internal(input, length, 0, secret, secretSize, XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSecret); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t -XXH3_64bits_withSecret(const void* input, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize) +XXH3_64bits_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length, XXH64_hash_t seed) { - return XXH3_64bits_internal(input, len, 0, secret, secretSize, XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSecret); + return XXH3_64bits_internal(input, length, seed, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed); } XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t -XXH3_64bits_withSeed(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) +XXH3_64bits_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t length, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed) { - return XXH3_64bits_internal(input, len, seed, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed); + if (length <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) + return XXH3_64bits_internal(input, length, seed, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), NULL); + return XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSecret(input, length, seed, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize); } /* === XXH3 streaming === */ - +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM /* * Malloc's a pointer that is always aligned to align. * @@ -3906,7 +5769,7 @@ XXH3_64bits_withSeed(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) * * Align must be a power of 2 and 8 <= align <= 128. */ -static void* XXH_alignedMalloc(size_t s, size_t align) +static XXH_MALLOCF void* XXH_alignedMalloc(size_t s, size_t align) { XXH_ASSERT(align <= 128 && align >= 8); /* range check */ XXH_ASSERT((align & (align-1)) == 0); /* power of 2 */ @@ -3948,6 +5811,13 @@ static void XXH_alignedFree(void* p) XXH_free(base); } } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +/*! + * @brief Allocate an @ref XXH3_state_t. + * + * Must be freed with XXH3_freeState(). + * @return An allocated XXH3_state_t on success, `NULL` on failure. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH3_state_t* XXH3_createState(void) { XXH3_state_t* const state = (XXH3_state_t*)XXH_alignedMalloc(sizeof(XXH3_state_t), 64); @@ -3956,22 +5826,31 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH3_state_t* XXH3_createState(void) return state; } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +/*! + * @brief Frees an @ref XXH3_state_t. + * + * Must be allocated with XXH3_createState(). + * @param statePtr A pointer to an @ref XXH3_state_t allocated with @ref XXH3_createState(). + * @return XXH_OK. + */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_freeState(XXH3_state_t* statePtr) { XXH_alignedFree(statePtr); return XXH_OK; } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API void -XXH3_copyState(XXH3_state_t* dst_state, const XXH3_state_t* src_state) +XXH3_copyState(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* dst_state, XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH3_state_t* src_state) { - memcpy(dst_state, src_state, sizeof(*dst_state)); + XXH_memcpy(dst_state, src_state, sizeof(*dst_state)); } static void -XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, - XXH64_hash_t seed, - const void* secret, size_t secretSize) +XXH3_reset_internal(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, + XXH64_hash_t seed, + const void* secret, size_t secretSize) { size_t const initStart = offsetof(XXH3_state_t, bufferedSize); size_t const initLength = offsetof(XXH3_state_t, nbStripesPerBlock) - initStart; @@ -3988,95 +5867,153 @@ XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, statePtr->acc[6] = XXH_PRIME64_5; statePtr->acc[7] = XXH_PRIME32_1; statePtr->seed = seed; + statePtr->useSeed = (seed != 0); statePtr->extSecret = (const unsigned char*)secret; XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN); statePtr->secretLimit = secretSize - XXH_STRIPE_LEN; statePtr->nbStripesPerBlock = statePtr->secretLimit / XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE; } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_64bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr) +XXH3_64bits_reset(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr) { if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; - XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, XXH3_kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); + XXH3_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, XXH3_kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); return XXH_OK; } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize) +XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize) { if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; - XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, secret, secretSize); + XXH3_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, secret, secretSize); if (secret == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; if (secretSize < XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) return XXH_ERROR; return XXH_OK; } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed) +XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed) { if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; if (seed==0) return XXH3_64bits_reset(statePtr); - if (seed != statePtr->seed) XXH3_initCustomSecret(statePtr->customSecret, seed); - XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, seed, NULL, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); + if ((seed != statePtr->seed) || (statePtr->extSecret != NULL)) + XXH3_initCustomSecret(statePtr->customSecret, seed); + XXH3_reset_internal(statePtr, seed, NULL, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); return XXH_OK; } -/* Note : when XXH3_consumeStripes() is invoked, - * there must be a guarantee that at least one more byte must be consumed from input - * so that the function can blindly consume all stripes using the "normal" secret segment */ -XXH_FORCE_INLINE void +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode +XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed64) +{ + if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; + if (secret == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; + if (secretSize < XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) return XXH_ERROR; + XXH3_reset_internal(statePtr, seed64, secret, secretSize); + statePtr->useSeed = 1; /* always, even if seed64==0 */ + return XXH_OK; +} + +/*! + * @internal + * @brief Processes a large input for XXH3_update() and XXH3_digest_long(). + * + * Unlike XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(), this can process data that overlaps a block. + * + * @param acc Pointer to the 8 accumulator lanes + * @param nbStripesSoFarPtr In/out pointer to the number of leftover stripes in the block* + * @param nbStripesPerBlock Number of stripes in a block + * @param input Input pointer + * @param nbStripes Number of stripes to process + * @param secret Secret pointer + * @param secretLimit Offset of the last block in @p secret + * @param f_acc Pointer to an XXH3_accumulate implementation + * @param f_scramble Pointer to an XXH3_scrambleAcc implementation + * @return Pointer past the end of @p input after processing + */ +XXH_FORCE_INLINE const xxh_u8 * XXH3_consumeStripes(xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, size_t* XXH_RESTRICT nbStripesSoFarPtr, size_t nbStripesPerBlock, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t nbStripes, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretLimit, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512, + XXH3_f_accumulate f_acc, XXH3_f_scrambleAcc f_scramble) { - XXH_ASSERT(nbStripes <= nbStripesPerBlock); /* can handle max 1 scramble per invocation */ - XXH_ASSERT(*nbStripesSoFarPtr < nbStripesPerBlock); - if (nbStripesPerBlock - *nbStripesSoFarPtr <= nbStripes) { - /* need a scrambling operation */ - size_t const nbStripesToEndofBlock = nbStripesPerBlock - *nbStripesSoFarPtr; - size_t const nbStripesAfterBlock = nbStripes - nbStripesToEndofBlock; - XXH3_accumulate(acc, input, secret + nbStripesSoFarPtr[0] * XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE, nbStripesToEndofBlock, f_acc512); - f_scramble(acc, secret + secretLimit); - XXH3_accumulate(acc, input + nbStripesToEndofBlock * XXH_STRIPE_LEN, secret, nbStripesAfterBlock, f_acc512); - *nbStripesSoFarPtr = nbStripesAfterBlock; - } else { - XXH3_accumulate(acc, input, secret + nbStripesSoFarPtr[0] * XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE, nbStripes, f_acc512); + const xxh_u8* initialSecret = secret + *nbStripesSoFarPtr * XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE; + /* Process full blocks */ + if (nbStripes >= (nbStripesPerBlock - *nbStripesSoFarPtr)) { + /* Process the initial partial block... */ + size_t nbStripesThisIter = nbStripesPerBlock - *nbStripesSoFarPtr; + + do { + /* Accumulate and scramble */ + f_acc(acc, input, initialSecret, nbStripesThisIter); + f_scramble(acc, secret + secretLimit); + input += nbStripesThisIter * XXH_STRIPE_LEN; + nbStripes -= nbStripesThisIter; + /* Then continue the loop with the full block size */ + nbStripesThisIter = nbStripesPerBlock; + initialSecret = secret; + } while (nbStripes >= nbStripesPerBlock); + *nbStripesSoFarPtr = 0; + } + /* Process a partial block */ + if (nbStripes > 0) { + f_acc(acc, input, initialSecret, nbStripes); + input += nbStripes * XXH_STRIPE_LEN; *nbStripesSoFarPtr += nbStripes; } + /* Return end pointer */ + return input; } +#ifndef XXH3_STREAM_USE_STACK +# if XXH_SIZE_OPT <= 0 && !defined(__clang__) /* clang doesn't need additional stack space */ +# define XXH3_STREAM_USE_STACK 1 +# endif +#endif /* * Both XXH3_64bits_update and XXH3_128bits_update use this routine. */ XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_errorcode -XXH3_update(XXH3_state_t* state, - const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512, +XXH3_update(XXH3_state_t* XXH_RESTRICT const state, + const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, + XXH3_f_accumulate f_acc, XXH3_f_scrambleAcc f_scramble) { - if (input==NULL) -#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1) + if (input==NULL) { + XXH_ASSERT(len == 0); return XXH_OK; -#else - return XXH_ERROR; -#endif + } + XXH_ASSERT(state != NULL); { const xxh_u8* const bEnd = input + len; const unsigned char* const secret = (state->extSecret == NULL) ? state->customSecret : state->extSecret; - +#if defined(XXH3_STREAM_USE_STACK) && XXH3_STREAM_USE_STACK >= 1 + /* For some reason, gcc and MSVC seem to suffer greatly + * when operating accumulators directly into state. + * Operating into stack space seems to enable proper optimization. + * clang, on the other hand, doesn't seem to need this trick */ + XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64 acc[8]; + XXH_memcpy(acc, state->acc, sizeof(acc)); +#else + xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT const acc = state->acc; +#endif state->totalLen += len; + XXH_ASSERT(state->bufferedSize <= XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE); - if (state->bufferedSize + len <= XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE) { /* fill in tmp buffer */ + /* small input : just fill in tmp buffer */ + if (len <= XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE - state->bufferedSize) { XXH_memcpy(state->buffer + state->bufferedSize, input, len); state->bufferedSize += (XXH32_hash_t)len; return XXH_OK; } - /* total input is now > XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE */ + /* total input is now > XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE */ #define XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_STRIPES (XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE / XXH_STRIPE_LEN) XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE % XXH_STRIPE_LEN == 0); /* clean multiple */ @@ -4088,44 +6025,45 @@ XXH3_update(XXH3_state_t* state, size_t const loadSize = XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE - state->bufferedSize; XXH_memcpy(state->buffer + state->bufferedSize, input, loadSize); input += loadSize; - XXH3_consumeStripes(state->acc, + XXH3_consumeStripes(acc, &state->nbStripesSoFar, state->nbStripesPerBlock, state->buffer, XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_STRIPES, secret, state->secretLimit, - f_acc512, f_scramble); + f_acc, f_scramble); state->bufferedSize = 0; } XXH_ASSERT(input < bEnd); + if (bEnd - input > XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE) { + size_t nbStripes = (size_t)(bEnd - 1 - input) / XXH_STRIPE_LEN; + input = XXH3_consumeStripes(acc, + &state->nbStripesSoFar, state->nbStripesPerBlock, + input, nbStripes, + secret, state->secretLimit, + f_acc, f_scramble); + XXH_memcpy(state->buffer + sizeof(state->buffer) - XXH_STRIPE_LEN, input - XXH_STRIPE_LEN, XXH_STRIPE_LEN); - /* Consume input by a multiple of internal buffer size */ - if (input+XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE < bEnd) { - const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE; - do { - XXH3_consumeStripes(state->acc, - &state->nbStripesSoFar, state->nbStripesPerBlock, - input, XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_STRIPES, - secret, state->secretLimit, - f_acc512, f_scramble); - input += XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE; - } while (input<limit); - /* for last partial stripe */ - memcpy(state->buffer + sizeof(state->buffer) - XXH_STRIPE_LEN, input - XXH_STRIPE_LEN, XXH_STRIPE_LEN); } - XXH_ASSERT(input < bEnd); - /* Some remaining input (always) : buffer it */ + XXH_ASSERT(input < bEnd); + XXH_ASSERT(bEnd - input <= XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE); + XXH_ASSERT(state->bufferedSize == 0); XXH_memcpy(state->buffer, input, (size_t)(bEnd-input)); state->bufferedSize = (XXH32_hash_t)(bEnd-input); +#if defined(XXH3_STREAM_USE_STACK) && XXH3_STREAM_USE_STACK >= 1 + /* save stack accumulators into state */ + XXH_memcpy(state->acc, acc, sizeof(acc)); +#endif } return XXH_OK; } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_64bits_update(XXH3_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) +XXH3_64bits_update(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* state, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len) { return XXH3_update(state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, - XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc); + XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc); } @@ -4134,36 +6072,40 @@ XXH3_digest_long (XXH64_hash_t* acc, const XXH3_state_t* state, const unsigned char* secret) { + xxh_u8 lastStripe[XXH_STRIPE_LEN]; + const xxh_u8* lastStripePtr; + /* * Digest on a local copy. This way, the state remains unaltered, and it can * continue ingesting more input afterwards. */ - memcpy(acc, state->acc, sizeof(state->acc)); + XXH_memcpy(acc, state->acc, sizeof(state->acc)); if (state->bufferedSize >= XXH_STRIPE_LEN) { + /* Consume remaining stripes then point to remaining data in buffer */ size_t const nbStripes = (state->bufferedSize - 1) / XXH_STRIPE_LEN; size_t nbStripesSoFar = state->nbStripesSoFar; XXH3_consumeStripes(acc, &nbStripesSoFar, state->nbStripesPerBlock, state->buffer, nbStripes, secret, state->secretLimit, - XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc); - /* last stripe */ - XXH3_accumulate_512(acc, - state->buffer + state->bufferedSize - XXH_STRIPE_LEN, - secret + state->secretLimit - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START); + XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc); + lastStripePtr = state->buffer + state->bufferedSize - XXH_STRIPE_LEN; } else { /* bufferedSize < XXH_STRIPE_LEN */ - xxh_u8 lastStripe[XXH_STRIPE_LEN]; + /* Copy to temp buffer */ size_t const catchupSize = XXH_STRIPE_LEN - state->bufferedSize; XXH_ASSERT(state->bufferedSize > 0); /* there is always some input buffered */ - memcpy(lastStripe, state->buffer + sizeof(state->buffer) - catchupSize, catchupSize); - memcpy(lastStripe + catchupSize, state->buffer, state->bufferedSize); - XXH3_accumulate_512(acc, - lastStripe, - secret + state->secretLimit - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START); + XXH_memcpy(lastStripe, state->buffer + sizeof(state->buffer) - catchupSize, catchupSize); + XXH_memcpy(lastStripe + catchupSize, state->buffer, state->bufferedSize); + lastStripePtr = lastStripe; } + /* Last stripe */ + XXH3_accumulate_512(acc, + lastStripePtr, + secret + state->secretLimit - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START); } -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* state) +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH3_state_t* state) { const unsigned char* const secret = (state->extSecret == NULL) ? state->customSecret : state->extSecret; if (state->totalLen > XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) { @@ -4174,56 +6116,12 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* state) (xxh_u64)state->totalLen * XXH_PRIME64_1); } /* totalLen <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX: digesting a short input */ - if (state->seed) + if (state->useSeed) return XXH3_64bits_withSeed(state->buffer, (size_t)state->totalLen, state->seed); return XXH3_64bits_withSecret(state->buffer, (size_t)(state->totalLen), secret, state->secretLimit + XXH_STRIPE_LEN); } - - -#define XXH_MIN(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (y) : (x)) - -XXH_PUBLIC_API void -XXH3_generateSecret(void* secretBuffer, const void* customSeed, size_t customSeedSize) -{ - XXH_ASSERT(secretBuffer != NULL); - if (customSeedSize == 0) { - memcpy(secretBuffer, XXH3_kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); - return; - } - XXH_ASSERT(customSeed != NULL); - - { size_t const segmentSize = sizeof(XXH128_hash_t); - size_t const nbSegments = XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE / segmentSize; - XXH128_canonical_t scrambler; - XXH64_hash_t seeds[12]; - size_t segnb; - XXH_ASSERT(nbSegments == 12); - XXH_ASSERT(segmentSize * nbSegments == XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); /* exact multiple */ - XXH128_canonicalFromHash(&scrambler, XXH128(customSeed, customSeedSize, 0)); - - /* - * Copy customSeed to seeds[], truncating or repeating as necessary. - */ - { size_t toFill = XXH_MIN(customSeedSize, sizeof(seeds)); - size_t filled = toFill; - memcpy(seeds, customSeed, toFill); - while (filled < sizeof(seeds)) { - toFill = XXH_MIN(filled, sizeof(seeds) - filled); - memcpy((char*)seeds + filled, seeds, toFill); - filled += toFill; - } } - - /* generate secret */ - memcpy(secretBuffer, &scrambler, sizeof(scrambler)); - for (segnb=1; segnb < nbSegments; segnb++) { - size_t const segmentStart = segnb * segmentSize; - XXH128_canonical_t segment; - XXH128_canonicalFromHash(&segment, - XXH128(&scrambler, sizeof(scrambler), XXH_readLE64(seeds + segnb) + segnb) ); - memcpy((char*)secretBuffer + segmentStart, &segment, sizeof(segment)); - } } -} +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /* ========================================== @@ -4243,7 +6141,7 @@ XXH3_generateSecret(void* secretBuffer, const void* customSeed, size_t customSee * fast for a _128-bit_ hash on 32-bit (it usually clears XXH64). */ -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_len_1to3_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { /* A doubled version of 1to3_64b with different constants. */ @@ -4272,7 +6170,7 @@ XXH3_len_1to3_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_ } } -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_len_4to8_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL); @@ -4292,14 +6190,14 @@ XXH3_len_4to8_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_ m128.low64 ^= (m128.high64 >> 3); m128.low64 = XXH_xorshift64(m128.low64, 35); - m128.low64 *= 0x9FB21C651E98DF25ULL; + m128.low64 *= PRIME_MX2; m128.low64 = XXH_xorshift64(m128.low64, 28); m128.high64 = XXH3_avalanche(m128.high64); return m128; } } -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_len_9to16_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL); @@ -4374,7 +6272,7 @@ XXH3_len_9to16_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64 /* * Assumption: `secret` size is >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN */ -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_len_0to16_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed) { XXH_ASSERT(len <= 16); @@ -4405,7 +6303,7 @@ XXH128_mix32B(XXH128_hash_t acc, const xxh_u8* input_1, const xxh_u8* input_2, } -XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_len_17to128_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed) @@ -4416,6 +6314,16 @@ XXH3_len_17to128_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, { XXH128_hash_t acc; acc.low64 = len * XXH_PRIME64_1; acc.high64 = 0; + +#if XXH_SIZE_OPT >= 1 + { + /* Smaller, but slightly slower. */ + unsigned int i = (unsigned int)(len - 1) / 32; + do { + acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input+16*i, input+len-16*(i+1), secret+32*i, seed); + } while (i-- != 0); + } +#else if (len > 32) { if (len > 64) { if (len > 96) { @@ -4426,6 +6334,7 @@ XXH3_len_17to128_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input+16, input+len-32, secret+32, seed); } acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input, input+len-16, secret, seed); +#endif { XXH128_hash_t h128; h128.low64 = acc.low64 + acc.high64; h128.high64 = (acc.low64 * XXH_PRIME64_1) @@ -4438,7 +6347,7 @@ XXH3_len_17to128_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, } } -XXH_NO_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH_NO_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_len_129to240_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed) @@ -4447,25 +6356,34 @@ XXH3_len_129to240_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH_ASSERT(128 < len && len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX); { XXH128_hash_t acc; - int const nbRounds = (int)len / 32; - int i; + unsigned i; acc.low64 = len * XXH_PRIME64_1; acc.high64 = 0; - for (i=0; i<4; i++) { + /* + * We set as `i` as offset + 32. We do this so that unchanged + * `len` can be used as upper bound. This reaches a sweet spot + * where both x86 and aarch64 get simple agen and good codegen + * for the loop. + */ + for (i = 32; i < 160; i += 32) { acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, - input + (32 * i), - input + (32 * i) + 16, - secret + (32 * i), + input + i - 32, + input + i - 16, + secret + i - 32, seed); } acc.low64 = XXH3_avalanche(acc.low64); acc.high64 = XXH3_avalanche(acc.high64); - XXH_ASSERT(nbRounds >= 4); - for (i=4 ; i < nbRounds; i++) { + /* + * NB: `i <= len` will duplicate the last 32-bytes if + * len % 32 was zero. This is an unfortunate necessity to keep + * the hash result stable. + */ + for (i=160; i <= len; i += 32) { acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, - input + (32 * i), - input + (32 * i) + 16, - secret + XXH3_MIDSIZE_STARTOFFSET + (32 * (i - 4)), + input + i - 32, + input + i - 16, + secret + XXH3_MIDSIZE_STARTOFFSET + i - 160, seed); } /* last bytes */ @@ -4473,7 +6391,7 @@ XXH3_len_129to240_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, input + len - 16, input + len - 32, secret + XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN - XXH3_MIDSIZE_LASTOFFSET - 16, - 0ULL - seed); + (XXH64_hash_t)0 - seed); { XXH128_hash_t h128; h128.low64 = acc.low64 + acc.high64; @@ -4490,12 +6408,12 @@ XXH3_len_129to240_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512, + XXH3_f_accumulate f_acc, XXH3_f_scrambleAcc f_scramble) { XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64 acc[XXH_ACC_NB] = XXH3_INIT_ACC; - XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(acc, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, secret, secretSize, f_acc512, f_scramble); + XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(acc, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, secret, secretSize, f_acc, f_scramble); /* converge into final hash */ XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(acc) == 64); @@ -4513,46 +6431,50 @@ XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, } /* - * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. + * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong() is not inlined. */ -XXH_NO_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH_NO_INLINE XXH_PUREF XXH128_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_128b_default(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed64, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretLen) { (void)seed64; (void)secret; (void)secretLen; return XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(input, len, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), - XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc); + XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc); } /* - * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. + * It's important for performance to pass @p secretLen (when it's static) + * to the compiler, so that it can properly optimize the vectorized loop. + * + * When the secret size is unknown, or on GCC 12 where the mix of NO_INLINE and FORCE_INLINE + * breaks -Og, this is XXH_NO_INLINE. */ -XXH_NO_INLINE XXH128_hash_t +XXH3_WITH_SECRET_INLINE XXH128_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSecret(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed64, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretLen) { (void)seed64; return XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretLen, - XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc); + XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc); } XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSeed_internal(const void* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed64, - XXH3_f_accumulate_512 f_acc512, + XXH3_f_accumulate f_acc, XXH3_f_scrambleAcc f_scramble, XXH3_f_initCustomSecret f_initSec) { if (seed64 == 0) return XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(input, len, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), - f_acc512, f_scramble); + f_acc, f_scramble); { XXH_ALIGN(XXH_SEC_ALIGN) xxh_u8 secret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE]; f_initSec(secret, seed64); return XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, sizeof(secret), - f_acc512, f_scramble); + f_acc, f_scramble); } } @@ -4565,7 +6487,7 @@ XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSeed(const void* input, size_t len, { (void)secret; (void)secretLen; return XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSeed_internal(input, len, seed64, - XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc, XXH3_initCustomSecret); + XXH3_accumulate, XXH3_scrambleAcc, XXH3_initCustomSecret); } typedef XXH128_hash_t (*XXH3_hashLong128_f)(const void* XXH_RESTRICT, size_t, @@ -4595,87 +6517,93 @@ XXH3_128bits_internal(const void* input, size_t len, /* === Public XXH128 API === */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits(const void* input, size_t len) +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len) { return XXH3_128bits_internal(input, len, 0, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_hashLong_128b_default); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t -XXH3_128bits_withSecret(const void* input, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize) +XXH3_128bits_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize) { return XXH3_128bits_internal(input, len, 0, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize, XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSecret); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t -XXH3_128bits_withSeed(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) +XXH3_128bits_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) { return XXH3_128bits_internal(input, len, seed, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSeed); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t +XXH3_128bits_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed) +{ + if (len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) + return XXH3_128bits_internal(input, len, seed, XXH3_kSecret, sizeof(XXH3_kSecret), NULL); + return XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSecret(input, len, seed, secret, secretSize); +} + +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t -XXH128(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) +XXH128(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed) { return XXH3_128bits_withSeed(input, len, seed); } /* === XXH3 128-bit streaming === */ - +#ifndef XXH_NO_STREAM /* - * All the functions are actually the same as for 64-bit streaming variant. - * The only difference is the finalizatiom routine. + * All initialization and update functions are identical to 64-bit streaming variant. + * The only difference is the finalization routine. */ -static void -XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, - XXH64_hash_t seed, - const void* secret, size_t secretSize) +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode +XXH3_128bits_reset(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr) { - XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, seed, secret, secretSize); + return XXH3_64bits_reset(statePtr); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_128bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr) +XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize) { - if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; - XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, XXH3_kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); - return XXH_OK; + return XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(statePtr, secret, secretSize); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize) +XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed) { - if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; - XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, secret, secretSize); - if (secret == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; - if (secretSize < XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) return XXH_ERROR; - return XXH_OK; + return XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(statePtr, seed); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed) +XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecretandSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* secret, size_t secretSize, XXH64_hash_t seed) { - if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; - if (seed==0) return XXH3_128bits_reset(statePtr); - if (seed != statePtr->seed) XXH3_initCustomSecret(statePtr->customSecret, seed); - XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(statePtr, seed, NULL, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); - return XXH_OK; + return XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecretandSeed(statePtr, secret, secretSize, seed); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode -XXH3_128bits_update(XXH3_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len) +XXH3_128bits_update(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH3_state_t* state, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* input, size_t len) { - return XXH3_update(state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, - XXH3_accumulate_512, XXH3_scrambleAcc); + return XXH3_64bits_update(state, input, len); } -XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* state) +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH3_state_t* state) { const unsigned char* const secret = (state->extSecret == NULL) ? state->customSecret : state->extSecret; if (state->totalLen > XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) { @@ -4699,12 +6627,13 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* state) return XXH3_128bits_withSecret(state->buffer, (size_t)(state->totalLen), secret, state->secretLimit + XXH_STRIPE_LEN); } - +#endif /* !XXH_NO_STREAM */ /* 128-bit utility functions */ #include <string.h> /* memcmp, memcpy */ /* return : 1 is equal, 0 if different */ +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_isEqual(XXH128_hash_t h1, XXH128_hash_t h2) { /* note : XXH128_hash_t is compact, it has no padding byte */ @@ -4712,10 +6641,11 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_isEqual(XXH128_hash_t h1, XXH128_hash_t h2) } /* This prototype is compatible with stdlib's qsort(). - * return : >0 if *h128_1 > *h128_2 - * <0 if *h128_1 < *h128_2 - * =0 if *h128_1 == *h128_2 */ -XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_cmp(const void* h128_1, const void* h128_2) + * @return : >0 if *h128_1 > *h128_2 + * <0 if *h128_1 < *h128_2 + * =0 if *h128_1 == *h128_2 */ +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_cmp(XXH_NOESCAPE const void* h128_1, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* h128_2) { XXH128_hash_t const h1 = *(const XXH128_hash_t*)h128_1; XXH128_hash_t const h2 = *(const XXH128_hash_t*)h128_2; @@ -4727,20 +6657,22 @@ XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_cmp(const void* h128_1, const void* h128_2) /*====== Canonical representation ======*/ +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API void -XXH128_canonicalFromHash(XXH128_canonical_t* dst, XXH128_hash_t hash) +XXH128_canonicalFromHash(XXH_NOESCAPE XXH128_canonical_t* dst, XXH128_hash_t hash) { XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(XXH128_canonical_t) == sizeof(XXH128_hash_t)); if (XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) { hash.high64 = XXH_swap64(hash.high64); hash.low64 = XXH_swap64(hash.low64); } - memcpy(dst, &hash.high64, sizeof(hash.high64)); - memcpy((char*)dst + sizeof(hash.high64), &hash.low64, sizeof(hash.low64)); + XXH_memcpy(dst, &hash.high64, sizeof(hash.high64)); + XXH_memcpy((char*)dst + sizeof(hash.high64), &hash.low64, sizeof(hash.low64)); } +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t -XXH128_hashFromCanonical(const XXH128_canonical_t* src) +XXH128_hashFromCanonical(XXH_NOESCAPE const XXH128_canonical_t* src) { XXH128_hash_t h; h.high64 = XXH_readBE64(src); @@ -4748,19 +6680,94 @@ XXH128_hashFromCanonical(const XXH128_canonical_t* src) return h; } + + +/* ========================================== + * Secret generators + * ========================================== + */ +#define XXH_MIN(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (y) : (x)) + +XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH3_combine16(void* dst, XXH128_hash_t h128) +{ + XXH_writeLE64( dst, XXH_readLE64(dst) ^ h128.low64 ); + XXH_writeLE64( (char*)dst+8, XXH_readLE64((char*)dst+8) ^ h128.high64 ); +} + +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode +XXH3_generateSecret(XXH_NOESCAPE void* secretBuffer, size_t secretSize, XXH_NOESCAPE const void* customSeed, size_t customSeedSize) +{ +#if (XXH_DEBUGLEVEL >= 1) + XXH_ASSERT(secretBuffer != NULL); + XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN); +#else + /* production mode, assert() are disabled */ + if (secretBuffer == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; + if (secretSize < XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) return XXH_ERROR; +#endif + + if (customSeedSize == 0) { + customSeed = XXH3_kSecret; + customSeedSize = XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE; + } +#if (XXH_DEBUGLEVEL >= 1) + XXH_ASSERT(customSeed != NULL); +#else + if (customSeed == NULL) return XXH_ERROR; +#endif + + /* Fill secretBuffer with a copy of customSeed - repeat as needed */ + { size_t pos = 0; + while (pos < secretSize) { + size_t const toCopy = XXH_MIN((secretSize - pos), customSeedSize); + memcpy((char*)secretBuffer + pos, customSeed, toCopy); + pos += toCopy; + } } + + { size_t const nbSeg16 = secretSize / 16; + size_t n; + XXH128_canonical_t scrambler; + XXH128_canonicalFromHash(&scrambler, XXH128(customSeed, customSeedSize, 0)); + for (n=0; n<nbSeg16; n++) { + XXH128_hash_t const h128 = XXH128(&scrambler, sizeof(scrambler), n); + XXH3_combine16((char*)secretBuffer + n*16, h128); + } + /* last segment */ + XXH3_combine16((char*)secretBuffer + secretSize - 16, XXH128_hashFromCanonical(&scrambler)); + } + return XXH_OK; +} + +/*! @ingroup XXH3_family */ +XXH_PUBLIC_API void +XXH3_generateSecret_fromSeed(XXH_NOESCAPE void* secretBuffer, XXH64_hash_t seed) +{ + XXH_ALIGN(XXH_SEC_ALIGN) xxh_u8 secret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE]; + XXH3_initCustomSecret(secret, seed); + XXH_ASSERT(secretBuffer != NULL); + memcpy(secretBuffer, secret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE); +} + + + /* Pop our optimization override from above */ #if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2 /* AVX2 */ \ && defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) /* GCC, not Clang */ \ - && defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && !defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) /* respect -O0 and -Os */ + && defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && XXH_SIZE_OPT <= 0 /* respect -O0 and -Os */ # pragma GCC pop_options #endif #endif /* XXH_NO_LONG_LONG */ +#endif /* XXH_NO_XXH3 */ +/*! + * @} + */ #endif /* XXH_IMPLEMENTATION */ #if defined (__cplusplus) -} +} /* extern "C" */ #endif diff --git a/contrib/libs/xxhash/ya.make b/contrib/libs/xxhash/ya.make index d1b2b97fdf9..3ab278a6680 100644 --- a/contrib/libs/xxhash/ya.make +++ b/contrib/libs/xxhash/ya.make @@ -2,14 +2,14 @@ LIBRARY() -VERSION(0.8.0) - -ORIGINAL_SOURCE(https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/archive/v0.8.0.tar.gz) - LICENSE(BSD-2-Clause) LICENSE_TEXTS(.yandex_meta/licenses.list.txt) +VERSION(0.8.2) + +ORIGINAL_SOURCE(https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/archive/v0.8.2.tar.gz) + NO_COMPILER_WARNINGS() NO_RUNTIME() |
